Municipal Waste Management - A Comprehensive Understanding
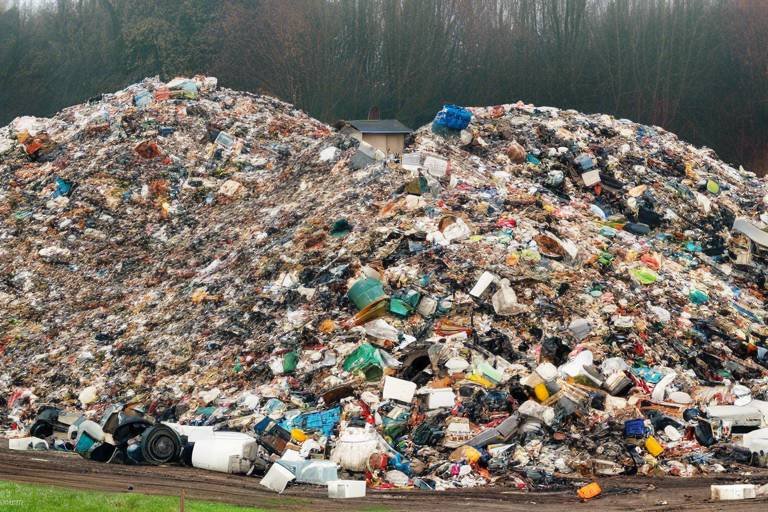
Municipal waste management is an essential component of urban living that affects every individual in a community. Imagine living in a city where waste is left uncollected, piling up on the streets, emitting foul odors, and attracting pests. Not a pretty picture, right? This is why effective municipal waste management is crucial—it not only safeguards public health but also protects our environment and ensures the sustainability of urban areas. As cities continue to grow, the volume of waste generated increases, making efficient waste management practices more important than ever. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of municipal waste management, including its significance, the types of waste generated, the challenges faced, and innovative solutions that are paving the way for a cleaner, greener future.
Effective waste management is crucial for a multitude of reasons. First and foremost, it plays a vital role in protecting public health. Poor waste management can lead to the spread of diseases, as waste can harbor bacteria and attract vermin. Moreover, proper waste disposal helps to minimize pollution, which can have devastating effects on our air, soil, and water quality. Consider this: when waste is improperly disposed of, it can leach harmful chemicals into the ground, contaminating groundwater supplies. This is a significant concern for communities that rely on these water sources for drinking and agriculture. Furthermore, effective waste management contributes to urban sustainability. By implementing recycling and composting programs, communities can reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, conserving valuable resources and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions.
Municipal waste is a broad term that encompasses various categories of waste generated within urban areas. Understanding these categories is crucial for developing effective waste management strategies. The three primary types of municipal waste include:
- Residential Waste: This category includes waste generated from households, such as food scraps, packaging materials, and recyclable items.
- Commercial Waste: Waste produced by businesses, including offices, restaurants, and retail stores, falls under this category.
- Industrial Waste: This includes waste generated by manufacturing processes, factories, and construction activities.
Recognizing these types of waste is essential for tailoring management strategies that address the specific needs and challenges associated with each category. For instance, residential waste often contains a higher percentage of organic materials, making composting initiatives particularly effective in reducing landfill contributions.
Residential waste is primarily composed of household items, food scraps, and recyclable materials. Understanding its composition is key to implementing effective recycling programs. For example, did you know that a significant portion of residential waste consists of organic materials? By identifying and promoting composting initiatives, we can divert a large amount of this waste from landfills and transform it into valuable compost for gardening and landscaping. Moreover, educating the public on proper sorting of recyclable materials can significantly increase recycling rates. When people know what can and cannot be recycled, they are more likely to participate actively in recycling programs.
Identifying recyclable materials within residential waste is essential for promoting recycling practices. Common recyclable materials include:
- Paper and cardboard
- Plastics (check for recycling symbols)
- Metals (aluminum cans, tin cans)
- Glass bottles and jars
By educating the public on proper sorting, communities can significantly increase recycling rates and reduce landfill waste. It's all about making it easy and accessible for everyone!
Organic waste, which includes food scraps and yard waste, contributes significantly to municipal waste. In fact, a large percentage of what we throw away could be composted instead. Implementing composting initiatives can divert this waste from landfills and promote sustainable practices. Imagine turning your kitchen scraps into nutrient-rich soil for your garden! Not only does composting reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, but it also enriches the soil and supports healthy plant growth.
Commercial and industrial waste includes materials generated by businesses and factories. Proper management of this waste is vital to minimize environmental impact and comply with regulations. Businesses can adopt strategies such as waste audits to identify areas for improvement and implement recycling programs tailored to their specific waste streams. For instance, restaurants can work on reducing food waste through better inventory management and donation programs, while factories can explore ways to recycle materials like metal and plastic.
Municipal waste management faces numerous challenges that can hinder its effectiveness. One of the most pressing issues is inadequate infrastructure. Many municipalities struggle with outdated or insufficient waste management systems, leading to inefficiencies in waste collection and processing. Investing in modern facilities and technologies is essential for enhancing efficiency and effectiveness in waste processing.
Outdated waste management infrastructure can lead to a host of problems, including increased costs and environmental impacts. Municipalities must prioritize investment in modern waste management technologies to tackle these issues head-on. This could include upgrading recycling facilities, implementing waste-to-energy technologies, and adopting smart waste management systems that optimize collection routes.
Engaging the community in waste management efforts is critical. Increasing public awareness about recycling and waste reduction can lead to higher participation rates and more sustainable practices. Communities can host educational workshops, create informative campaigns, and leverage social media to spread the word about the importance of waste management. When people understand the impact of their actions, they are more likely to participate in initiatives that promote a cleaner environment.
Emerging technologies and innovative strategies are transforming municipal waste management. Exploring these solutions can lead to more efficient and environmentally friendly waste disposal practices. For instance, smart waste management technologies, such as IoT-enabled waste bins and data analytics, can optimize waste collection routes and schedules, reducing costs and improving service efficiency.
Smart technologies are revolutionizing the way we manage waste. By utilizing sensors and data analytics, municipalities can monitor waste levels in real-time, allowing for more efficient collection schedules. This not only reduces operational costs but also minimizes the environmental footprint associated with waste collection.
Zero waste initiatives aim to eliminate waste through redesigning resource life cycles. These programs encourage recycling, composting, and sustainable practices to minimize waste generation at the source. Imagine a community where everything is reused, recycled, or composted—this is the vision behind zero waste initiatives. By fostering a culture of sustainability, we can work towards a future where waste is a thing of the past.
Q: What is municipal waste management?
A: Municipal waste management refers to the collection, treatment, and disposal of waste generated in urban areas, including residential, commercial, and industrial waste.
Q: Why is waste management important?
A: Effective waste management is crucial for protecting public health, minimizing environmental pollution, and promoting urban sustainability.
Q: What are some common types of municipal waste?
A: Common types of municipal waste include residential waste, commercial waste, and industrial waste.
Q: How can individuals contribute to better waste management?
A: Individuals can contribute by recycling properly, composting organic waste, and participating in community clean-up initiatives.
Q: What are zero waste initiatives?
A: Zero waste initiatives aim to redesign resource life cycles to eliminate waste, encouraging practices like recycling and composting to minimize waste generation.

The Importance of Municipal Waste Management
Effective waste management is not just a mundane task; it's a critical pillar for ensuring public health, safeguarding our environment, and fostering urban sustainability. Imagine living in a city where overflowing trash bins and littered streets are the norm. It’s not just an eyesore; it poses serious health risks and diminishes the quality of life for residents. When waste is improperly managed, it can lead to pollution of our air, soil, and waterways, creating a ripple effect that impacts both ecosystems and human health. Therefore, understanding the significance of municipal waste management is crucial for communities to prioritize proper disposal and recycling practices.
At its core, municipal waste management is about creating a framework that effectively handles waste from various sources, ensuring that it is disposed of responsibly and sustainably. The importance of this management extends beyond just keeping our neighborhoods clean. It plays a vital role in:
- Public Health: Proper waste management reduces the risk of disease outbreaks caused by waste-related pathogens.
- Environmental Protection: Effective waste management minimizes pollution and conserves natural resources.
- Urban Sustainability: A well-structured waste management system is essential for the long-term sustainability of urban areas.
Moreover, when communities actively engage in waste management practices, they contribute to a circular economy where materials are reused and recycled, rather than discarded. This not only conserves resources but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions, which is a significant contributor to climate change. By prioritizing waste management, municipalities can create a cleaner, healthier environment that benefits everyone.
In summary, the importance of municipal waste management cannot be overstated. It is a fundamental aspect of urban living that impacts public health, environmental sustainability, and overall community well-being. By recognizing its significance, we can foster a culture of responsibility and stewardship towards our waste, ultimately leading to a cleaner and more sustainable world.
- What is municipal waste management? It refers to the processes and systems involved in collecting, treating, and disposing of waste generated in urban areas.
- Why is waste management important? It is essential for protecting public health, preserving the environment, and ensuring sustainable urban development.
- How can communities improve waste management practices? By increasing public awareness, investing in infrastructure, and promoting recycling and composting programs.

Types of Municipal Waste
Municipal waste is a broad term that encompasses a variety of waste types generated within urban areas. Understanding these different categories is essential for effective waste management strategies. Waste can be broadly classified into three main categories: residential waste, commercial waste, and industrial waste. Each type has its unique characteristics and challenges, which must be addressed to create a sustainable waste management system.
Residential waste is primarily generated from households and includes everyday items such as food scraps, packaging materials, and old furniture. This type of waste is significant because it forms a large portion of what ends up in landfills. The composition of residential waste can vary significantly depending on factors like location, season, and community engagement in recycling programs. For instance, during holidays, the amount of packaging waste can spike, while organic waste from food preparation may increase during summer months when fresh produce is abundant.
To tackle residential waste effectively, it’s crucial to identify and promote recyclable materials. These materials often include paper, cardboard, glass, and certain plastics. By educating the public on how to properly sort their waste, municipalities can drastically increase recycling rates and reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills. For example, a recent study showed that communities with robust educational programs saw a recycling rate increase of up to 30% within a year.
Another significant component of residential waste is organic waste, which includes food scraps, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials. This type of waste not only contributes to landfill overflow but also produces harmful greenhouse gases when decomposing in landfills. To combat this issue, many cities are implementing composting initiatives that encourage residents to divert organic waste from landfills. Composting not only reduces waste volume but also creates nutrient-rich soil for gardening, promoting a circular economy.
On the other hand, commercial and industrial waste consists of materials generated by businesses, factories, and institutions. This waste category includes everything from packaging materials and office supplies to manufacturing byproducts. Proper management of commercial and industrial waste is vital, as it often contains hazardous materials that can pose serious environmental risks if not disposed of correctly. Businesses are increasingly adopting waste reduction strategies and recycling programs to minimize their environmental footprint and comply with stringent regulations.
In summary, recognizing the different types of municipal waste is crucial for developing tailored management strategies that address the specific needs and challenges of each waste category. By focusing on residential, commercial, and industrial waste, municipalities can implement effective programs that promote recycling, composting, and responsible waste disposal, ultimately leading to a cleaner and more sustainable urban environment.
- What is municipal waste? Municipal waste refers to waste generated within urban areas, including residential, commercial, and industrial waste.
- Why is it important to sort waste? Sorting waste helps in recycling and composting efforts, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills and promoting environmental sustainability.
- How can I reduce my residential waste? You can reduce residential waste by practicing mindful consumption, composting organic waste, and actively participating in local recycling programs.
- What types of materials can be recycled? Common recyclable materials include paper, cardboard, glass, certain plastics, and metals. Always check your local recycling guidelines for specifics.

Residential Waste
When we talk about , we’re diving into the everyday items that households generate. Think about it—each day, families across the globe toss out a variety of materials that, if not managed properly, can pile up in landfills and contribute to environmental degradation. Residential waste primarily consists of household items, food scraps, and recyclable materials. Understanding the composition of this waste is crucial for implementing effective recycling programs and reducing the overall impact on our planet.
Imagine your kitchen after a week of cooking: leftover food, packaging from groceries, and maybe some old newspapers lying around. This is the essence of residential waste. By recognizing what we throw away, we can start to make a difference. For instance, the typical household waste can be categorized into:
- Organic Waste: This includes food scraps, yard waste, and other biodegradable materials.
- Recyclables: Items like plastics, glass, and paper that can be processed and reused.
- General Waste: Non-recyclable items that end up in landfills.
Now, let’s focus on the recyclable materials within our residential waste. Identifying these items is essential for promoting recycling practices. Did you know that a significant portion of what we throw away can be recycled? By educating the public on proper sorting techniques, we can significantly increase recycling rates. For example, many people are unaware that certain types of plastics can be recycled, or that glass bottles can be turned into new containers. This knowledge can empower individuals to take action and reduce their waste footprint.
Moreover, we can't forget about organic waste. It might surprise you to learn that food scraps and yard waste contribute significantly to municipal waste. In fact, organic waste can account for up to 30% of the total waste generated by households. Implementing composting initiatives not only diverts this waste from landfills but also promotes sustainable practices that enrich the soil and reduce the need for chemical fertilizers. It’s like turning trash into treasure! By composting, we can create nutrient-rich soil that supports healthy gardens and landscapes.
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of residential waste is not just about managing what we throw away; it’s about fostering a culture of recycling and sustainability. By taking small steps—like sorting our waste, participating in composting programs, and educating ourselves and others—we can contribute to a cleaner, healthier environment for future generations. It’s all about making informed choices and encouraging our communities to do the same.
- What is the most common type of residential waste? The most common types include organic waste, plastics, paper, and glass.
- How can I start composting at home? You can start by collecting kitchen scraps and yard waste in a compost bin or pile, ensuring a good mix of greens (nitrogen-rich materials) and browns (carbon-rich materials).
- What should I do with items that can’t be recycled? Items that can’t be recycled should be disposed of in the general waste bin, but consider donating usable items to charities or thrift stores.

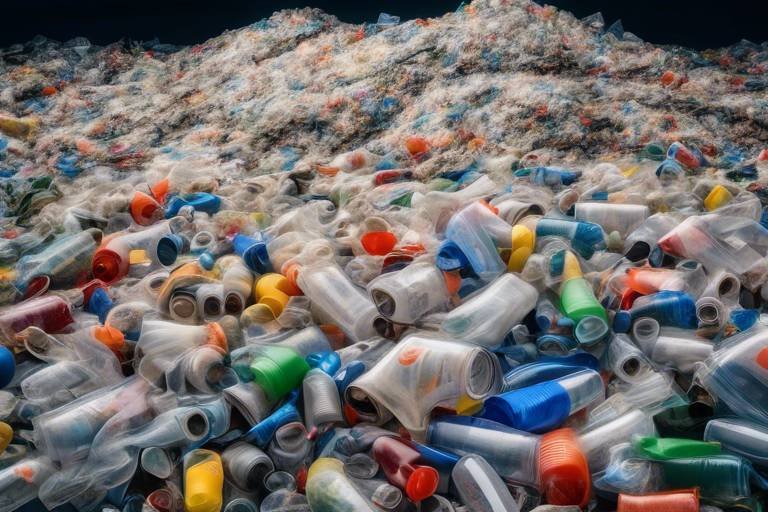
Recyclable Materials
When it comes to municipal waste, one of the most significant aspects is understanding what can be recycled. play a crucial role in reducing the overall waste that ends up in landfills, and knowing what these materials are can empower individuals and communities to make informed decisions about their waste disposal practices. It's like having a treasure map; once you know where to look, you can uncover valuable resources that can be reused and repurposed.
Recyclable materials typically include a variety of items found in our daily lives. For instance, common household recyclables such as paper, cardboard, glass, metals, and certain plastics can be collected and processed to create new products. By recycling these materials, we not only conserve natural resources but also save energy and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. To give you a clearer picture, here's a brief overview of some of the most commonly recycled materials:
| Material Type | Examples | Recycling Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Paper | Newspapers, magazines, office paper | Reduces deforestation, conserves water |
| Cardboard | Shipping boxes, cereal boxes | Reduces landfill waste, saves energy |
| Glass | Bottles, jars | 100% recyclable, reduces raw material extraction |
| Metals | Cans, aluminum foil | Recycling metals saves energy and reduces mining |
| Plastics | Bottles, containers | Reduces petroleum use, conserves resources |
However, despite the clear benefits of recycling, many people still struggle with the sorting process. It's essential to educate the public on how to properly sort their recyclables. For example, rinsing out food containers before tossing them in the recycling bin can significantly improve the quality of the recycled material. Moreover, contamination—when non-recyclable items are mixed with recyclables—can lead to entire batches being sent to landfills instead of being processed. This is why community education and awareness campaigns are vital in promoting effective recycling practices.
In addition to traditional recycling, there are also innovative approaches like upcycling, where old materials are transformed into new products without going through the recycling process. This creative reuse not only diverts waste from landfills but also encourages a culture of sustainability. Think of it as giving a second life to items that would otherwise be discarded. For instance, turning old glass jars into stylish storage containers or using wooden pallets to create furniture can inspire others to think outside the box.
In conclusion, understanding recyclable materials is not just about knowing what can be thrown in the recycling bin; it's about fostering a mindset of sustainability and resourcefulness. By actively participating in recycling and educating others, we can collectively work towards a cleaner and greener future. So, the next time you reach for that bottle or box, ask yourself: Can this be recycled? Your answer can make a world of difference!
- What types of materials can be recycled? Most common recyclable materials include paper, cardboard, glass, metals, and certain plastics.
- How can I ensure my recyclables are not contaminated? Rinse out food containers and avoid mixing non-recyclable items with your recyclables.
- What happens if I put the wrong items in the recycling bin? Contaminated recyclables can lead to entire batches being sent to landfills, undermining recycling efforts.
- Can I recycle items that are not accepted by my local program? Explore upcycling options or check for specialized recycling programs in your area.

Organic Waste
Organic waste is a significant component of municipal waste, comprising materials that are biodegradable and can naturally decompose. This category primarily includes food scraps, yard waste, and other compostable materials. The sheer volume of organic waste generated in urban areas is staggering, with households contributing a substantial portion. For instance, did you know that an average family can produce up to 1,000 pounds of organic waste each year? That's a lot of potential compost!
Addressing the challenges posed by organic waste is not just about reducing landfill contributions; it's also about harnessing the potential of these materials for sustainable practices. Implementing effective composting initiatives can divert organic waste from landfills, where it would otherwise generate harmful methane emissions—a potent greenhouse gas. By composting, we not only reduce waste but also create nutrient-rich soil amendments that can enhance our gardens and landscapes.
To better understand the impact of organic waste management, consider the following benefits:
- Environmental Protection: Reducing organic waste in landfills minimizes greenhouse gas emissions.
- Soil Enrichment: Composting returns valuable nutrients to the soil, promoting healthier plant growth.
- Cost Savings: By reducing waste disposal costs, municipalities can allocate resources to other essential services.
Moreover, educating the public about the importance of separating organic waste from general trash can significantly boost participation in composting programs. Simple actions like setting up a compost bin in your backyard or participating in community composting initiatives can make a huge difference. Think of it as turning your kitchen scraps into a treasure for your garden!
In summary, organic waste is not merely a problem to be managed; it is an opportunity to practice sustainability and environmental stewardship. By implementing composting initiatives and educating the community, we can transform organic waste into a valuable resource, ultimately paving the way for a cleaner, greener future.
Q: What types of materials can be composted?
A: Common compostable materials include fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, eggshells, grass clippings, and leaves. Avoid composting meats, dairy, and oils.
Q: How can I start composting at home?
A: You can start composting by setting up a compost bin in your backyard or using a compost tumbler. Layer green materials (like food scraps) with brown materials (like dried leaves) to create a balanced compost pile.
Q: What are the benefits of composting?
A: Composting reduces waste sent to landfills, decreases greenhouse gas emissions, enriches soil, and helps conserve water by improving soil structure.

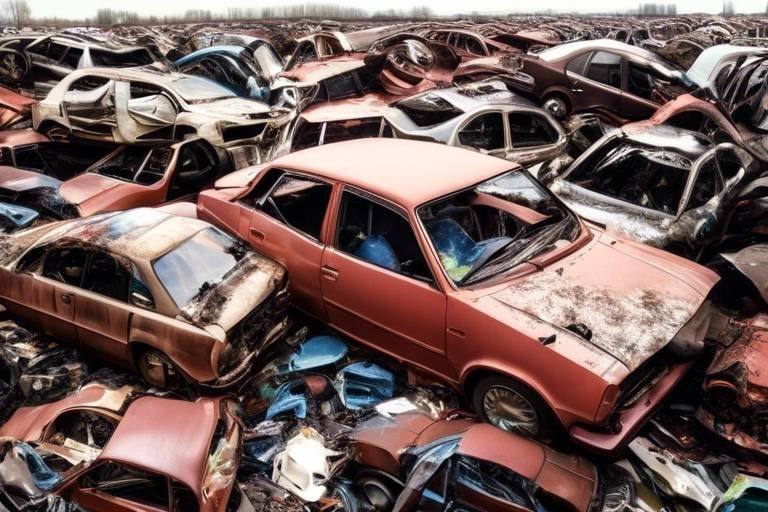
Commercial and Industrial Waste
The landscape of municipal waste management is not just shaped by the waste we generate at home; it also heavily relies on the waste produced by businesses and industries. encompasses a wide array of materials, including packaging, manufacturing by-products, and even hazardous substances. This type of waste is generated by various entities, such as retail stores, restaurants, factories, and construction sites, and understanding its impact is crucial for effective waste management strategies.
One of the primary challenges associated with managing commercial and industrial waste is its sheer volume and variety. Unlike residential waste, which is largely composed of organic materials and recyclables, commercial waste can include:
- Packaging materials: Cardboard, plastics, and other materials used for product packaging.
- Manufacturing waste: Scrap metal, wood, and other by-products from production processes.
- Hazardous waste: Chemicals, batteries, and electronic waste that require special handling and disposal.
To effectively tackle these challenges, municipalities must implement tailored strategies that not only comply with environmental regulations but also promote sustainability. For instance, many cities are now encouraging businesses to adopt recycling programs and waste reduction initiatives. By establishing partnerships with local businesses, municipalities can facilitate better waste sorting practices, ensuring that recyclable and hazardous materials are properly handled. This collaboration is vital, as it helps reduce the burden on landfills and promotes a cleaner environment.
Moreover, the economic implications of managing commercial and industrial waste cannot be overlooked. Businesses that prioritize waste management often see a reduction in disposal costs and an improvement in their public image. A well-implemented waste management plan can lead to:
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Cost Savings | Reducing waste disposal fees and increasing recycling can lower overall waste management costs. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adhering to local waste management laws helps avoid fines and enhances operational efficiency. |
| Enhanced Reputation | Companies that engage in sustainable practices often attract environmentally-conscious consumers. |
In conclusion, addressing commercial and industrial waste is not just a regulatory requirement; it's an opportunity for businesses to contribute positively to their communities. By embracing sustainable practices and collaborating with local authorities, companies can play a pivotal role in shaping a cleaner, greener future. As we move forward, it’s essential that we recognize the interconnectedness of our waste management efforts and work together towards innovative solutions that benefit both the environment and our economy.
Q: What is the difference between commercial and industrial waste?
A: Commercial waste is generated by businesses such as retail and restaurants, while industrial waste comes from manufacturing and production processes. Each type has its own set of management challenges.
Q: How can businesses reduce their waste?
A: Businesses can implement recycling programs, reduce packaging, and engage in composting initiatives to minimize waste generation.
Q: What are the consequences of improper waste disposal?
A: Improper disposal can lead to environmental contamination, health risks, and legal penalties for businesses. It’s crucial to follow local regulations and best practices for waste management.

Challenges in Waste Management
Municipal waste management is no walk in the park; it presents a myriad of challenges that can make even the most seasoned professionals scratch their heads. From infrastructure limitations to the need for greater public awareness, these hurdles can significantly hinder effective waste management systems. Understanding these challenges is crucial for municipalities aiming to create a cleaner, more sustainable environment.
One of the primary issues plaguing waste management is the inadequate infrastructure. Many municipalities are stuck with outdated systems that struggle to keep pace with the growing population and increasing waste generation. Imagine trying to fit a square peg into a round hole; that’s what it feels like when old facilities are forced to handle modern waste challenges. Upgrading waste processing facilities and investing in advanced technologies is not just a luxury; it’s a necessity to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
Another significant challenge lies in public awareness and participation. It’s one thing to have a solid waste management plan, but if the community isn’t on board, it’s like trying to steer a ship with a broken rudder. Many residents are simply unaware of how their actions impact waste generation and disposal. For instance, improper sorting of recyclables can lead to contamination, making entire batches of materials unusable. Therefore, engaging the community through educational programs and outreach initiatives is vital. Here are a few strategies that can be employed:
- Organizing community workshops to teach proper recycling techniques.
- Launching social media campaigns to raise awareness about waste reduction.
- Incentivizing participation in local recycling programs.
Moreover, funding poses another considerable challenge. Many municipalities operate on tight budgets, and waste management often takes a backseat to other pressing needs such as public safety and infrastructure development. This lack of funding can result in insufficient resources for waste collection, recycling programs, and public education initiatives. Without adequate financial support, even the best-laid plans can fall flat.
In summary, the challenges in municipal waste management are multifaceted and require a comprehensive approach to tackle effectively. By addressing infrastructure limitations, enhancing public awareness, and securing necessary funding, municipalities can pave the way for a more sustainable future. It’s a tough road ahead, but with commitment and innovative thinking, it’s a journey worth taking.
- What are the main challenges in municipal waste management?
The main challenges include inadequate infrastructure, public awareness, and funding issues. - How can public awareness improve waste management?
Increased public awareness can lead to better recycling practices and more community participation in waste reduction efforts. - Why is funding important for waste management?
Adequate funding is crucial for improving waste processing facilities, implementing recycling programs, and conducting public education initiatives.

Infrastructure Limitations
When we talk about municipal waste management, one of the most pressing issues that often comes up is the that many municipalities face. Imagine trying to build a house without a solid foundation—it's bound to crumble, right? Well, the same principle applies to waste management systems. Many cities are grappling with outdated facilities, insufficient waste processing technologies, and a lack of resources to develop modern solutions. This situation leads to inefficiencies that not only hinder effective waste management but also pose serious risks to public health and the environment.
For instance, consider a city that relies on old garbage trucks that break down frequently. This not only delays collection but also increases fuel consumption, leading to higher emissions. Moreover, without adequate sorting facilities, recyclable materials often end up in landfills, which is a missed opportunity for sustainability. The infrastructure gap can be illustrated in the following table:
| Infrastructure Element | Current Status | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Waste Collection Vehicles | Outdated and insufficient | Increased delays and costs |
| Sorting Facilities | Inadequate capacity | Lower recycling rates |
| Composting Sites | Limited availability | Higher organic waste in landfills |
Additionally, the lack of funding often exacerbates these infrastructure challenges. Municipalities may struggle to allocate budgets for upgrading facilities or investing in new technologies. This financial strain can lead to a vicious cycle where poor waste management systems result in increased operational costs, which in turn limit funding for improvements. It's a bit like trying to fill a leaky bucket—no matter how much water you pour in, it just keeps draining out.
So, what can be done to tackle these infrastructure limitations? Well, first and foremost, municipalities need to prioritize waste management in their planning and budgeting processes. This might mean advocating for policy changes that allocate more resources to waste management or seeking partnerships with private companies that specialize in waste processing technologies. Moreover, public-private partnerships can be a game-changer, allowing cities to leverage expertise and funding from the private sector.
In conclusion, addressing infrastructure limitations in municipal waste management is not just about improving services; it's about creating a sustainable future for our communities. By investing in modern facilities and technologies, cities can enhance their waste management systems, reduce environmental impact, and ultimately provide a cleaner, healthier living environment for their residents.
- What are the main challenges in municipal waste management? The primary challenges include inadequate infrastructure, lack of public awareness, and insufficient funding.
- How can communities improve their waste management systems? By investing in modern technologies, increasing public engagement, and prioritizing waste management in local policies.
- What role does recycling play in waste management? Recycling helps divert waste from landfills, conserves resources, and reduces environmental pollution.
Public Awareness and Participation
When it comes to municipal waste management, one of the most significant challenges is engaging the community. Why is public awareness so crucial? Well, think of it this way: if a tree falls in a forest and no one is around to hear it, does it make a sound? Similarly, if waste management programs are in place but the community isn't aware of them, their effectiveness diminishes. Public participation is not just a nice-to-have; it’s a necessity for creating a sustainable future.
Imagine a bustling city where every resident is informed and actively participating in waste reduction efforts. This vision can become a reality through targeted education and outreach programs. For instance, municipalities can host workshops, distribute informative brochures, and utilize social media campaigns to spread awareness about proper waste disposal and recycling practices. These initiatives can help residents understand not just the "how," but also the "why" behind these practices. After all, when people grasp the impact of their actions, they are more likely to change their habits.
Moreover, community involvement can take many forms. Here are a few examples of how individuals can contribute:
- Participating in Local Clean-Up Events: These events not only beautify neighborhoods but also foster a sense of community and responsibility.
- Joining Recycling Programs: Many cities offer programs that encourage residents to recycle more effectively, often with rewards for high participation rates.
- Advocating for Policy Changes: Residents can engage with local governments to advocate for better waste management policies and infrastructure.
Additionally, schools play a vital role in fostering awareness among younger generations. By integrating waste management education into the curriculum, children can learn the importance of sustainability from an early age. Imagine kids coming home and teaching their parents about composting or the benefits of reducing plastic use. This ripple effect can lead to a more informed and responsible community overall.
However, it’s not just about education; it’s also about creating a culture of participation. Municipalities can incentivize participation through programs that reward households for reducing waste or increasing recycling efforts. For example, a points-based system could be implemented where residents earn points for recycling correctly, which can be redeemed for discounts at local businesses. This not only encourages responsible behavior but also strengthens community ties.
In conclusion, enhancing public awareness and encouraging participation in municipal waste management is essential for creating a cleaner, more sustainable environment. By engaging residents through education, community events, and incentive programs, municipalities can foster a culture of responsibility that benefits everyone. After all, when the community works together, the impact can be transformative, turning waste management from a daunting task into a collaborative effort that everyone can be proud of.
Q1: How can I get involved in local waste management initiatives?
A1: You can start by checking with your local municipality for events, workshops, and programs focused on waste management. Participating in community clean-ups or joining recycling programs are great ways to contribute.
Q2: What are the benefits of recycling?
A2: Recycling helps reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills, conserves natural resources, saves energy, and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. It’s an essential part of sustainable waste management.
Q3: How can schools promote waste management awareness?
A3: Schools can integrate waste management topics into their curriculum, organize recycling competitions, or host workshops that engage students in hands-on activities related to sustainability.
Q4: What incentives can municipalities offer to encourage recycling?
A4: Municipalities can implement reward systems, offer discounts for eco-friendly products, or provide recognition for neighborhoods that excel in recycling and waste reduction efforts.

Innovative Solutions in Waste Management
As we navigate through the complexities of urban living, the need for effective waste management has never been more pressing. Fortunately, innovative solutions are emerging to tackle these challenges head-on. The integration of technology in waste management practices is revolutionizing how municipalities handle waste, making processes not only more efficient but also environmentally friendly. Imagine a world where waste collection is optimized using real-time data and smart technologies; this is no longer a distant dream but a reality that many cities are beginning to embrace.
One of the most exciting developments is the use of smart waste management technologies. These include IoT-enabled waste bins that can monitor fill levels and communicate with waste collection services. This technology allows for the optimization of collection routes and schedules, which can significantly reduce fuel consumption and operational costs. For instance, cities that have implemented smart bins have reported a decrease in collection frequency by up to 30%, leading to substantial savings and reduced environmental impact.
Moreover, the implementation of data analytics in waste management is another game-changer. By analyzing waste generation patterns, municipalities can identify peak waste production times and adjust their services accordingly. This not only ensures that waste is collected promptly but also helps in planning for future waste management needs. The table below illustrates how data analytics can improve efficiency in waste collection:
| Analytics Type | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Fill Level Monitoring | Optimizes collection routes and schedules |
| Waste Composition Analysis | Informs recycling and composting initiatives |
| Trend Analysis | Helps forecast future waste generation |
Another noteworthy approach is the Zero Waste Initiative, which aims to redesign resource life cycles to eliminate waste entirely. This initiative encourages communities to rethink their consumption habits and promotes practices such as recycling and composting. By focusing on waste reduction at the source, municipalities can significantly minimize the amount of waste that ends up in landfills. It's about creating a circular economy where resources are reused and recycled, rather than discarded.
Implementing zero waste strategies requires collaboration among various stakeholders, including local governments, businesses, and residents. This collective effort can lead to more sustainable practices, such as community composting programs and enhanced recycling campaigns. By engaging the public through educational programs, municipalities can foster a culture of sustainability that empowers individuals to take action in their waste management practices.
In conclusion, the future of municipal waste management lies in innovation and collaboration. By leveraging smart technologies and adopting zero waste initiatives, cities can transform their waste management systems into models of efficiency and sustainability. The journey towards a cleaner and greener urban environment is not just a possibility; it’s an achievable goal that requires the commitment of everyone involved.
- What are smart waste management technologies? These technologies include IoT-enabled waste bins and data analytics that optimize waste collection and reduce costs.
- What is a Zero Waste Initiative? It is a strategy aimed at eliminating waste through redesigning resource life cycles, encouraging recycling and composting.
- How can communities participate in waste management? Communities can engage by participating in recycling programs, composting initiatives, and educational campaigns about waste reduction.

Smart Waste Management Technologies
In today's fast-paced world, are revolutionizing how municipalities handle waste disposal and recycling. Imagine a city where waste collection is not just a routine task but a finely tuned operation that maximizes efficiency and minimizes environmental impact. This is becoming a reality thanks to innovations like IoT-enabled waste bins, which are equipped with sensors that monitor waste levels in real-time. These smart bins communicate with waste management systems to optimize collection routes, ensuring that trucks only visit when bins are nearly full. This not only saves fuel but also reduces greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment.
Moreover, data analytics plays a crucial role in smart waste management. By analyzing patterns in waste generation, municipalities can identify peak times for waste disposal and adjust their services accordingly. For example, if data shows that a particular neighborhood generates more waste during weekends, waste collection schedules can be adapted to meet this demand. This proactive approach leads to better resource allocation and improved service delivery, making waste management more responsive to community needs.
Another exciting development is the integration of mobile applications that empower residents to participate actively in waste management. These apps can provide users with information on recycling guidelines, collection schedules, and even reward systems for proper waste disposal. Imagine being able to track your recycling habits and earn points that can be redeemed for local discounts or community rewards! This kind of engagement fosters a sense of responsibility among citizens and encourages them to adopt sustainable practices.
Furthermore, municipalities are exploring the use of automated sorting technologies in recycling facilities. These advanced systems utilize artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify and sort recyclable materials more efficiently than human workers. By automating the sorting process, cities can significantly increase their recycling rates and reduce contamination, which is a common issue in recycling programs. The result is a more streamlined operation that enhances the overall effectiveness of waste management.
In summary, smart waste management technologies are not just about improving efficiency; they represent a holistic approach to urban sustainability. By leveraging cutting-edge innovations, cities can create a more responsive and responsible waste management system. The future looks bright, as these technologies pave the way for cleaner, greener urban spaces where waste is managed intelligently and sustainably.
- What are smart waste management technologies? Smart waste management technologies include IoT-enabled bins, data analytics, and automated sorting systems that enhance the efficiency of waste collection and recycling processes.
- How do IoT-enabled waste bins work? These bins have sensors that monitor waste levels and communicate with waste management systems to optimize collection routes, reducing costs and environmental impact.
- Can residents participate in smart waste management? Yes, many municipalities offer mobile applications that inform residents about recycling guidelines and collection schedules, encouraging community involvement.
- What benefits do automated sorting technologies provide? Automated sorting technologies improve recycling rates by efficiently identifying and sorting recyclable materials, reducing contamination and increasing overall effectiveness.

Zero Waste Initiatives
are revolutionary approaches aimed at fundamentally changing how we view waste. The idea is simple yet profound: instead of seeing waste as a byproduct of consumption, we should treat it as a resource. Imagine living in a world where everything we use is designed to be reused, repaired, or recycled. This vision is not just a dream; it's a tangible goal that communities around the globe are striving to achieve.
At the heart of zero waste initiatives is the concept of circular economy. This model emphasizes the importance of redesigning product life cycles to minimize waste generation. Instead of the traditional linear model—where we take, make, and dispose—zero waste encourages us to rethink our consumption habits. For instance, instead of throwing away a broken appliance, we should consider repairing it or recycling its components. This shift not only conserves resources but also reduces the environmental impact of manufacturing new products.
Zero waste initiatives often involve a combination of strategies, including:
- Education and Awareness: Educating the public about the importance of waste reduction and sustainable practices is crucial. Workshops, community events, and social media campaigns can help spread the message.
- Community Engagement: Getting the community involved fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility. Local groups can organize clean-up events, swap meets, and recycling drives to promote participation.
- Policy Advocacy: Advocating for policies that support zero waste practices, such as banning single-use plastics or incentivizing businesses to adopt sustainable practices, can lead to significant changes at the municipal level.
Implementing zero waste initiatives often requires collaboration between various stakeholders, including local governments, businesses, and residents. A successful example is the city of Capannori, Italy, which has achieved a remarkable 44% reduction in waste sent to landfills by adopting zero waste principles. This success story demonstrates that with commitment and innovation, it is possible to create a sustainable community.
Moreover, technology plays a crucial role in supporting zero waste initiatives. From apps that help users find recycling centers to platforms that connect people for sharing or exchanging goods, technology can enhance community engagement and streamline waste reduction efforts. These tools empower individuals to make informed choices about their consumption and disposal habits.
In conclusion, zero waste initiatives are not just about reducing the amount of waste we produce; they are about reimagining our relationship with resources. By embracing a mindset of sustainability, we can work together to create a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable future for generations to come.
1. What are zero waste initiatives?
Zero waste initiatives are strategies aimed at reducing waste to the point where it is eliminated entirely, focusing on reusing, recycling, and composting materials to minimize environmental impact.
2. How can individuals contribute to zero waste initiatives?
Individuals can contribute by reducing their consumption, choosing reusable products, participating in community clean-up events, and advocating for sustainable practices in their local communities.
3. What are some successful examples of zero waste initiatives?
Capannori, Italy, is a leading example, having significantly reduced its landfill waste through community engagement and policy changes that support sustainable practices.
4. How does technology support zero waste initiatives?
Technology supports zero waste initiatives through apps and platforms that facilitate recycling, sharing, and community engagement, making it easier for individuals to participate in sustainable practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is municipal waste management?
Municipal waste management refers to the processes involved in collecting, treating, and disposing of waste generated in urban areas. It includes everything from household garbage to commercial waste, ensuring that waste is handled in a way that protects public health and the environment.
- Why is municipal waste management important?
Effective municipal waste management is crucial for several reasons. It helps reduce pollution, protects natural resources, and promotes public health. By managing waste properly, communities can improve their quality of life and create a more sustainable environment.
- What types of waste are included in municipal waste?
Municipal waste includes various types of waste such as residential waste (household items, food scraps), commercial waste (from businesses), and industrial waste (from factories). Each type requires different management strategies to address its specific challenges.
- How can I reduce my household waste?
Reducing household waste can be achieved by practicing the 3 R's: Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle. This means cutting down on what you buy, finding new uses for items instead of throwing them away, and properly sorting recyclable materials to ensure they are processed correctly.
- What are recyclable materials?
Recyclable materials are items that can be processed and turned into new products instead of being sent to landfills. Common recyclable materials include paper, cardboard, glass, plastic bottles, and certain metals. Knowing what can be recycled helps increase recycling rates.
- What is organic waste and how can it be managed?
Organic waste consists of biodegradable materials like food scraps and yard waste. Managing organic waste effectively can involve composting, which not only reduces landfill contributions but also produces nutrient-rich soil for gardening and landscaping.
- What challenges does municipal waste management face?
Municipal waste management faces various challenges, including inadequate infrastructure, lack of public awareness, and insufficient funding. Overcoming these challenges is vital for developing efficient waste management systems that can handle increasing waste volumes.
- How can technology improve waste management?
Emerging technologies, such as smart waste management systems, can significantly enhance waste collection and processing. For instance, IoT-enabled waste bins can optimize collection routes, while data analytics can help municipalities make informed decisions about resource allocation.
- What are zero waste initiatives?
Zero waste initiatives aim to redesign resource life cycles to eliminate waste entirely. These programs encourage practices like recycling, composting, and reducing consumption to minimize waste generation right from the source, fostering a more sustainable community.



















