Why Recycling is not enough in the Battle against Climate Change
As the world grapples with the escalating consequences of climate change, recycling has emerged as a popular buzzword in the quest for sustainability. While it’s true that recycling plays a significant role in reducing waste and conserving resources, it is crucial to recognize that it is not a panacea. The reality is that recycling alone cannot address the multifaceted challenges posed by climate change. In fact, relying solely on recycling can lead to a false sense of security, diverting attention from the more comprehensive strategies that are essential for effective environmental stewardship.
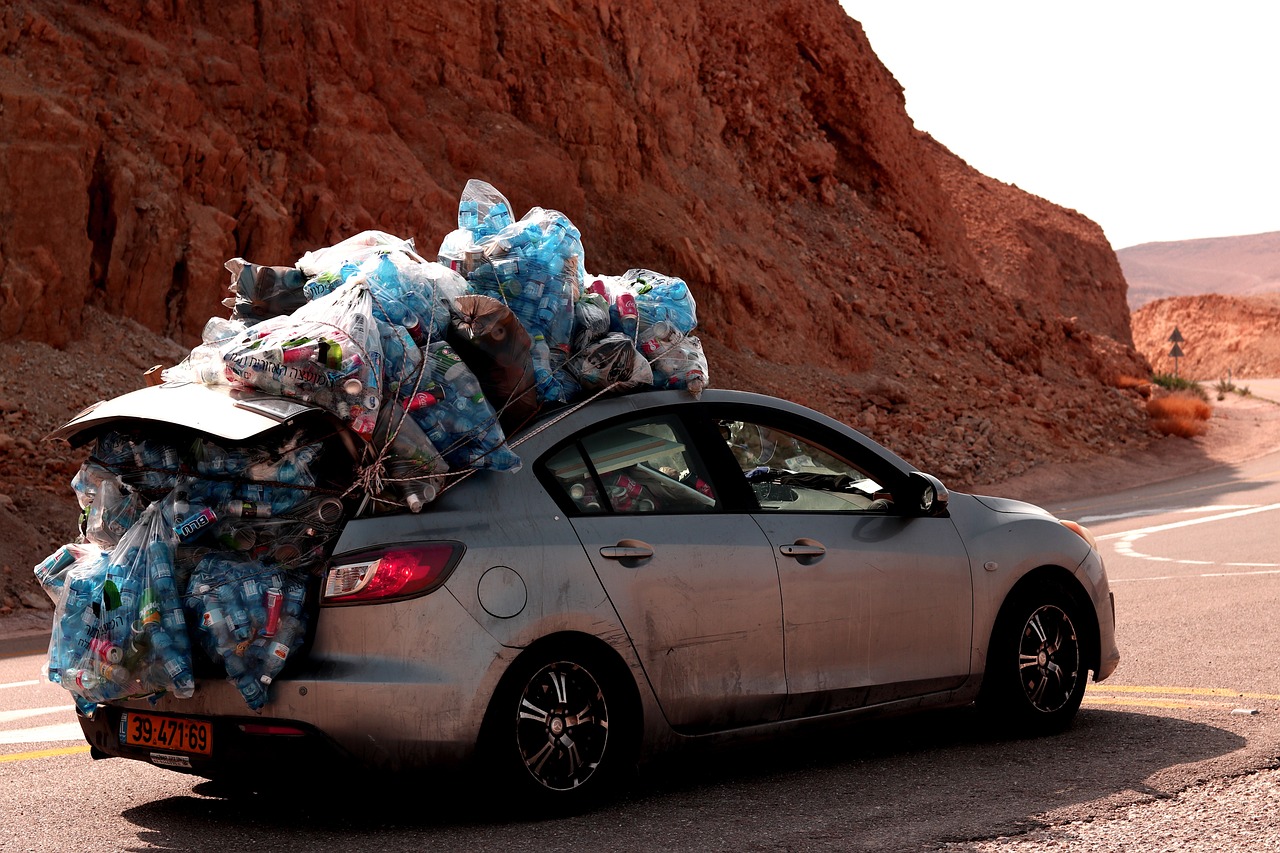
To illustrate this point, let’s consider the lifecycle of a plastic bottle. When you toss it into the recycling bin, it may be processed and turned into a new product. However, the energy used in the recycling process, the emissions released during transportation, and the fact that not all plastics are recyclable can undermine the benefits of recycling. Moreover, many recyclable materials still end up in landfills due to contamination or lack of infrastructure. This cycle raises the question: Is recycling enough to combat climate change?
Furthermore, recycling often focuses on the end of a product’s life rather than the beginning. It encourages a linear economy where products are consumed, discarded, and then recycled, rather than fostering a circular economy that prioritizes reducing and reusing. In this context, it’s vital to shift our mindset from merely recycling to embracing a more holistic approach that includes waste reduction and sustainable consumption.
Ultimately, the fight against climate change requires a multi-pronged strategy that goes beyond recycling. This includes innovative waste management practices, stricter regulations, and a collective commitment to sustainability. By understanding the limitations of recycling, we can better appreciate the need for comprehensive solutions that address the root causes of environmental degradation. So, as we champion recycling efforts, let’s also advocate for a broader perspective that embraces all aspects of waste management and sustainability.
Recycling, while beneficial, has significant limitations that prevent it from being a complete solution to climate change. Understanding these limitations is crucial for developing more effective environmental strategies.
Beyond recycling, various waste management strategies can contribute to reducing climate impact. Exploring alternatives like composting and waste reduction can provide a more holistic approach to environmental sustainability.
Composting transforms organic waste into valuable resources, reducing landfill use and greenhouse gas emissions. This practice not only enriches soil but also plays a vital role in sustainable waste management.
Composting offers numerous benefits, including improved soil health, reduced need for chemical fertilizers, and decreased methane emissions from landfills. These advantages make composting an essential component of waste management.
Starting a composting system is accessible for individuals and communities. Simple steps can be taken to create an effective compost pile, encouraging more people to participate in sustainable practices.
Implementing waste reduction techniques can significantly minimize environmental impact. Strategies such as mindful consumption and product reuse are essential for fostering a culture of sustainability.
Effective policies play a critical role in enhancing recycling efforts. Government regulations and incentives can drive innovation and improve recycling rates, making a substantial difference in environmental outcomes.
Incentives can motivate businesses and consumers to engage in recycling practices. Programs that reward recycling behaviors can lead to increased participation and improved overall recycling rates.
Various global initiatives aim to enhance recycling efforts and promote sustainability. Collaborations between countries can lead to innovative solutions and shared resources for combating climate change.
Emerging technologies are transforming waste management practices. Innovations in recycling processes and waste treatment can significantly improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Advanced recycling technologies, such as chemical recycling, offer new possibilities for processing materials that traditional methods cannot handle. These innovations can help close the loop in material recovery.
Smart waste management solutions utilize data and technology to optimize waste collection and processing. These systems enhance efficiency while minimizing environmental impact, paving the way for smarter, sustainable cities.
- Why isn’t recycling enough to combat climate change? Recycling is just one part of a larger solution. It doesn’t address the root causes of waste and pollution.
- What are some effective alternatives to recycling? Composting and waste reduction techniques are effective alternatives that can significantly decrease environmental impact.
- How can individuals contribute to waste reduction? Individuals can practice mindful consumption, reuse items, and participate in community composting initiatives.
- What role does policy play in recycling? Effective policies can enhance recycling efforts through regulations and incentives that encourage sustainable practices.

The Limitations of Recycling
Recycling is often heralded as a hero in the fight against climate change. It's like the shiny knight in armor, promising to save the day by reducing waste and conserving resources. However, when we peel back the layers, we find that recycling has significant limitations that prevent it from being a silver bullet solution. First and foremost, not all materials are recyclable. For instance, while plastics are widely recycled, many types, especially those labeled with numbers 3, 6, and 7, often end up in landfills despite our best intentions. This brings us to the reality that even the most well-meaning recycling efforts can fall short.
Moreover, the recycling process itself consumes energy and resources. The transportation of recyclables, the energy used in processing, and the chemicals involved can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, which ironically counteracts some of the environmental benefits we aim to achieve. To illustrate this, consider the following table that outlines the energy consumption involved in recycling various materials compared to their production from virgin materials:
| Material | Energy Consumption (MJ/kg) | Recycling Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | 5 | 70 |
| Paper | 2 | 60 |
| Plastic | 8 | 30 |
| Glass | 3 | 35 |
This table highlights that while recycling can save energy compared to producing new materials, the overall impact is still limited by the percentage of materials that are actually recycled. This leads to another significant limitation: contamination. When recyclables are mixed with non-recyclables, it can spoil entire batches, leading to more waste. For example, a single greasy pizza box can ruin a whole load of paper recycling. It's like trying to bake a cake and accidentally adding salt instead of sugar—everything goes wrong!
Furthermore, recycling often creates a false sense of security. Many consumers believe that as long as they recycle, they are doing enough to combat climate change. This mindset can lead to a lack of action in other critical areas, such as reducing consumption and choosing sustainable products. In reality, recycling should be just one part of a much larger strategy for environmental stewardship. It's vital to shift our focus from merely recycling to embracing a circular economy, where we rethink our entire approach to production and consumption.
In conclusion, while recycling is undoubtedly important, it is not enough to solely rely on it in our battle against climate change. We need to recognize its limitations and pursue a more comprehensive approach that includes reducing waste, reusing materials, and adopting sustainable practices. Only then can we hope to make a meaningful impact on our environment.
Alternative Waste Management Strategies
When it comes to tackling the ever-growing issue of waste and its impact on our planet, recycling alone simply doesn't cut it. While recycling is a noble effort, we need to broaden our horizons and embrace that can complement and enhance our environmental efforts. These strategies not only help reduce waste but also promote sustainability and resource conservation. Think of it as a toolbox—recycling is just one tool, and we need a full set to effectively combat climate change.
One of the most effective alternatives to recycling is composting. This natural process allows organic waste, such as food scraps and yard waste, to decompose and transform into nutrient-rich soil. Rather than sending these materials to a landfill, where they would generate harmful methane gas, composting recycles them back into the ecosystem. By enriching the soil, composting not only reduces waste but also supports healthy plant growth, creating a win-win situation for both the environment and our gardens.
Another powerful strategy is waste reduction. This approach encourages individuals and businesses to rethink their consumption habits. By being mindful of what we buy and how we use products, we can significantly decrease the amount of waste generated. For example, opting for products with minimal packaging, choosing reusable items instead of single-use plastics, and practicing minimalism can lead to substantial reductions in waste. In essence, waste reduction is about making conscious choices that prioritize sustainability over convenience.
In addition to composting and waste reduction, there are also innovative practices such as product reuse and repairing items instead of discarding them. These methods not only extend the life of products but also reduce the demand for new resources, effectively lowering our overall environmental footprint. Imagine a world where we fix our broken appliances instead of throwing them away—this shift in mindset could lead to monumental changes in how we manage waste.
To further illustrate the importance of these strategies, consider the following table that compares the environmental impact of traditional waste management versus alternative strategies:
| Strategy | Environmental Impact | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Recycling | Reduces landfill waste but doesn't eliminate it | Conserves resources, reduces energy use |
| Composting | Reduces organic waste in landfills, lowers methane emissions | Enriches soil, supports biodiversity |
| Waste Reduction | Minimizes waste generation at the source | Conserves resources, lowers environmental footprint |
| Product Reuse | Decreases demand for new products, less waste | Promotes a circular economy, saves money |
As we explore these alternative waste management strategies, it becomes clear that we must act collectively. Communities, businesses, and governments all have roles to play in promoting sustainable practices. By prioritizing composting, waste reduction, and product reuse, we can work towards a healthier planet. It's not just about recycling; it's about creating a comprehensive approach that addresses the root causes of waste and environmental degradation.
- What is composting? Composting is the process of recycling organic waste, such as food scraps and yard waste, into nutrient-rich soil.
- How can I start composting at home? You can start composting by creating a compost pile or bin in your backyard and adding organic materials like vegetable peels, coffee grounds, and leaves.
- What are some waste reduction techniques? Techniques include mindful purchasing, using reusable bags and containers, and avoiding single-use plastics.
- Why is product reuse important? Reusing products reduces the need for new resources, decreases waste, and promotes a sustainable lifestyle.

Composting: A Sustainable Solution
Composting is more than just a trend; it's a sustainable solution that transforms organic waste into a valuable resource. Imagine turning your kitchen scraps and yard waste into nutrient-rich soil that can nourish plants and gardens. This process not only reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills but also plays a vital role in mitigating climate change by lowering greenhouse gas emissions. When organic waste decomposes in landfills, it produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas. However, through composting, we can significantly cut down on these emissions while creating a beneficial product for our environment.
One of the most exciting aspects of composting is its ability to enrich soil health. Healthy soil is the foundation of sustainable agriculture and gardening, providing essential nutrients for plant growth. When compost is added to the soil, it improves its structure, enhancing its ability to retain moisture and nutrients. This means that plants can thrive with less water and fewer chemical fertilizers, making composting an essential practice for anyone interested in gardening or farming sustainably.
Moreover, composting is incredibly accessible. You don’t need to be a gardening expert to start composting. Whether you have a large backyard or just a small balcony, there are various methods to create a compost pile. For instance, you can use a simple compost bin, a worm composting system, or even a compost tumbler. The beauty of composting lies in its flexibility and adaptability to different lifestyles. By engaging in this practice, individuals and communities can contribute to a larger movement toward sustainability.
To kickstart your composting journey, you can follow these simple steps:
- Choose a Composting Method: Decide whether you want an outdoor compost pile, a compost bin, or an indoor worm bin.
- Gather Materials: Collect organic waste like fruit and vegetable peels, coffee grounds, eggshells, and yard waste.
- Maintain Your Compost: Turn the pile regularly and monitor moisture levels to ensure optimal decomposition.
- Harvest Your Compost: Once it turns dark and crumbly, your compost is ready to enrich your garden!
In conclusion, composting is not just a waste management technique; it’s a powerful tool for environmental sustainability. By choosing to compost, we’re not only reducing waste but also enhancing the health of our soil and contributing to a more sustainable future. So, why not take that first step today? Your garden (and the planet) will thank you!
1. What can I compost?
You can compost a variety of organic materials, including fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, eggshells, grass clippings, and leaves. Avoid composting meat, dairy, and oily foods as they can attract pests.
2. How long does it take for compost to be ready?
Compost can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months to decompose, depending on factors like temperature, moisture, and the materials used.
3. Can I compost indoors?
Yes! Indoor composting methods, such as worm bins (vermicomposting), are great for apartments and small spaces.
4. Is composting difficult?
Not at all! Composting is relatively easy and can be adapted to fit your lifestyle. With a little patience and practice, anyone can do it.

Benefits of Composting
Composting is more than just a trendy buzzword; it’s a powerful tool in our environmental arsenal. When we compost, we're not merely throwing kitchen scraps into a pile; we're engaging in a transformative process that benefits both our planet and our communities. One of the most significant advantages of composting is its ability to improve soil health. Healthy soil is the foundation of thriving ecosystems, and compost enriches it with essential nutrients. Think of compost as a multivitamin for the earth—packed with the good stuff that helps plants grow strong and resilient.
Moreover, composting reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, which can be harmful to the environment. By using compost, gardeners and farmers can cultivate their crops in a more sustainable manner. This practice not only leads to healthier produce but also fosters a more sustainable agricultural system. It’s like nurturing a garden with natural resources instead of relying on synthetic chemicals that can leach into our waterways and disrupt local ecosystems.
Another compelling benefit is the reduction of methane emissions from landfills. When organic waste decomposes in landfills, it produces methane—a greenhouse gas that is significantly more potent than carbon dioxide. Composting diverts this organic material from landfills, thus mitigating climate change impacts. It’s a simple yet effective way to cut down on our carbon footprint and contribute to a healthier atmosphere.
Let’s not forget the community aspect of composting. By participating in local composting programs, individuals can foster a sense of community and shared responsibility. Many neighborhoods have started community composting initiatives, turning waste management into a collective effort. This not only enhances community ties but also educates individuals about sustainable practices. When we compost together, we’re not just reducing waste; we’re building a culture of sustainability.
In summary, the benefits of composting are vast and interconnected. From enhancing soil health and reducing the need for chemicals to cutting down on methane emissions and strengthening community bonds, composting is a multifaceted solution to some of our most pressing environmental challenges. So, why not roll up your sleeves and dive into composting? It’s a rewarding practice that nurtures both the earth and our communities.
- What materials can I compost? You can compost fruit and vegetable scraps, coffee grounds, eggshells, grass clippings, and dry leaves. Avoid meat, dairy, and oily foods.
- How long does it take for compost to be ready? Composting can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on factors like temperature, moisture, and the materials used.
- Can I compost indoors? Yes! There are various indoor composting systems available, such as worm bins and bokashi composting, which are perfect for small spaces.
- Is composting expensive? Composting can be very affordable. You can start with a simple bin made from recycled materials, or even just a pile in your backyard!

How to Start Composting
Starting a composting system might sound daunting, but it's actually quite simple and can be a rewarding experience. Imagine turning your kitchen scraps and yard waste into nutrient-rich soil for your garden—it's like giving back to the earth while reducing waste! To kick off your composting journey, you don't need fancy equipment or a huge yard; you just need a little space and some basic knowledge.
First, choose a location for your compost pile or bin. It should be a spot that is easily accessible and has good drainage. Ideally, it should be a little shady to prevent the compost from drying out too quickly. If you're using a bin, make sure it has proper ventilation to allow air circulation, which is crucial for the composting process.
Next, gather your materials. Composting requires a mix of green materials (nitrogen-rich) and brown materials (carbon-rich). Green materials include kitchen scraps like fruit and vegetable peels, coffee grounds, and grass clippings, while brown materials consist of dried leaves, cardboard, and paper. The ideal ratio is about 2:1, brown to green, which helps maintain the right balance for decomposition.
Once you have your materials, start layering them in your compost bin or pile. Begin with a layer of brown materials to promote drainage, then alternate layers of green and brown materials. Aim for a pile that is at least three feet wide and three feet tall for optimal heat generation, which speeds up the composting process. Don't forget to turn your compost every few weeks to aerate it and speed up decomposition. This is where the magic happens—turning those scraps into black gold!
As your compost pile breaks down, you might wonder how long it will take. Typically, it can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, depending on various factors like temperature, moisture, and the materials used. When the compost is ready, it will be dark, crumbly, and have an earthy smell. You can use it to enrich your garden soil, potted plants, or even as a top dressing for your lawn.
Lastly, composting is not just for individuals; communities can also get involved! Consider starting a community composting initiative. This not only helps reduce waste but also fosters a sense of community and shared responsibility for our environment.
- What can I compost? You can compost fruit and vegetable scraps, eggshells, coffee grounds, grass clippings, leaves, and cardboard. Avoid meat, dairy, and oily foods as they can attract pests.
- How often should I turn my compost? It's best to turn your compost every 2-4 weeks to aerate it and speed up the decomposition process.
- Can I compost in an apartment? Absolutely! You can use indoor composting systems like worm bins or bokashi composting to recycle your kitchen scraps.
- What do I do if my compost smells? A smelly compost pile usually indicates too many green materials or insufficient aeration. Try adding more brown materials and turning the pile more frequently.

Waste Reduction Techniques
This article explores the limitations of recycling as a standalone solution to climate change and emphasizes the need for comprehensive strategies to address environmental challenges effectively.
Recycling, while beneficial, has significant limitations that prevent it from being a complete solution to climate change. Understanding these limitations is crucial for developing more effective environmental strategies.
Beyond recycling, various waste management strategies can contribute to reducing climate impact. Exploring alternatives like composting and waste reduction can provide a more holistic approach to environmental sustainability.
Composting transforms organic waste into valuable resources, reducing landfill use and greenhouse gas emissions. This practice not only enriches soil but also plays a vital role in sustainable waste management.
Composting offers numerous benefits, including improved soil health, reduced need for chemical fertilizers, and decreased methane emissions from landfills. These advantages make composting an essential component of waste management.
Starting a composting system is accessible for individuals and communities. Simple steps can be taken to create an effective compost pile, encouraging more people to participate in sustainable practices.
Implementing waste reduction techniques can significantly minimize environmental impact. One of the most effective methods is practicing mindful consumption. This involves being aware of what we buy and how much of it we truly need. For instance, instead of purchasing single-use plastics, opting for reusable containers can drastically cut down on waste. Additionally, product reuse is another powerful strategy. This can include anything from donating old clothes to repurposing glass jars for storage. The goal here is to extend the lifecycle of products as much as possible.
Moreover, businesses can play a pivotal role in waste reduction by adopting practices like lean manufacturing, which focuses on minimizing waste during production. By optimizing processes, companies can reduce the amount of raw materials consumed and the waste generated. This not only benefits the environment but also enhances profitability.
To further illustrate the impact of waste reduction, consider the following table that outlines the potential savings from various waste reduction strategies:
| Waste Reduction Technique | Potential Annual Savings (per household) |
|---|---|
| Mindful Consumption | $500 |
| Product Reuse | $300 |
| Composting | $200 |
| Bulk Purchasing | $150 |
These techniques not only lead to financial savings but also foster a culture of sustainability. When individuals and communities come together to adopt these practices, the cumulative effect can be substantial. It's like planting seeds of change; each small action contributes to a larger movement towards a more sustainable future.
In conclusion, waste reduction techniques are essential in our fight against climate change. By embracing mindful consumption and product reuse, we can significantly lessen our environmental footprint. The journey towards sustainability may seem daunting, but every step counts, and together we can make a difference.
Effective policies play a critical role in enhancing recycling efforts. Government regulations and incentives can drive innovation and improve recycling rates, making a substantial difference in environmental outcomes.
Incentives can motivate businesses and consumers to engage in recycling practices. Programs that reward recycling behaviors can lead to increased participation and improved overall recycling rates.
Various global initiatives aim to enhance recycling efforts and promote sustainability. Collaborations between countries can lead to innovative solutions and shared resources for combating climate change.
Emerging technologies are transforming waste management practices. Innovations in recycling processes and waste treatment can significantly improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Advanced recycling technologies, such as chemical recycling, offer new possibilities for processing materials that traditional methods cannot handle. These innovations can help close the loop in material recovery.
Smart waste management solutions utilize data and technology to optimize waste collection and processing. These systems enhance efficiency while minimizing environmental impact, paving the way for smarter, sustainable cities.
Q: Why is recycling not enough to combat climate change?
A: Recycling is a crucial part of waste management, but it doesn't address the root causes of waste generation. Comprehensive strategies, including waste reduction and composting, are necessary to tackle the broader environmental challenges.
Q: What are some easy ways to reduce waste at home?
A: Simple actions like using reusable bags, avoiding single-use plastics, and composting organic waste can significantly reduce household waste.
Q: How can businesses contribute to waste reduction?
A: Businesses can implement lean manufacturing practices, encourage product reuse, and promote recycling among employees and customers to reduce waste.

The Role of Policy in Recycling
Effective policies play a critical role in enhancing recycling efforts across the globe. Without a robust framework of regulations and incentives, recycling initiatives can falter, leading to less-than-ideal outcomes for our environment. Governments and organizations must collaborate to create policies that not only promote recycling but also ensure that these practices are sustainable and widely adopted. For instance, government regulations can set mandatory recycling rates for businesses and municipalities, pushing them to take recycling seriously.
One vital aspect of policy-making in recycling is the implementation of incentives. These incentives can motivate both businesses and consumers to engage more actively in recycling practices. For example, some communities have seen success with programs that offer financial rewards for recycling participation, effectively turning waste into a resource. This not only increases recycling rates but also fosters a culture where recycling is viewed as a shared responsibility. A well-structured incentive program could look like this:
| Incentive Type | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Rebates | Financial incentives for businesses that recycle a certain percentage of their waste. | Increased recycling rates and reduced landfill use. |
| Community Rewards | Programs that reward households for meeting recycling targets. | Higher community engagement and participation in recycling. |
| Grants for Innovation | Funding for businesses developing new recycling technologies. | Enhanced recycling processes and reduced costs. |
Moreover, effective recycling policies should also focus on public education and awareness. When people understand the benefits of recycling and how to do it properly, they are more likely to participate. Campaigns that educate the public about what can and cannot be recycled, as well as the environmental benefits of recycling, are essential. This awareness can be further amplified through partnerships with local schools, community groups, and businesses. By fostering a sense of community around recycling efforts, we can create a culture where recycling becomes second nature.
In addition to local initiatives, there are also numerous global recycling initiatives aimed at enhancing recycling efforts and promoting sustainability on a larger scale. Countries are beginning to collaborate on recycling strategies, sharing resources and knowledge to combat climate change more effectively. For instance, international agreements can set benchmarks for recycling rates, encouraging nations to improve their performance and learn from one another. This collaborative approach not only enhances recycling rates but also drives innovation in waste management practices.
Ultimately, the role of policy in recycling cannot be overstated. It is the backbone of any successful recycling program, providing the necessary framework to ensure that recycling is not just a choice but a priority. By implementing effective regulations, offering incentives, and promoting public awareness, we can create a robust recycling ecosystem that significantly contributes to the fight against climate change.
- Why is recycling important? Recycling reduces waste, conserves natural resources, and decreases pollution, all of which are essential for combating climate change.
- What role do incentives play in recycling? Incentives encourage participation in recycling programs by rewarding individuals and businesses for their efforts, leading to higher recycling rates.
- How can I participate in recycling in my community? Check with local waste management services to understand what can be recycled and participate in community recycling programs.
- What are some global initiatives for recycling? Various international agreements and collaborations focus on improving recycling rates and sharing best practices among countries.

Incentives for Better Recycling
When it comes to recycling, motivation is key. can transform the way individuals and businesses engage with waste management. Imagine a world where every bottle you recycle not only contributes to a cleaner planet but also rewards you in some tangible way. This is not just a dream; it's a reality that can be achieved through well-structured incentive programs. By introducing financial rewards, community recognition, and educational initiatives, we can encourage more people to participate in recycling efforts.
One effective way to foster recycling is through financial incentives. For instance, deposit return schemes allow consumers to receive a small refund for returning beverage containers. This simple yet effective model has proven successful in various countries, leading to significantly higher recycling rates. In fact, studies show that regions with such programs can achieve recycling rates of over 90% for certain materials. This demonstrates that when people see a direct benefit, they are more likely to take action.
Moreover, local governments can implement tax incentives for businesses that actively engage in recycling practices. By offering deductions or credits for companies that recycle a certain percentage of their waste, municipalities can motivate businesses to adopt eco-friendly practices. This not only benefits the environment but also enhances the company’s public image, potentially attracting more customers who prioritize sustainability.
Community recognition is another powerful motivator. Programs that celebrate neighborhoods or organizations with the highest recycling rates can create a sense of competition and pride. For example, a city could host an annual recycling competition, rewarding the winning community with funds for local projects or events. This fosters a culture of sustainability and encourages residents to take recycling seriously.
Education plays a crucial role in maximizing the effectiveness of these incentives. Many people are unaware of the recycling options available to them or the impact their actions can have on the environment. By providing educational resources and workshops, communities can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their waste. When people understand the benefits of recycling—not just for the planet but for their local community—they are more likely to participate actively.
To summarize, the path towards better recycling practices is paved with incentives that resonate with individuals and businesses alike. By combining financial rewards, community recognition, and educational initiatives, we can create an environment where recycling becomes second nature. The future of our planet depends on these collective efforts, and it’s time we all play our part.
- What are the most effective incentives for recycling? Financial rewards, community recognition, and educational programs have all proven effective in encouraging recycling.
- How can businesses benefit from recycling incentives? Businesses can receive tax deductions, improve their public image, and potentially attract more eco-conscious customers.
- What role does education play in recycling? Education helps individuals understand the importance of recycling and how to participate effectively, leading to higher engagement.
- Are there successful examples of recycling incentives? Yes, deposit return schemes in various countries have significantly increased recycling rates for beverage containers.

Global Recycling Initiatives
In the fight against climate change, have emerged as a beacon of hope, uniting countries, organizations, and communities in a shared mission. These initiatives aim to enhance recycling efforts and promote sustainability on an international scale. Imagine a world where materials are continuously reused, waste is minimized, and the environment thrives. This vision is becoming a reality through collaborative efforts around the globe.
One of the most notable initiatives is the European Union's Circular Economy Action Plan, which aims to make sustainable products the norm in the EU. This action plan emphasizes the importance of recycling and sets ambitious targets for waste reduction and resource efficiency. By 2025, the EU aims to recycle 65% of municipal waste and 70% of packaging waste. Such goals not only help reduce landfill waste but also encourage innovation in recycling technologies.
Across the Atlantic, the United States has seen various states implement their own recycling programs, with some regions leading the charge. For example, California has introduced stringent laws that require a significant percentage of waste to be recycled. These state-level initiatives are crucial in driving local communities to adopt better recycling practices, and they serve as models for other states to follow.
Moreover, international collaborations such as the Global Recycling Partnership bring together nations to share best practices, resources, and technologies. This partnership fosters a sense of community among countries, encouraging them to learn from one another. Through workshops, conferences, and joint projects, nations can tackle common challenges in recycling and waste management.
To illustrate the impact of these initiatives, consider the following table that highlights some key global recycling programs and their objectives:
| Initiative | Region | Main Objectives |
|---|---|---|
| European Union Circular Economy Action Plan | Europe | Increase recycling rates to 65% by 2025 |
| California Recycling Initiative | USA | Mandate recycling targets for municipalities |
| Global Recycling Partnership | Global | Share best practices and technologies among nations |
These initiatives not only focus on recycling but also emphasize the importance of education and awareness. By informing citizens about the benefits of recycling and how to do it effectively, these programs can lead to a cultural shift towards sustainability. It's not just about the act of recycling; it's about creating a mindset that values resources and recognizes the impact of waste on our planet.
As we move forward, the role of technology in these global initiatives cannot be overlooked. Innovations such as blockchain for tracking recyclables and AI for sorting waste are paving the way for more efficient recycling processes. These advancements not only enhance the effectiveness of recycling programs but also inspire confidence in consumers and businesses alike.
In conclusion, global recycling initiatives are essential in the battle against climate change. They foster collaboration, set ambitious goals, and leverage technology to create a more sustainable future. However, the success of these initiatives depends on the active participation of individuals, businesses, and governments. Together, we can turn the tide on waste and build a cleaner, greener world.
- What are global recycling initiatives? Global recycling initiatives are collaborative efforts among countries and organizations aimed at improving recycling rates and promoting sustainability.
- Why are these initiatives important? They are crucial for reducing waste, conserving resources, and mitigating climate change impacts.
- How can individuals contribute to these initiatives? By participating in local recycling programs, educating themselves about proper recycling practices, and advocating for sustainable policies.

Innovative Technologies in Waste Management
In today’s rapidly evolving world, the need for effective waste management has never been more pressing. Traditional methods of waste disposal are becoming increasingly inadequate to address the growing environmental challenges we face. Fortunately, innovative technologies are stepping in to revolutionize how we manage waste, making it more efficient and sustainable. These technologies not only enhance recycling processes but also introduce new ways to minimize waste generation at the source.
One of the most exciting advancements in waste management is the development of advanced recycling technologies. Unlike conventional recycling methods, which often struggle with certain types of plastics and materials, advanced techniques such as chemical recycling are designed to break down complex materials into their basic components. This process allows for the recovery of valuable resources that would otherwise end up in landfills. For instance, chemical recycling can convert mixed plastics back into their original monomers, enabling the creation of new, high-quality plastic products.
Another area where technology is making waves is in the realm of smart waste management solutions. These systems leverage data analytics and the Internet of Things (IoT) to optimize waste collection and processing. By using sensors in waste bins, municipalities can monitor fill levels in real-time, allowing for more efficient collection routes and schedules. This not only reduces fuel consumption and operational costs but also minimizes the carbon footprint associated with waste collection. Imagine a city where garbage trucks only travel when necessary—what a game changer!
Moreover, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into waste sorting processes is proving to be a significant advancement. AI-powered sorting systems can identify and separate recyclables from waste with remarkable accuracy, drastically improving recycling rates. These systems can analyze materials on the conveyor belt and make split-second decisions, ensuring that more items are diverted from landfills and sent to recycling facilities. This level of efficiency was unimaginable just a few years ago, but it’s now becoming a reality.
Furthermore, many companies are exploring the use of biotechnology in waste management. This includes the development of microorganisms that can break down organic waste more efficiently. These microbes can be harnessed to accelerate composting processes, turning food scraps and yard waste into nutrient-rich compost in a fraction of the time it would take through traditional methods. Not only does this reduce the volume of waste sent to landfills, but it also enriches soil, promoting healthier ecosystems.
To illustrate the impact of these technologies, consider the following table that highlights some key innovations and their benefits:
| Technology | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Recycling | Breaks down plastics into monomers for reuse. | Enables recycling of complex materials, reduces landfill waste. |
| Smart Waste Solutions | Uses IoT sensors to optimize waste collection. | Reduces operational costs, improves efficiency. |
| AI Sorting Systems | Automated systems for identifying recyclables. | Increases recycling rates, minimizes contamination. |
| Biotechnology | Utilizes microbes to accelerate composting. | Reduces waste volume, enhances soil health. |
As we can see, the future of waste management is bright with these innovative technologies paving the way for a more sustainable approach. However, it’s essential to remember that technology alone won’t solve our waste crisis. It must be paired with a cultural shift towards responsible consumption and waste reduction. By embracing these advancements and fostering a collective commitment to sustainability, we can make significant strides in reducing our environmental footprint.
- What is chemical recycling? Chemical recycling is a process that breaks down plastic waste into its basic building blocks, allowing for the creation of new plastic products.
- How do smart waste management solutions work? These solutions use IoT technology to monitor waste levels in bins, optimizing collection routes and schedules for efficiency.
- What role does AI play in waste management? AI can automate the sorting process in recycling facilities, improving accuracy and increasing recycling rates.
- Can composting help reduce landfill waste? Yes, composting transforms organic waste into valuable compost, significantly reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills.

Advanced Recycling Technologies
In the ever-evolving landscape of waste management, are emerging as a beacon of hope in our fight against climate change. Traditional recycling methods, while beneficial, often struggle to process complex materials, leading to a significant amount of waste ending up in landfills. This is where advanced techniques, such as chemical recycling and pyrolysis, come into play, offering innovative solutions that can transform the way we handle waste.
Chemical recycling, for instance, breaks down plastics into their original monomers, allowing them to be reconstituted into new, high-quality products. Unlike mechanical recycling, which can degrade the material quality over time, chemical recycling can effectively create a closed-loop system. This means that the same materials can be recycled repeatedly without losing their integrity. Imagine a world where your plastic bottle could be transformed back into a new bottle, endlessly—this is the promise of chemical recycling.
Another exciting technology is pyrolysis, which uses heat in the absence of oxygen to decompose organic materials into oil, gas, and char. This process not only reduces the volume of waste but also converts it into usable energy. The byproducts can be harnessed for electricity generation or even as raw materials for new products. It’s akin to turning trash into treasure, showcasing the potential of waste as a valuable resource rather than a burden.
Here’s a quick comparison of traditional recycling versus advanced recycling technologies:
| Aspect | Traditional Recycling | Advanced Recycling |
|---|---|---|
| Material Types | Limited to specific materials | Can process a wider range of materials |
| Quality of Recycled Product | Degrades over time | Maintains original quality |
| End Products | Often downcycled | Can produce high-quality raw materials |
| Environmental Impact | Less efficient | Reduces landfill waste significantly |
Moreover, the integration of smart technology into recycling processes is revolutionizing the industry. Smart waste management solutions leverage data analytics and IoT (Internet of Things) to optimize collection routes, monitor recycling bins, and even predict waste generation trends. This not only enhances efficiency but also minimizes the carbon footprint associated with waste collection. Imagine a city where waste is collected only when bins are full, drastically reducing unnecessary trips and emissions—this is becoming a reality with smart solutions.
As we look towards the future, it’s clear that embracing these advanced recycling technologies is not just an option; it’s a necessity. By investing in innovation and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in waste management, we can significantly reduce our environmental impact and pave the way for a more sustainable future. The question remains: are we ready to embrace these changes and make a concerted effort to shift our waste management practices?
- What is chemical recycling? Chemical recycling is a process that breaks down plastics into their original monomers, allowing for the creation of new products without degrading material quality.
- How does pyrolysis work? Pyrolysis uses heat in the absence of oxygen to decompose organic materials into oil, gas, and char, thus reducing waste volume and generating usable energy.
- What are smart waste management solutions? These are technologies that utilize data and IoT to optimize waste collection and processing, improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact.

Smart Waste Management Solutions
As we dive deeper into the realm of waste management, it's clear that traditional methods just won't cut it anymore. Enter —a game changer in how we handle our garbage. Imagine a world where waste collection is not only efficient but also environmentally friendly. This is the promise of smart technology. By leveraging data and advanced technologies, cities can optimize waste collection routes, reduce operational costs, and ultimately, minimize their carbon footprint.
At the heart of these solutions are sensor-equipped bins that monitor waste levels in real-time. This technology allows waste management companies to schedule pickups only when necessary, rather than following a rigid timetable. The result? Fuel savings, reduced emissions, and less wear and tear on collection vehicles. It's like having a personal assistant for your trash—only it helps the planet!
Moreover, smart waste management systems can analyze data to identify patterns in waste generation. For instance, if a neighborhood consistently produces more organic waste, local authorities can implement targeted composting programs. This tailored approach not only promotes sustainability but also fosters community engagement. Residents become active participants in their waste management, leading to a culture of responsibility and awareness.
To further illustrate the impact of smart waste management, consider the following table that outlines the benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Efficiency | Optimized collection routes save time and fuel, reducing operational costs. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions from collection vehicles contribute to cleaner air. |
| Enhanced Recycling | Data analysis helps identify materials that can be recycled more effectively. |
| Community Engagement | Localized solutions foster a sense of responsibility among residents. |
In addition to these benefits, smart waste management solutions can also integrate with other city services. For example, linking waste data with street cleaning schedules can ensure that public spaces remain clean and appealing. It's all about creating a seamless urban experience that prioritizes sustainability.
As we move forward, the adoption of smart waste management technologies will be crucial in our fight against climate change. By embracing innovation, cities can transform their waste management practices into a powerful tool for environmental stewardship. So, the next time you think about your trash, remember that there’s a smarter way to manage it—one that benefits not just our cities, but our planet as well.
- What are smart waste management solutions? Smart waste management solutions utilize technology and data analytics to optimize waste collection and processing.
- How do sensor-equipped bins work? These bins monitor waste levels and notify collection services when they need to be emptied, reducing unnecessary pickups.
- Can smart waste management help with recycling? Yes, by analyzing waste data, cities can improve recycling rates and identify materials that are frequently discarded.
- Are there any downsides to implementing smart waste management? Initial costs for technology and infrastructure can be high, but the long-term savings and environmental benefits often outweigh these costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Why is recycling not enough to combat climate change?
Recycling is a great step in the right direction, but it has limitations. It doesn't address the root causes of waste production and often only deals with a fraction of materials. Additionally, not all recyclable materials are processed, and some end up in landfills anyway. So, while recycling is important, it needs to be part of a broader strategy that includes waste reduction and alternative management practices.
- What are some effective alternatives to recycling?
There are several alternatives to recycling that can significantly reduce environmental impact. Composting is one of the best options, turning organic waste into nutrient-rich soil. Another effective strategy is waste reduction, which encourages mindful consumption and reusing products rather than discarding them. Together, these methods create a more sustainable approach to managing waste.
- How can I start composting at home?
Starting a composting system at home is easier than you might think! Begin by collecting organic waste like fruit peels, vegetable scraps, and coffee grounds. Create a compost pile or use a compost bin, layering green materials (like food scraps) with brown materials (like dry leaves). Keep it moist and turn it regularly to aerate. In a few months, you'll have rich compost to enrich your garden!
- What role do policies play in improving recycling rates?
Policies are crucial in enhancing recycling efforts. Effective regulations can set recycling targets, provide funding for recycling programs, and create incentives for businesses and consumers to recycle more. When governments take action, it can lead to innovation in recycling technologies and increased participation in recycling initiatives.
- What are some global initiatives focused on recycling?
There are numerous global initiatives aimed at improving recycling efforts. Organizations like the Global Recycling Foundation and various international collaborations work to share resources and best practices. These initiatives help countries innovate and develop strategies that can be implemented locally to combat climate change effectively.
- What advanced technologies are being used in waste management?
Emerging technologies are revolutionizing waste management. For instance, chemical recycling allows for materials that traditional methods can't handle to be processed. Additionally, smart waste management solutions use data analytics to optimize waste collection routes and improve processing efficiency, ultimately reducing environmental impact.



















