How Rapid Urbanisation Is Affecting Bird Species
The phenomenon of rapid urbanisation has become a defining characteristic of our modern world. As cities expand and populations surge, the natural habitats that once thrived are increasingly being replaced by concrete jungles. This transformation has profound implications for the countless bird species that inhabit these areas. Imagine a bustling cityscape where the melodic chirping of birds is drowned out by the cacophony of traffic and construction. It’s a stark reminder of how urban growth can disrupt the delicate balance of nature. In this article, we will explore the multifaceted impacts of urbanisation on bird species, delving into habitat loss, behavioral changes, and the concerted efforts being made to conserve these avian populations in an ever-evolving urban environment.
Urbanisation leads to significant habitat destruction, forcing many bird species to adapt or relocate. As forests, wetlands, and grasslands are replaced by buildings and roads, birds lose their natural homes. This loss of habitat is not just about the physical space; it also means a loss of food sources, nesting sites, and safe areas for raising their young. For instance, species that once flourished in open fields may find themselves squeezed into smaller and smaller patches of green, struggling to survive amidst the encroaching urban sprawl. Understanding these changes helps us grasp the broader implications for biodiversity and ecosystem health. The question we must ask ourselves is: what happens to the intricate web of life when one strand is pulled away?
As urban environments evolve, birds exhibit altered behaviors, including changes in nesting, feeding, and migration patterns. These adaptations highlight the resilience of species in the face of environmental challenges. For example, some birds have learned to nest in the nooks and crannies of buildings, while others have adjusted their migration routes to avoid busy urban areas. This adaptability is remarkable, yet it raises a critical concern: are these changes sustainable in the long run? The survival of many species now hinges on their ability to navigate this new urban landscape.
Urban birds often modify their diets to exploit new food sources, such as human refuse. This shift can affect their health and reproductive success, raising concerns for long-term survival. Birds that once relied on natural food sources may find themselves scavenging in dumpsters or foraging in parks where people feed them. While this may sound like an easy meal, it can lead to nutritional deficiencies and increased vulnerability to disease. The reliance on human-provided food can create a cycle of dependency that may not be sustainable. Have we inadvertently created a scenario where our waste becomes their lifeline?
Increased human presence alters bird feeding habits, with some species becoming overly reliant on human-provided food. This dependency can lead to maladaptive behaviors and population declines. For instance, birds that frequent parks may lose their natural foraging instincts, making them less capable of surviving in the wild. It's a troubling thought: by trying to help, are we actually harming them? The balance of nature is delicate, and our interventions must be carefully considered.
Urban settings may intensify competition among bird species for limited resources, impacting their survival. As various species vie for the same food and nesting sites, some may thrive while others decline. This competitive pressure can lead to shifts in local bird populations, with more adaptable species outcompeting their less flexible counterparts. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for effective conservation strategies. We must recognize that every species plays a role in the ecosystem, and losing even one can have ripple effects throughout the community.
Urbanisation often forces birds to adapt their nesting strategies, utilizing artificial structures. These changes can influence reproductive success and population dynamics in urban bird communities. For example, some species may nest in the eaves of buildings or in hanging planters, while others may take advantage of abandoned structures. While these adaptations showcase the ingenuity of birds, they also pose risks, such as exposure to predators and human disturbances. How can we create environments that support these nesting behaviors while minimizing risks?
Pollution in urban areas poses significant risks to bird species, affecting their health and habitat quality. Addressing these threats is essential for safeguarding avian populations in cities. From air pollution to contaminated waterways, the impacts of urban pollution are far-reaching. Birds, being at the top of the food chain in many ecosystems, often serve as indicators of environmental health. Their decline can signal deeper issues within our urban environments.
Poor air quality can lead to respiratory issues in birds, impacting their overall health and reproductive success. Monitoring air quality is vital for understanding its effects on urban wildlife. High levels of pollutants can stress bird populations, leading to decreased fertility and increased mortality rates. It’s a sobering reality that the air we breathe can have dire consequences for our feathered friends.
Contaminated water sources can harm aquatic birds, affecting their food supply and breeding success. Effective water management practices are necessary to protect these vulnerable species. Polluted lakes and rivers can lead to a decline in fish populations, which many birds rely on for food. Additionally, toxins in the water can have harmful effects on the birds themselves, leading to health problems that can ripple through entire populations. Isn’t it time we prioritized the health of our waterways for the sake of all life?
To combat the negative effects of urbanisation, various conservation initiatives aim to create bird-friendly environments. These efforts are crucial for maintaining biodiversity in rapidly developing regions. From creating green roofs to establishing wildlife corridors, cities can become havens for birds if we make conscious choices about urban planning.
Establishing parks and green corridors in urban areas provides essential habitats for birds. These spaces enhance biodiversity and promote ecological balance in cities. By integrating nature into urban design, we can create environments where both humans and birds can thrive. Imagine a city where parks are not just patches of green, but vibrant ecosystems teeming with life!
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts fosters awareness and support for bird protection initiatives. Community involvement is key to creating sustainable urban ecosystems for wildlife. When residents take an active role in preserving their local environment, it leads to a greater appreciation for the natural world. Simple actions, such as planting native species or participating in birdwatching groups, can make a significant difference.
- How does urbanisation impact bird populations? Urbanisation leads to habitat loss, altered behaviors, and increased competition for resources among bird species.
- What are some common adaptations birds make in urban environments? Birds often modify their diets, nesting habits, and migration patterns to survive in cities.
- How can we help urban birds? Creating green spaces, reducing pollution, and engaging in local conservation efforts are effective ways to support urban bird populations.
- What role do community initiatives play in bird conservation? Community involvement fosters awareness and encourages sustainable practices that benefit local wildlife.
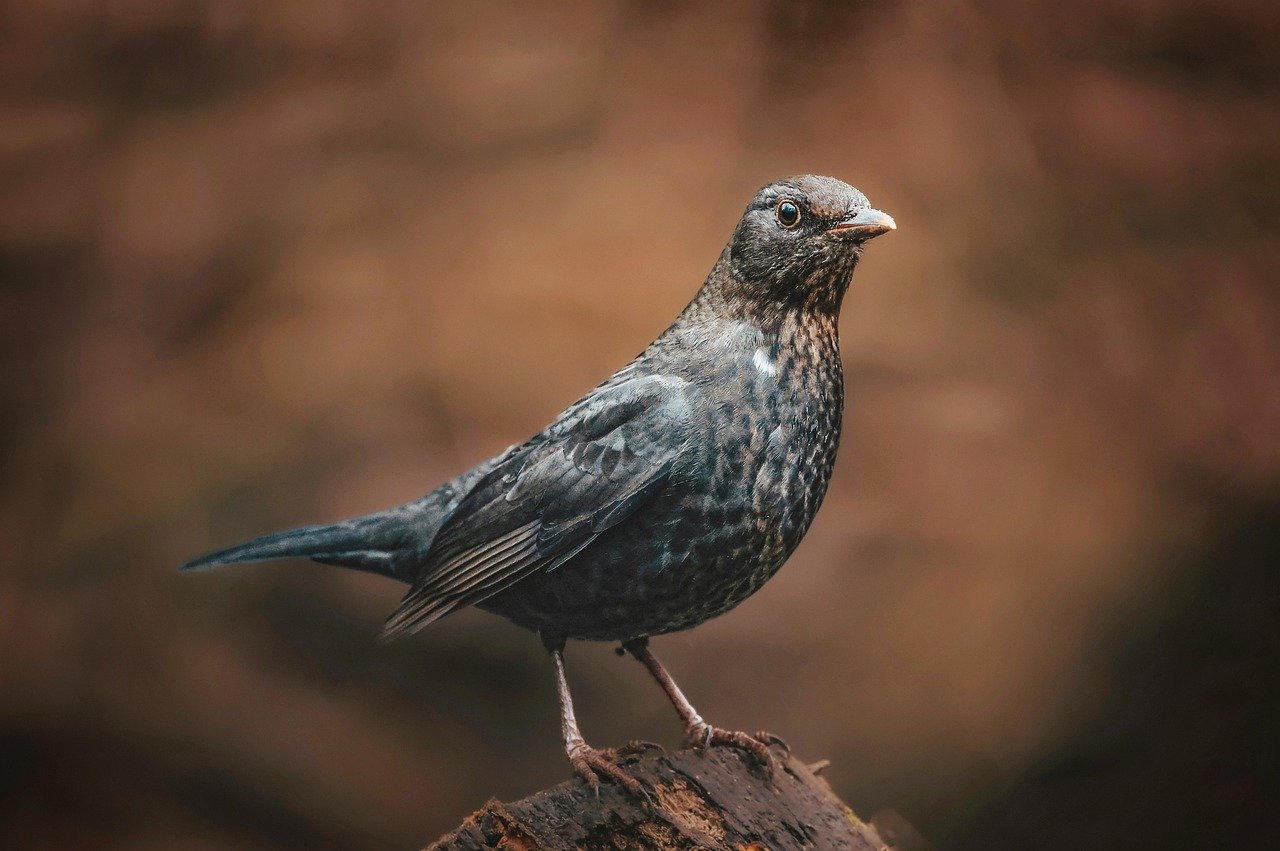

Impact on Habitat Loss
Urbanisation is a double-edged sword—it brings development and progress, yet it also leads to significant habitat destruction for countless bird species. As cities expand, forests, wetlands, and grasslands are often cleared to make way for buildings, roads, and infrastructure. This transformation of the landscape doesn't just displace birds; it fundamentally alters their ecosystems, which can have dire consequences for biodiversity. Imagine a once-thriving forest filled with chirping birds, now reduced to concrete and steel. The impact is profound and far-reaching.
When we talk about habitat loss, we're not just discussing the physical space that birds occupy; we're also referring to the intricate web of life that supports them. Birds rely on specific habitats for nesting, feeding, and shelter. As these environments vanish, many species find themselves in a precarious position, forced to adapt to new surroundings or relocate entirely. Unfortunately, not all birds are equipped to make such drastic changes. For instance, species that require large territories or specific nesting sites may struggle to survive in fragmented urban landscapes.
To illustrate the severity of habitat loss, consider the following statistics:
| Year | Habitat Loss (%) | Bird Species Affected |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 10% | 50 |
| 2010 | 20% | 100 |
| 2020 | 30% | 150 |
This table highlights the increasing habitat loss over the years and its direct impact on bird populations. As urbanisation continues to rise, the number of species affected grows alarmingly. The loss of habitat not only threatens individual species but also disrupts the balance of entire ecosystems. Birds play a crucial role in pollination, seed dispersal, and pest control, and their decline can lead to a cascading effect on other wildlife.
Moreover, as we witness these changes, it becomes clear that urban habitats are not merely barren landscapes devoid of life. Many birds have shown remarkable resilience, adapting to urban environments in unexpected ways. However, this adaptability comes with its own set of challenges. For example, species that thrive in urban settings may outcompete their rural counterparts, leading to a decline in biodiversity. To truly understand the impact of habitat loss, we must consider both the immediate effects on bird populations and the long-term implications for our ecosystems.
In summary, the impact of urbanisation on habitat loss is both profound and complex. It forces birds to adapt, relocate, or face extinction. As we continue to develop our urban landscapes, it is crucial to remember the intricate connections within our ecosystems and the importance of preserving natural habitats for the birds that enrich our lives.
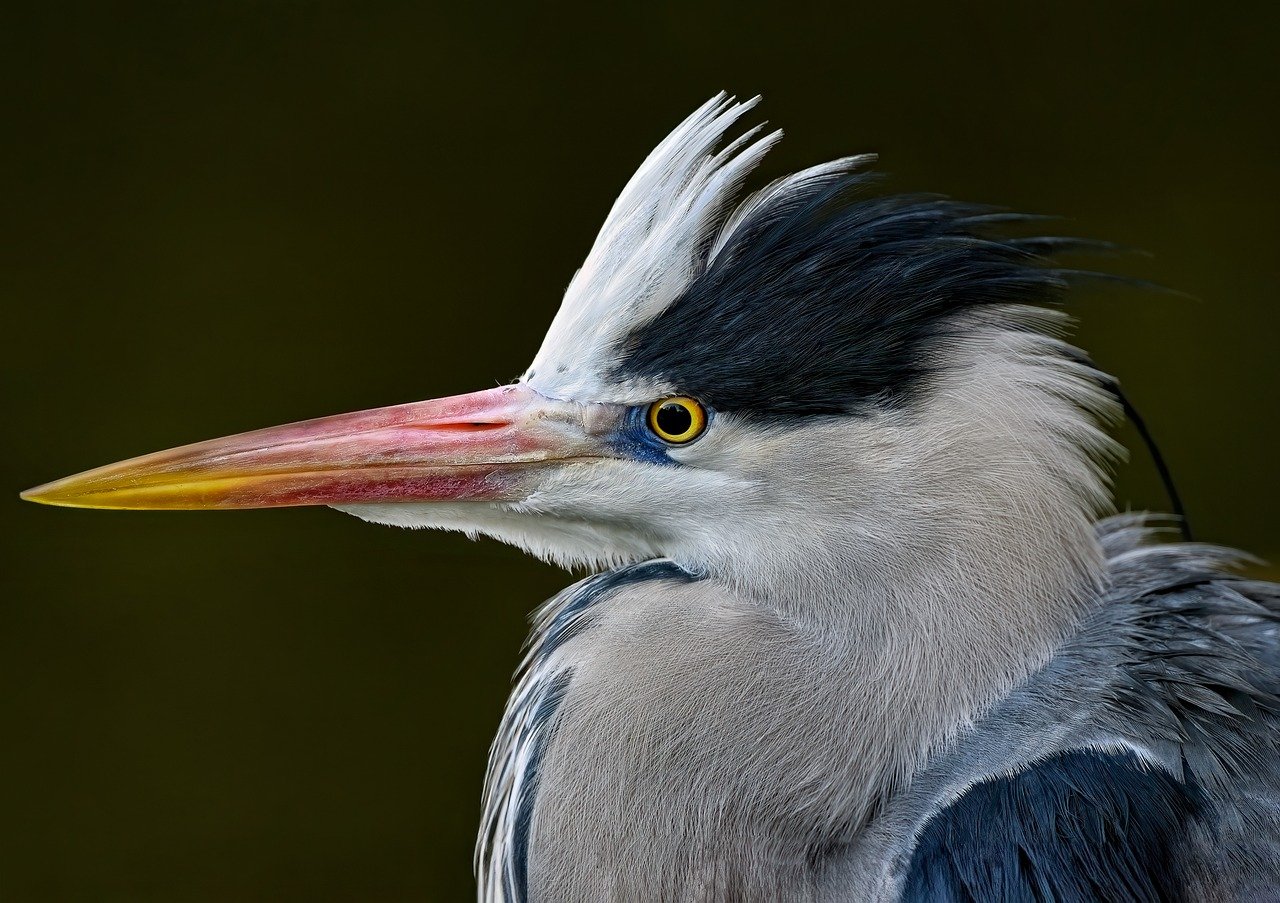

Behavioral Changes in Birds
As urban environments evolve, birds are not just passive observers; they are dynamic actors adapting to their changing surroundings. The hustle and bustle of city life brings about a myriad of challenges, prompting birds to modify their behaviors in fascinating ways. One of the most notable changes is in their feeding habits. Urban birds have become adept at exploiting new food sources, often turning to human refuse as a primary diet component. This shift can be likened to a child discovering a candy store; the abundance of easily accessible food can be tempting, but it may not always be the healthiest option.
In addition to altering their diets, urban birds are also changing their nesting behaviors. With natural habitats disappearing, many species have taken to utilizing artificial structures for nesting. From the nooks of buildings to the ledges of bridges, these birds are demonstrating remarkable ingenuity. However, this adaptation can come with its own set of challenges. For instance, nesting in urban areas often exposes birds to increased predation and disturbances from human activities. This can lead to lower reproductive success rates, further complicating their survival in these environments.
Moreover, the presence of humans greatly influences bird behavior. Many species have become increasingly tolerant of human activities, often foraging in parks and backyards where food is plentiful. However, this dependency on human-provided resources can lead to maladaptive behaviors. Birds that rely too heavily on human food sources may find themselves at a disadvantage when natural food becomes scarce or when they attempt to migrate. It's a classic case of being too comfortable in one’s environment, which can ultimately jeopardize their long-term survival.
Competition for resources is another pressing issue in urban settings. With many bird species vying for limited food and nesting sites, the struggle for survival intensifies. This competition can lead to shifts in population dynamics, where some species thrive while others decline. Understanding these interactions is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies. After all, if we want to create a harmonious coexistence between urban development and wildlife, we must first recognize the intricate dance of adaptation that birds are performing in our cities.
Urban birds often modify their diets to exploit new food sources, such as human refuse. This shift can affect their health and reproductive success, raising concerns for long-term survival. The table below summarizes some common urban feeding adaptations observed in various bird species:
| Bird Species | Common Urban Food Sources | Potential Health Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Pigeons | Breadcrumbs, fast food waste | Obesity, malnutrition |
| Starlings | Insects, human leftovers | Dependency, reduced foraging skills |
| Sparrows | Seeds, discarded food | Increased competition, disease transmission |
This table highlights the complex relationship between urban birds and their food sources, illustrating the challenges they face in adapting to city life. As we continue to observe these changes, it becomes increasingly clear that our urban landscapes are not just concrete jungles but vital habitats that require our attention and protection.
Increased human presence alters bird feeding habits, with some species becoming overly reliant on human-provided food. This dependency can lead to maladaptive behaviors and population declines. The cycle of feeding and interaction can create a false sense of security for these birds, making them vulnerable to changes in human behavior or environmental conditions.
Urban settings may intensify competition among bird species for limited resources, impacting their survival. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for effective conservation strategies. By recognizing the changes in behavior and adaptations of birds, we can better appreciate the delicate balance of urban ecosystems and work towards solutions that benefit both wildlife and human communities.
- How does urbanization affect bird migration? Urbanization can disrupt traditional migration routes and timings, forcing birds to adapt their migratory behavior.
- Are all bird species equally affected by urbanization? No, some species are more adaptable and thrive in urban environments, while others struggle to survive.
- What can individuals do to help urban birds? Creating bird-friendly spaces, such as gardens with native plants, can provide essential habitats for urban birds.
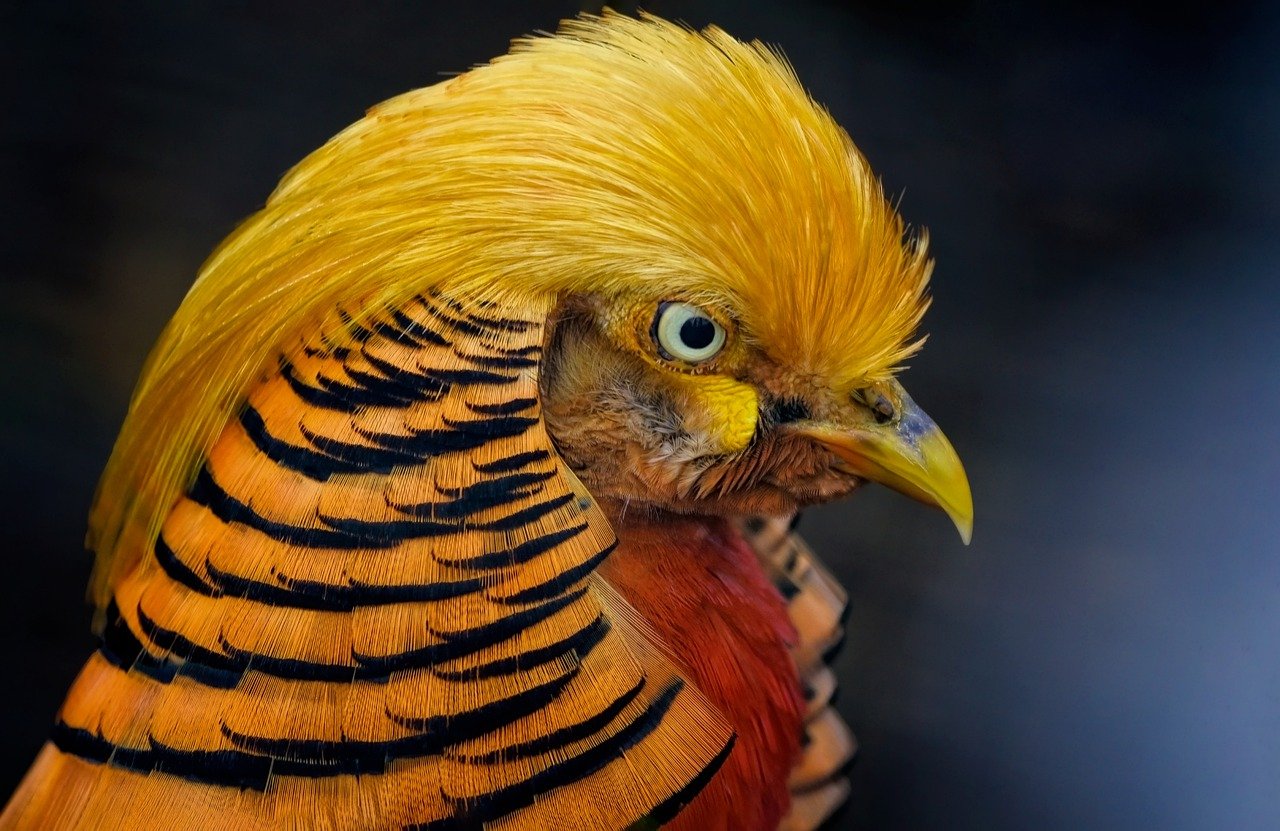

Feeding Adaptations
Urban environments present a unique challenge for birds, forcing them to adapt their feeding habits to survive in a rapidly changing landscape. As cities expand, natural food sources become scarce, leading many species to modify their diets. You might be surprised to learn that some birds have become quite adept at scavenging human refuse! This shift in diet can sometimes lead to an abundance of food, but it also comes with significant risks. For instance, while urban birds might feast on leftovers, they also consume unhealthy items that can affect their health and reproductive success.
Take the common pigeon, for example. Once primarily seed eaters, these birds have learned to thrive on discarded fast food and other human waste. While this adaptability showcases their resilience, it raises a critical question: what does this mean for their long-term survival? The reliance on human-provided food can lead to a decline in natural foraging skills, making these birds vulnerable if their urban food sources were to dwindle.
Additionally, urbanization can create a competitive environment. With multiple bird species vying for the same limited resources, the competition can become fierce. Some birds may even resort to aggressive behaviors to secure their meals. This intensified competition can disrupt established feeding patterns and have cascading effects on the entire avian community. Understanding these dynamics is vital for conservationists aiming to protect urban bird populations. After all, when one species thrives at the expense of another, the balance of the ecosystem is at risk.
Moreover, human interaction plays a significant role in shaping these feeding adaptations. Birds like crows and gulls have become increasingly bold, often foraging in close proximity to people. While this behavior may seem amusing, it can lead to maladaptive behaviors, where birds rely too heavily on human food sources. This dependency can result in a decline in their natural instincts and behaviors, which is concerning for their overall survival.
In summary, the feeding adaptations of birds in urban areas are a fascinating yet complex phenomenon. As they navigate the challenges of city life, these birds demonstrate remarkable resilience. However, the implications of their dietary changes can have profound effects on their health and the broader ecosystem. To better understand these adaptations, we must consider not only the immediate benefits of urban food sources but also the long-term consequences that come with them.
- How do urban birds adapt their feeding habits?
Urban birds often change their diets to exploit human refuse and other readily available food sources, which can lead to both benefits and risks for their health. - What are the potential dangers of urban birds relying on human food?
Reliance on human food can result in poor nutrition, loss of foraging skills, and maladaptive behaviors, ultimately threatening their survival. - How does competition for food affect urban bird species?
Increased competition for limited resources can lead to aggressive behaviors among species and disrupt the balance of the urban avian community.
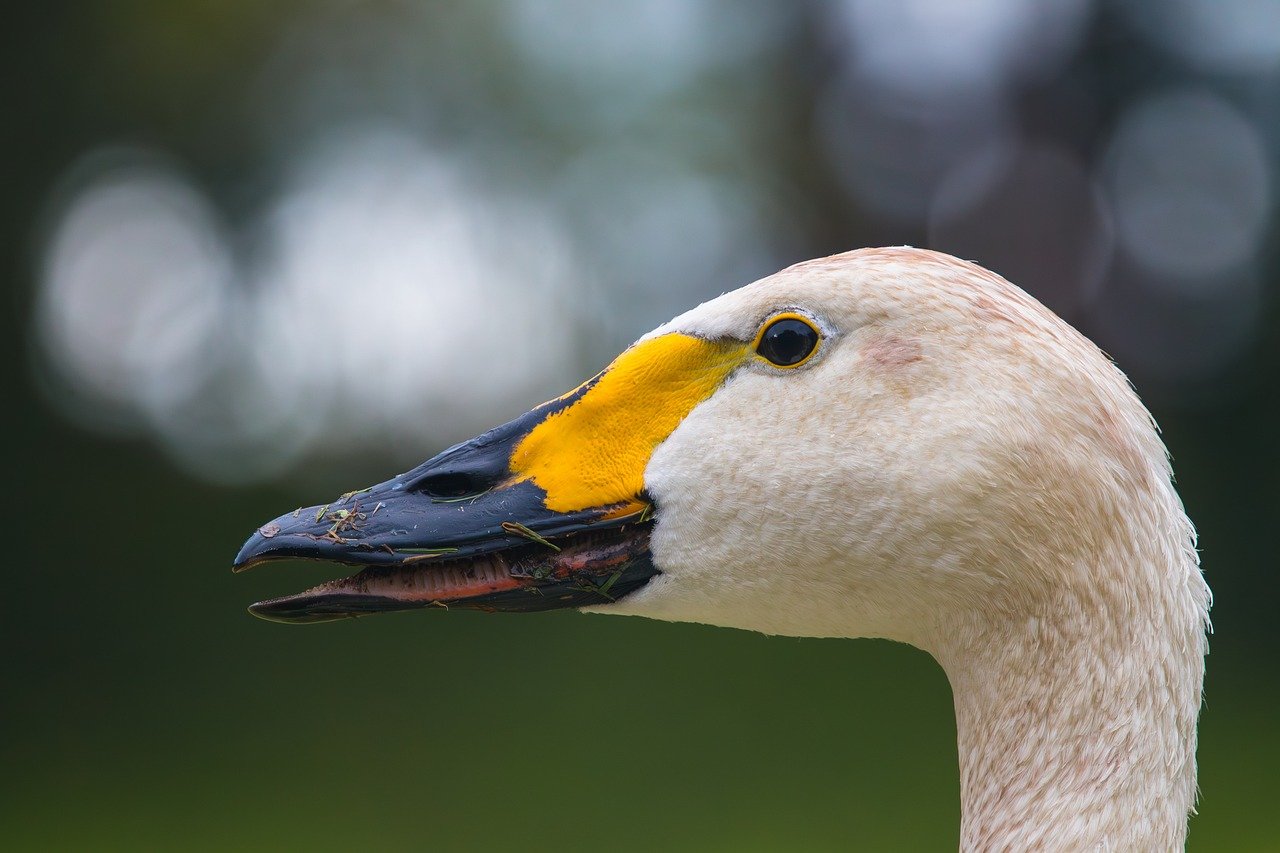

Human Interaction
As urban landscapes expand, the relationship between birds and humans has become increasingly complicated. Birds, once accustomed to vast natural habitats, now find themselves navigating a world dominated by human activity. This shift has led to significant changes in their feeding habits, nesting behaviors, and overall survival strategies. For instance, many bird species have adapted to rely on human-provided food sources, such as scraps from parks or leftovers discarded in urban areas. While this might seem like a boon for the birds, it can often lead to maladaptive behaviors that threaten their long-term survival.
Consider the common pigeon, which has become a symbol of urban wildlife. These birds have learned to thrive in cities, feeding on everything from discarded pizza crusts to bird feeders in parks. However, this dependency on human food can create a cycle of reliance that diminishes their natural foraging skills. When faced with a sudden change in human behavior—like a city-wide initiative to reduce litter—these birds may struggle to adapt. This situation illustrates a broader concern: as birds become more reliant on human-provided resources, they may lose their ability to survive independently in their natural habitats.
Moreover, the increased human presence in urban environments can lead to heightened stress levels among birds. Constant disturbances from noise, traffic, and human activity can disrupt their natural behaviors. For example, birds may alter their nesting sites to avoid human interactions, opting for less ideal locations that offer some level of safety but may not provide the best resources for raising their young. This shift can impact reproductive success and ultimately affect population dynamics.
In addition to these behavioral changes, the interaction between humans and birds can also lead to increased competition for resources. With more people living in urban areas, the demand for space and food intensifies. This competition can be particularly fierce among species that are already vulnerable or have specialized dietary needs. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies that support both bird populations and human communities.
To mitigate these challenges, it is essential for urban planners and conservationists to consider the needs of birds in their designs. Creating bird-friendly environments involves more than just planting trees; it requires a holistic approach that considers how birds interact with their surroundings. By fostering a deeper understanding of these interactions, we can create urban spaces that benefit both humans and wildlife, ensuring that our cities remain vibrant ecosystems.
- How does urbanization affect bird populations?
Urbanization leads to habitat loss, changes in behavior, and increased competition for resources, which can negatively impact bird populations. - What are some common adaptations birds make in urban environments?
Birds often adapt their diets to include human food, change their nesting sites to artificial structures, and alter their migration patterns. - How can communities help protect urban bird species?
Communities can create green spaces, participate in conservation initiatives, and reduce pollution to support bird populations in urban areas.

Competition for Resources
In the bustling chaos of urban life, where skyscrapers replace trees and concrete dominates the landscape, birds face an increasingly fierce competition for resources. Urban environments have a unique set of challenges that can drastically affect avian populations. With a plethora of species vying for limited food, nesting sites, and safe territories, the struggle for survival intensifies. Imagine a crowded marketplace where every vendor is fighting for the attention of customers; this is akin to what birds experience in cities.
As urbanization expands, natural habitats shrink, leading to an influx of bird species into these new territories. This sudden increase in bird populations can lead to heightened competition for essential resources. For example, consider the following factors that contribute to this competition:
- Food Sources: With fewer natural food sources available, many birds are forced to adapt to urban diets. This often means scavenging through human waste or competing for scraps left behind. Such dietary shifts can lead to nutritional deficiencies and increased mortality rates.
- Nesting Sites: Urban landscapes offer limited natural nesting locations, pushing birds to utilize artificial structures such as buildings, bridges, and even streetlights. However, these sites may not always be safe or suitable, leading to increased competition among species that seek the same nesting spots.
- Territorial Disputes: As various species occupy the same urban areas, territorial disputes become more common. Birds may engage in aggressive behaviors to defend their claimed spaces, which can result in injuries and decreased reproductive success.
This competition can have cascading effects on the overall health of bird populations. For instance, when a dominant species outcompetes others for food and nesting sites, it can lead to a decline in less competitive species. This not only affects biodiversity but also disrupts the ecological balance within urban environments. Just like in a game of musical chairs, when the music stops, not every bird finds a seat.
Furthermore, understanding these competitive dynamics is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies. By identifying which species are most affected by resource competition, conservationists can tailor their efforts to protect vulnerable populations. This could include creating more green spaces or ensuring that urban planning considers the needs of local wildlife. In essence, fostering an environment where various bird species can coexist harmoniously is essential for maintaining the rich biodiversity that our urban landscapes desperately need.
- How does urbanization affect bird species?
Urbanization leads to habitat loss, changes in behavior, and increased competition for resources among bird species. - What are some common adaptations birds make in urban environments?
Birds often change their diets, nesting strategies, and even migration patterns to cope with urban challenges. - What can be done to help urban bird populations?
Creating green spaces, engaging communities in conservation, and monitoring pollution levels can significantly benefit urban bird populations. - Why is biodiversity important in urban areas?
Biodiversity helps maintain ecosystem balance, supports food webs, and contributes to the overall health of urban environments.

Nesting Behavior Changes
As urbanization spreads like wildfire, bird species find themselves in a unique predicament. Gone are the days when they could rely solely on natural habitats for nesting. Instead, they are now adapting to a world filled with concrete jungles and towering skyscrapers. This shift in nesting behavior is not just fascinating; it’s a critical survival strategy. Birds are becoming increasingly inventive, using available resources in urban settings to build their nests.
For instance, species such as pigeons and sparrows have taken to nesting in nooks and crannies of buildings, using materials like plastic, paper, and even discarded items to create their homes. This adaptation to artificial structures is a prime example of how resilient these creatures can be. However, this change does come with its own set of challenges. Urban nests are often exposed to higher risks from predators and human disturbances, which can lead to lower reproductive success rates.
Moreover, the urban landscape can significantly influence the types of materials birds choose for nesting. In a natural environment, birds might select twigs, leaves, and mud, but in urban areas, the availability of these materials can be limited. Instead, they may opt for:
- Plastic bags
- Straws
- Old newspapers
- Wires and strings
This shift raises critical questions about the long-term implications for bird populations. Are these materials safe for their health? Do they affect the structural integrity of the nests? As researchers delve deeper into these questions, it becomes evident that urban environments are not just backdrops for bird life; they are dynamic ecosystems that require careful study and understanding.
Interestingly, some species have been observed to nest in surprisingly creative locations. For example, common swifts have been known to build their nests in the eaves of buildings, while house finches often make their homes in hanging planters or on window ledges. Such behavior underscores the adaptability of birds but also highlights the need for urban planners to consider wildlife in their designs. By incorporating bird-friendly architecture, we can help mitigate the challenges these species face.
In summary, the changes in nesting behavior among birds in urban environments illustrate a remarkable resilience. However, these adaptations also signal the urgent need for conservation efforts to ensure that our feathered friends can thrive in a rapidly changing world. Understanding these behaviors not only enriches our knowledge of avian life but also emphasizes the importance of preserving biodiversity in our cities.
- How do urban birds choose nesting sites?
Urban birds often opt for locations that provide shelter from predators and human disturbances, such as building ledges, eaves, and even hanging planters. - What materials do urban birds use for nesting?
They tend to use available materials like plastic, paper, and other human-made items, which can sometimes pose health risks. - Are urban nests less successful than those in natural habitats?
Yes, urban nests may face higher risks from predators and disturbances, potentially leading to lower reproductive success. - How can we help support urban bird populations?
Creating bird-friendly spaces, such as parks and green corridors, and minimizing disturbances can help support urban bird populations.

Threats from Pollution
Pollution in urban areas poses significant risks to bird species, affecting their health and habitat quality. As cities expand and industrial activities increase, the natural environment becomes inundated with pollutants that can have dire consequences for avian populations. Birds, being highly sensitive to changes in their surroundings, often serve as indicators of environmental health. When pollution levels rise, the impacts on birds can be profound and multifaceted.
One of the most pressing issues is air pollution. Poor air quality can lead to a range of respiratory issues in birds, which not only affects their overall health but also their reproductive success. Imagine trying to breathe in a smoky room; it’s uncomfortable and harmful. For birds, inhaling polluted air can be just as detrimental. Studies have shown that birds exposed to high levels of air pollutants tend to have shorter lifespans and lower reproductive rates. Monitoring air quality is vital for understanding its effects on urban wildlife, and it’s essential for implementing effective conservation strategies.
Another significant concern is water pollution. Contaminated water sources can harm aquatic birds, affecting their food supply and breeding success. When waterways are tainted with chemicals, heavy metals, or plastics, the effects ripple through the ecosystem. Birds that rely on these water sources for drinking and feeding may suffer from poisoning or reduced reproductive success. For example, species like ducks and herons are particularly vulnerable, as their diets often include fish and invertebrates that may be contaminated. Effective water management practices are necessary to protect these vulnerable species, including regular monitoring of water quality and implementing measures to reduce runoff from urban areas.
Additionally, noise pollution is an often-overlooked factor that can disrupt bird communication and mating rituals. Urban areas are filled with sounds from traffic, construction, and other human activities, which can drown out the natural calls of birds. This interference can lead to stress and disorientation, affecting their ability to find mates and raise young. The impact of noise pollution is particularly concerning for species that rely heavily on vocalizations to communicate.
In summary, pollution in urban environments is a significant threat to bird species, impacting their health, habitat quality, and overall survival. Addressing these threats is essential for safeguarding avian populations in cities. As we continue to urbanize, it’s crucial to consider the implications of our actions on the natural world. By prioritizing cleaner air and water, we can help create a more sustainable environment for birds and other wildlife.
- How does air pollution affect birds?
Air pollution can lead to respiratory issues in birds, impacting their health and reproductive success. - What are the effects of water pollution on bird species?
Contaminated water sources can harm aquatic birds, affecting their food supply and breeding success. - Can noise pollution impact bird behavior?
Yes, noise pollution can disrupt bird communication and mating rituals, leading to stress and disorientation. - What can be done to protect birds from urban pollution?
Implementing effective conservation strategies, such as monitoring air and water quality, and creating green spaces, can help protect birds from urban pollution.

Air Quality and Bird Health
Air quality plays a crucial role in the health of bird species, particularly in urban environments where pollution levels can soar. Birds, much like humans, are susceptible to the detrimental effects of poor air quality. The pollutants that fill our skies—like carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter—pose serious risks to avian health. These substances can lead to respiratory issues and other health complications, ultimately affecting their ability to thrive.
Research indicates that birds exposed to high levels of air pollution often experience a range of health problems, including:
- Respiratory distress: Just as smog can irritate our lungs, it can cause similar issues in birds, making it difficult for them to breathe.
- Reduced reproductive success: Poor air quality can lead to lower fertility rates and fewer successful hatchlings, threatening the long-term survival of species.
- Weakened immune systems: Prolonged exposure to pollutants weakens birds' defenses against diseases, making them more vulnerable.
Moreover, the impact of air quality on bird health extends beyond individual species; it can disrupt entire ecosystems. For instance, when birds struggle to reproduce or survive due to pollution, their prey and predators are also affected, leading to a ripple effect throughout the food chain. This interconnectedness emphasizes the importance of monitoring air quality and implementing measures to improve it.
To illustrate the relationship between air quality and bird health, consider the following table that highlights key pollutants and their potential effects on avian species:
| Pollutant | Potential Effects on Birds |
|---|---|
| Carbon Monoxide | Causes respiratory distress and can lead to decreased oxygen levels in the bloodstream. |
| Sulfur Dioxide | Can irritate the respiratory system and impair reproductive success. |
| Particulate Matter | Associated with respiratory diseases and reduced immune function. |
As urbanization continues to expand, the need for effective air quality management becomes increasingly urgent. By implementing stricter regulations on emissions and promoting cleaner energy sources, we can help create healthier environments for our feathered friends. Additionally, community awareness and engagement are essential in advocating for policies that prioritize air quality improvements. After all, a city that cares for its birds is a city that cares for its future.
Q: How does air pollution specifically affect bird migration?
A: Air pollution can disrupt migration patterns by altering the availability of food and nesting sites. Birds may struggle to find clean habitats, leading to changes in their traditional routes.
Q: Are all bird species equally affected by air pollution?
A: No, some species are more resilient than others. However, many birds, especially those with smaller populations, are at greater risk due to their sensitivity to environmental changes.
Q: What can individuals do to help improve air quality for birds?
A: Individuals can advocate for local policies that reduce emissions, participate in tree-planting initiatives, and support conservation organizations focused on urban wildlife.

Water Pollution Effects
Water pollution is a critical issue that affects not only the quality of life for humans but also poses severe threats to bird species that rely on aquatic ecosystems. Contaminated water sources can have dire consequences for birds, particularly those that feed on fish or other aquatic organisms. As pollutants seep into rivers, lakes, and coastal areas, they disrupt the delicate balance of these habitats, leading to a decline in food availability for birds.
One of the most alarming aspects of water pollution is its impact on breeding success. Many birds, such as the Great Blue Heron and various species of ducks, depend on clean water for nesting and raising their young. Pollution can lead to poor water quality, which in turn affects the health of the fish and invertebrates that these birds consume. When food sources become scarce or contaminated, it can result in lower reproductive rates and increased mortality among chicks. This cycle of decline can have a cascading effect on local bird populations, threatening their survival.
Moreover, pollutants such as heavy metals, pesticides, and plastics can accumulate in the bodies of aquatic birds, leading to various health issues. For instance, mercury exposure can cause neurological problems, while ingestion of plastic can lead to internal injuries or starvation. The following table summarizes some common pollutants and their effects on bird health:
| Pollutant | Source | Effect on Birds |
|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals | Industrial discharges | Neurological damage, reproductive failure |
| Pesticides | Agricultural runoff | Reduced survival rates, developmental issues |
| Plastics | Improper waste disposal | Injury, starvation, digestive blockages |
In addition to these direct effects, water pollution can also lead to habitat degradation. Wetlands, which are essential for many bird species, can become choked with algae blooms caused by nutrient runoff. This not only reduces the available habitat but also decreases the oxygen levels in the water, making it uninhabitable for fish and other aquatic life. As these ecosystems deteriorate, birds are forced to migrate to less suitable areas, often leading to increased competition for resources.
Addressing water pollution is essential for the conservation of bird species in urban areas. Effective water management practices, such as reducing agricultural runoff, improving wastewater treatment, and restoring natural habitats, are crucial steps in mitigating these effects. By taking action to protect our water sources, we can safeguard the health of both birds and the ecosystems they inhabit.
- How does water pollution affect bird populations?
Water pollution can lead to reduced food availability, health issues, and lower reproductive success among birds. - What are some common pollutants that harm birds?
Common pollutants include heavy metals, pesticides, and plastics, all of which can have detrimental effects on bird health. - What can be done to reduce water pollution?
Implementing better waste management practices, reducing agricultural runoff, and restoring wetlands are effective strategies to combat water pollution.

Conservation Efforts in Urban Areas
As urban landscapes continue to expand, the need for effective conservation efforts has never been more critical. Cities, often seen as concrete jungles, can transform into havens for bird species if we approach urban planning with a focus on biodiversity. Various initiatives are underway to create bird-friendly environments, which not only benefit avian populations but also enhance the overall quality of urban life.
One of the most impactful strategies is the establishment of green spaces. Parks, community gardens, and green corridors serve as essential habitats for birds, offering food, shelter, and nesting sites. These green areas can be designed to mimic natural ecosystems, providing a sanctuary for various bird species. For instance, incorporating native plants into landscaping can attract local bird populations and promote ecological balance. Imagine a city where every park is a mini-ecosystem bustling with life—this is not just a dream; it’s a possibility with the right conservation strategies.
Another key aspect of conservation in urban settings is community engagement. Local residents play a crucial role in protecting bird species. By fostering awareness and encouraging participation in conservation activities, communities can significantly impact their local environments. Programs such as birdwatching clubs, educational workshops, and citizen science initiatives can mobilize residents, turning them into advocates for their feathered friends. When people feel connected to their environment, they are more likely to take action to protect it.
Moreover, urban planners and policymakers are increasingly recognizing the importance of integrating sustainable practices into city development. This includes the implementation of bird-safe building designs, which minimize hazards like window collisions. For example, using glass that is treated with patterns or films can help birds recognize barriers, reducing mortality rates. Additionally, creating regulations that encourage the use of green roofs and walls can provide much-needed habitats for nesting birds.
To illustrate these efforts, consider the following table that outlines some successful urban conservation projects:
| Project Name | Location | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urban Bird Initiative | New York City | A program aimed at increasing green spaces and bird-friendly habitats. | Increased bird diversity by 30% in participating neighborhoods. |
| Green Roofs for Birds | Toronto | Installation of green roofs to provide nesting sites. | Supported populations of native bird species. |
| Community Nesting Project | San Francisco | Engaging locals to build and maintain birdhouses. | Enhanced community awareness and increased nesting success rates. |
In conclusion, the path to conserving bird species in urban areas is multifaceted, involving collaboration between government bodies, conservation organizations, and local communities. By working together, we can create urban environments that not only accommodate human needs but also support the rich diversity of bird life. Every small effort counts, and as we learn to coexist with nature, we pave the way for a sustainable future.
- How can I help birds in my urban area? You can plant native vegetation, create bird feeders, and participate in local conservation efforts.
- What are the benefits of green spaces for birds? Green spaces provide essential habitats, food sources, and safe nesting sites for birds.
- Are there specific bird species that thrive in urban environments? Yes, species like sparrows, pigeons, and certain types of woodpeckers have adapted well to urban settings.

Creating Green Spaces
Establishing green spaces in urban environments is like planting seeds of hope amidst concrete jungles. These areas, whether they are parks, gardens, or green corridors, serve as vital habitats for birds and other wildlife. They not only provide essential resources such as food and shelter but also contribute to the overall health of urban ecosystems. Imagine a bustling city where birds can thrive, chirping joyfully as they flit between trees and shrubs. It's not just a dream; it's a possibility that can be realized through thoughtful urban planning.
Creating green spaces involves more than just planting a few trees. It requires a strategic approach to landscape design that considers the needs of various bird species. For instance, native plants should be prioritized as they offer the best food sources and shelter for local wildlife. Additionally, integrating water features such as ponds or streams can attract a diverse range of birds, enhancing biodiversity. The importance of these green spaces cannot be overstated; they act as ecological corridors that facilitate movement and migration for birds, allowing them to find mates, food, and nesting sites.
Moreover, community involvement plays a crucial role in the success of these initiatives. Engaging local residents in the creation and maintenance of green spaces fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility. When people are invested in their environment, they are more likely to adopt sustainable practices that benefit both birds and the ecosystem. Educational programs about the significance of urban biodiversity can also empower communities to take action, whether it’s through volunteering for clean-up days or participating in birdwatching events.
To illustrate the impact of green spaces, consider the following table that outlines the benefits of creating these areas:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Habitat Creation | Green spaces provide essential habitats for various bird species, supporting their survival and reproduction. |
| Biodiversity Enhancement | These areas promote a diverse range of flora and fauna, contributing to healthier ecosystems. |
| Community Well-being | Access to green spaces improves mental health and encourages outdoor activities among residents. |
| Climate Regulation | Vegetation helps mitigate urban heat, improving air quality and reducing pollution levels. |
In conclusion, creating green spaces is not merely an aesthetic endeavor; it is a crucial step toward fostering a healthier urban environment for birds and humans alike. By prioritizing these initiatives, we can ensure that our cities are not just places of residence but thriving ecosystems where wildlife can flourish. So, the next time you stroll through a park, take a moment to appreciate the birds that call it home and consider how you can contribute to making your urban area a more bird-friendly space.
- What types of plants should be included in urban green spaces to attract birds? Native plants are the best choice as they provide natural food sources and shelter for local bird species.
- How can communities get involved in creating green spaces? Communities can participate by volunteering for planting events, advocating for green initiatives, and educating others about the importance of biodiversity.
- What are the benefits of having green spaces in urban areas? Green spaces enhance biodiversity, improve air quality, provide recreational opportunities, and contribute to the mental well-being of residents.

Community Engagement
Community engagement plays a pivotal role in the conservation of bird species in urban environments. When local residents become actively involved in conservation efforts, the impact can be profound. Imagine a neighborhood where everyone is not just aware of the birds that share their space but is also invested in their well-being. This sense of ownership and responsibility can lead to significant improvements in the urban ecosystem.
One of the most effective ways to foster community engagement is through educational programs that highlight the importance of birds in our environment. Schools, community centers, and local organizations can host workshops and events that teach people about local bird species, their habitats, and the challenges they face due to urbanization. For instance, a simple workshop on birdwatching can ignite a passion for nature among participants, turning casual observers into dedicated conservationists.
Moreover, community-led initiatives can create tangible benefits for both the birds and the residents. Activities such as birdhouse building, habitat restoration, and clean-up drives in local parks not only improve the living conditions for birds but also strengthen community bonds. When people work together towards a common goal, they develop a sense of camaraderie and pride in their neighborhood.
To illustrate the effectiveness of community engagement, consider the following table that outlines various initiatives and their impacts:
| Initiative | Description | Impact on Bird Conservation |
|---|---|---|
| Birdwatching Clubs | Groups that organize birdwatching events and promote awareness. | Increased public interest in local bird species and habitats. |
| Habitat Restoration Projects | Community efforts to restore degraded habitats. | Improved nesting and feeding areas for various bird species. |
| Educational Workshops | Programs that educate the public about bird conservation. | Enhanced understanding of the ecological role of birds. |
| Clean-Up Drives | Community events focused on cleaning local parks and waterways. | Healthier environments for birds and other wildlife. |
Additionally, the role of social media cannot be overlooked in today’s digital age. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter can be powerful tools for spreading awareness and mobilizing community action. Local conservation groups can share success stories, upcoming events, and educational content, creating a virtual community of bird enthusiasts. This online engagement can translate into real-world actions, encouraging people to participate in local conservation efforts.
In conclusion, community engagement is not just a nice-to-have; it is a necessity for the survival of bird species in urban areas. By fostering a sense of connection between residents and their avian neighbors, we can create a more sustainable urban ecosystem. The more we invest in our communities, the more we invest in the future of our feathered friends. So, let’s get involved, spread the word, and make our cities a better place for birds and people alike!
- How can I get involved in local bird conservation efforts?
Look for local birdwatching clubs, conservation organizations, or community workshops in your area. - What is the impact of urbanization on bird species?
Urbanization leads to habitat loss, changes in behavior, and increased pollution, which can negatively affect bird populations. - Why is community engagement important for bird conservation?
Community engagement fosters awareness, encourages local action, and helps create sustainable environments for birds. - What are some simple actions I can take to help birds in my area?
You can create bird-friendly gardens, participate in clean-up drives, and avoid using pesticides that harm birds.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How does urbanisation affect bird habitats?
Urbanisation leads to significant habitat loss for many bird species. As cities expand, natural environments are destroyed, forcing birds to either adapt to new conditions or relocate. This change can disrupt their breeding, feeding, and migration patterns, ultimately threatening their survival.
- What are some behavioral changes observed in urban birds?
Urban birds often exhibit altered behaviors, such as changes in nesting and feeding habits. For example, they may start using artificial structures for nesting or adapt their diets to include human food sources. These changes demonstrate the resilience of birds but also raise concerns about their long-term health and reproductive success.
- How does pollution impact bird health in urban areas?
Pollution, particularly air and water quality, poses serious risks to urban birds. Poor air quality can lead to respiratory issues, while contaminated water can harm aquatic birds and disrupt their food supply. Monitoring and addressing these pollution sources are crucial for protecting bird populations in cities.
- What conservation efforts are being made to support urban birds?
Various conservation initiatives are underway to create bird-friendly environments in urban areas. These include establishing green spaces like parks and green corridors, which provide essential habitats. Additionally, engaging local communities in conservation efforts fosters awareness and support for protecting bird species.
- Can urban birds adapt to living in cities?
Yes, many urban birds show remarkable adaptability to city life. They modify their behaviors, diets, and nesting strategies to survive in altered environments. However, while some species thrive, others may struggle to cope with the challenges posed by urbanisation.
- What can individuals do to help urban bird populations?
Individuals can contribute to the well-being of urban birds by creating bird-friendly spaces, such as gardens with native plants, providing bird feeders, and participating in local conservation initiatives. Every small action counts towards creating a more sustainable environment for our feathered friends!