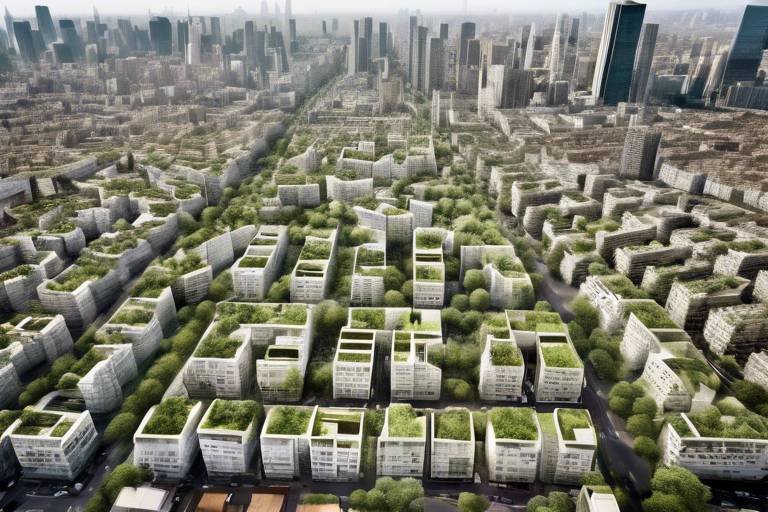
Is Urban Farming the Future of Feed Cities?
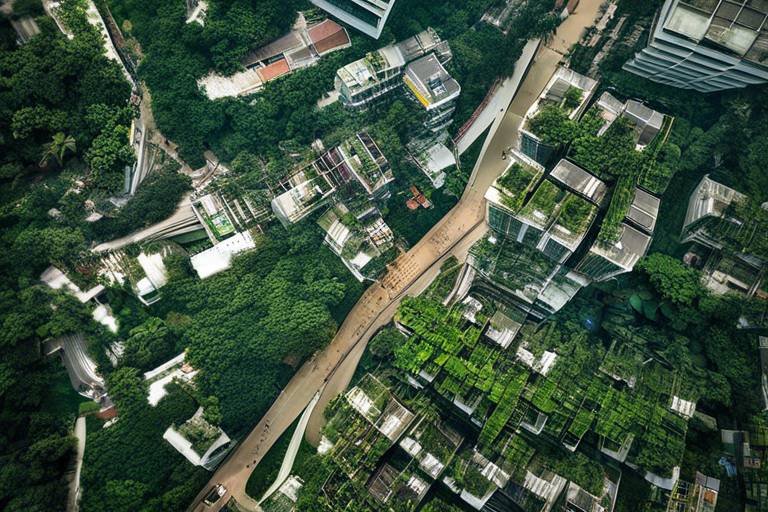
As cities expand and populations surge, the question of how to sustainably feed urban dwellers becomes increasingly pressing. Urban farming emerges as a beacon of hope, promising not just to provide fresh produce but also to reshape the very fabric of our urban environments. Imagine walking through a bustling city, and instead of just concrete and steel, you see vibrant green rooftops, community gardens, and vertical farms sprouting up like wildflowers. This transformation isn’t just a dream; it’s happening right now, and it’s revolutionizing how we think about food production.
With the world’s population projected to reach nearly 10 billion by 2050, the challenge of feeding everyone becomes more daunting. Urban farming presents a sustainable solution by utilizing underused spaces in cities—think vacant lots, rooftops, and even walls—to grow food. This not only helps to meet the demand for fresh produce but also reduces the environmental impact associated with traditional farming methods. The concept of food miles—the distance food travels from farm to table—takes on new significance as urban farms can dramatically shorten this distance, ensuring that food is fresher and more nutritious.
Moreover, urban farming isn’t just about food; it’s about community. These initiatives often encourage local residents to get involved, fostering a sense of ownership and pride in their neighborhoods. Picture a community gathering in a local garden, sharing tips on sustainable practices while enjoying the fruits of their labor. This social aspect of urban farming is crucial, as it promotes community engagement and education about healthy eating and sustainability.
However, it’s essential to acknowledge that urban farming is not without its challenges. Land access can be a significant hurdle, with high real estate prices and competing interests making it difficult for aspiring urban farmers to secure space. Additionally, complex regulations can stifle innovation, leaving many potential projects in limbo. Yet, despite these obstacles, the spirit of urban farming continues to thrive, with innovative techniques like vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics paving the way for a more resilient food system.
In the coming sections, we will delve deeper into the benefits of urban agriculture, explore the challenges it faces, and highlight the innovative practices that are shaping the future of food production in our cities. So, is urban farming the future of feeding cities? With its potential to enhance food security, reduce environmental impact, and build community, it certainly seems poised to play a pivotal role in our urban landscapes.

The Rise of Urban Farming
This article explores the potential of urban farming as a sustainable solution for feeding growing city populations, examining its benefits, challenges, and innovative practices shaping the future of food production.
Urban farming has witnessed a remarkable surge in popularity over the past decade, transforming the way we think about food production in densely populated areas. As cities expand and populations grow, the demand for fresh, local produce has skyrocketed. This shift is not merely a trend; it's a response to a pressing need for sustainable food sources that can thrive amidst urban chaos. But what exactly is driving this movement? One major factor is the increasing awareness of the environmental impact of traditional farming methods and the carbon footprint associated with transporting food over long distances. Urban farming offers a solution that not only brings food production closer to consumers but also promotes sustainability.
In addition, the rise of technology has played a pivotal role in making urban farming more accessible and efficient. Innovations such as vertical farming and hydroponics allow city dwellers to grow food in limited spaces, making it feasible to cultivate crops on rooftops, balconies, and even in basements. This technological advancement is like a breath of fresh air for urban agriculture, enabling it to flourish in places where conventional farming would be impossible.
Moreover, urban farming is becoming a community-driven initiative. People are coming together to create community gardens, rooftop farms, and even indoor farms within their neighborhoods. This sense of community not only fosters a spirit of collaboration but also educates individuals about the importance of local food systems. The urban farming movement is, in many ways, a grassroots response to the challenges posed by modern urban living, where food deserts and unhealthy eating habits have become prevalent.
As cities grapple with issues such as food insecurity and environmental degradation, urban farming emerges as a beacon of hope. It’s not just about growing food; it’s about cultivating a new way of life that prioritizes sustainability, health, and community engagement. The rise of urban farming is not just a passing phase; it’s a vital component of the future of food production in our cities. With its potential to reshape our food systems, it’s time we take notice and support this burgeoning movement.
- What is urban farming? Urban farming refers to the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas.
- Why is urban farming important? It helps reduce food miles, promotes sustainability, and enhances food security in cities.
- What are some common urban farming techniques? Techniques include vertical farming, hydroponics, aquaponics, and community gardening.
- How can I get involved in urban farming? Look for local community gardens, workshops, or urban farms that welcome volunteers.
Benefits of Urban Agriculture
Urban agriculture is not just a trend; it's a transformative movement that offers a plethora of benefits for cities and their inhabitants. As urban populations continue to swell, the need for sustainable food sources becomes increasingly urgent. Urban farming not only addresses this need but also brings a multitude of advantages that can enhance the quality of life in urban areas. Let's dive into some of the key benefits that make urban agriculture a compelling choice for city dwellers.
One of the most significant advantages of urban farming is its ability to increase food security. By growing food locally, communities can reduce their dependence on external food supplies and mitigate the risks associated with food shortages. Imagine being able to walk to a nearby farm and pick fresh vegetables instead of relying on grocery stores that might not always have what you need. This local approach ensures that people have access to fresh, nutritious food, which is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Moreover, urban agriculture plays a crucial role in reducing carbon footprints. Traditional farming methods often involve long transportation routes, which contribute to greenhouse gas emissions. In contrast, urban farms can significantly cut down on these emissions by producing food closer to where it is consumed. This not only helps the environment but also ensures that the food is fresher, retaining more of its nutritional value.
Another remarkable benefit of urban agriculture is its potential to enhance community engagement. Urban farms often serve as gathering spaces where people can come together, share knowledge, and participate in hands-on activities. These initiatives foster a sense of community and encourage individuals to learn about sustainable practices and the importance of local food systems. When people are involved in the growing process, they develop a deeper appreciation for their food and the environment.
The positive impact of urban farming on the environment cannot be overstated. Urban farms contribute to biodiversity by creating green spaces that support various plant and animal species. These farms often incorporate native plants and pollinator-friendly crops, which help sustain local ecosystems. Furthermore, urban agriculture can play a vital role in reducing waste. Many urban farms practice composting, turning organic waste into valuable soil amendments, thereby minimizing landfill contributions and promoting a circular economy.
By growing food locally, urban farms can significantly reduce the distance food travels from farm to table, commonly referred to as food miles. This reduction is critical for sustainability as it lessens the energy used in transportation and decreases the carbon emissions associated with long-distance food transport. The closer the food source, the fresher the produce, which can lead to better taste and higher nutritional value.
Urban farms can enhance urban biodiversity by creating green spaces that support various plant and animal species. These farms contribute to a healthier ecosystem in cities by providing habitats for pollinators, birds, and beneficial insects. The integration of green roofs, community gardens, and vertical farms can transform concrete jungles into thriving ecosystems. This not only beautifies the urban landscape but also promotes a more resilient environment capable of withstanding climate change.
Urban farming initiatives often involve local communities, fostering engagement and education about food systems. These projects promote awareness and skills related to sustainable agriculture, teaching individuals how to grow their own food and understand the importance of local food systems. Workshops, community events, and volunteer opportunities at urban farms allow residents to connect with their food sources, empowering them to make informed choices about their diets and lifestyles.
In conclusion, the benefits of urban agriculture extend far beyond just providing food. They encompass environmental sustainability, community building, and educational opportunities that enrich urban life. As we continue to explore innovative farming techniques and overcome challenges, urban agriculture stands as a beacon of hope for a sustainable future in our cities.
- What is urban agriculture? Urban agriculture refers to the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas.
- How does urban farming improve food security? By growing food locally, urban farms reduce reliance on external food sources and ensure access to fresh produce.
- What are some challenges urban farmers face? Urban farmers often struggle with land access, regulatory barriers, and financial sustainability.
- What innovative techniques are used in urban farming? Techniques like vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics are increasingly being adopted to maximize space and resources.

Environmental Impact
When we think about urban farming, it’s easy to get lost in the romantic notion of fresh herbs and vegetables growing in our backyards. But the of these green initiatives goes far beyond just aesthetics. Urban farming plays a crucial role in promoting sustainability and enhancing the quality of life in cities. By integrating agriculture into urban landscapes, we can tackle some pressing environmental issues that plague metropolitan areas.
One of the most significant contributions of urban farming is its ability to reduce waste. Many urban farms utilize composting techniques to recycle organic waste, turning food scraps into nutrient-rich soil. This not only diverts waste from landfills but also enriches the soil, creating a closed-loop system that benefits both the environment and the farmers. Additionally, urban farms often practice rainwater harvesting, which helps manage stormwater runoff and reduces the burden on city drainage systems.
Moreover, urban farms can significantly improve air quality in densely populated areas. Plants naturally filter pollutants from the air, absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen. By increasing the number of green spaces in cities, urban farms contribute to cleaner, healthier air. They also provide habitats for various species, thus promoting biodiversity. In a world where many species are on the brink of extinction, these green oases can serve as critical refuges for birds, insects, and other wildlife.
To illustrate the environmental benefits of urban farming, consider the following table, which outlines the key impacts:
| Environmental Impact | Description |
|---|---|
| Waste Reduction | Utilizing composting and recycling organic waste to enrich soil. |
| Air Quality Improvement | Plants filter pollutants, improving air quality in urban areas. |
| Biodiversity Promotion | Creating habitats that support various plant and animal species. |
| Carbon Footprint Reduction | Decreasing reliance on transportation by growing food locally. |
Urban farms also play a vital role in reducing food miles. The concept of food miles refers to the distance food travels from farm to plate. By growing food in urban settings, we can significantly cut down on the transportation required, thereby lowering carbon emissions associated with food distribution. This not only helps the environment but also ensures that the food we consume is fresher and more nutritious.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of urban farming is profound and multifaceted. From reducing waste and improving air quality to promoting biodiversity and lowering carbon footprints, urban farms are not just a trend; they are a necessary evolution in our approach to food production. As we continue to face the challenges of urbanization and climate change, embracing urban farming could very well be one of the most effective strategies for building sustainable cities.
Q: What is urban farming?
A: Urban farming refers to the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas. It can include various methods, such as community gardens, rooftop farms, and vertical farming.
Q: What are the benefits of urban farming?
A: Urban farming offers numerous benefits, including increased food security, reduced carbon footprints, improved air quality, and enhanced community engagement.
Q: How does urban farming impact the environment?
A: Urban farming positively impacts the environment by reducing waste, improving air quality, promoting biodiversity, and decreasing food miles through local food production.
Q: What challenges do urban farmers face?
A: Urban farmers often encounter challenges such as high land prices, regulatory barriers, and financial sustainability issues.

Reducing Food Miles
In today's fast-paced world, where everything is just a click away, the concept of food miles has become increasingly significant. Food miles refer to the distance food travels from where it is produced to where it is consumed. The longer the distance, the more energy is expended in transportation, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and environmental degradation. Urban farming presents a remarkable opportunity to reduce food miles dramatically.
Imagine biting into a fresh tomato, knowing it was picked from a rooftop garden just a few blocks away. This is the magic of urban farming—it allows cities to grow food right where it's consumed. By cultivating crops locally, urban farms can significantly shorten the supply chain, ensuring that produce is harvested at its peak freshness and delivered swiftly to local markets. This not only enhances the flavor and nutritional value of the food but also minimizes the need for preservatives and long-term storage methods.
Moreover, reducing food miles contributes to a more sustainable urban environment. It lessens the reliance on fossil fuels for transportation, thereby cutting down on carbon emissions. To put this into perspective, consider the following statistics:
| Food Type | Average Food Miles | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Local Vegetables | 50 miles | Low carbon footprint |
| Imported Fruits | 1,500 miles | High carbon footprint |
| Packaged Snacks | 2,000 miles | Very high carbon footprint |
As seen in the table, local vegetables have a significantly lower environmental impact compared to imported fruits and packaged snacks. This stark contrast highlights the importance of supporting local urban farms. When we choose to buy from these farms, we not only enjoy fresher produce but also play a role in fostering a sustainable food system.
Additionally, urban farms often adopt practices that further reduce their carbon footprint. For instance, many of these farms utilize renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, to power their operations. By embracing eco-friendly methods, urban farmers are setting an example of how food production can align with environmental stewardship.
In conclusion, reducing food miles is not just a trend; it's a necessity for creating sustainable cities. Urban farming stands at the forefront of this movement, offering a practical solution to the challenges posed by long-distance food transportation. By supporting local farms, we can all contribute to a healthier planet, one bite at a time.
- What are food miles? Food miles refer to the distance food travels from production to consumption, impacting its environmental footprint.
- How does urban farming reduce food miles? Urban farming allows food to be grown locally, minimizing transportation distances and associated carbon emissions.
- What are the benefits of eating locally sourced food? Eating locally sourced food ensures freshness, reduces the need for preservatives, and supports sustainable agricultural practices.
- Can urban farming be profitable? Yes, with the right business model and community support, urban farming can be a viable and profitable venture.

Promoting Biodiversity
Urban farming plays a crucial role in promoting biodiversity within city landscapes, transforming concrete jungles into vibrant ecosystems. When we think of cities, we often envision towering skyscrapers and bustling streets, but urban farms inject life into these environments, creating green spaces that serve as habitats for various species. These green oases not only provide fresh produce but also foster a rich tapestry of flora and fauna that enhances the overall health of urban areas.
By integrating plants, insects, and animals into urban farming practices, we can create a balanced ecosystem that benefits both nature and the community. For instance, urban farms can attract pollinators like bees and butterflies, which are essential for pollinating many crops. This symbiotic relationship not only boosts crop yields but also contributes to the resilience of the local ecosystem. It's like inviting nature back into the city, allowing it to flourish alongside human development.
Moreover, urban farms often utilize native plant species, which are better adapted to the local environment and require fewer resources to thrive. This practice can lead to a reduction in the need for pesticides and fertilizers, further supporting a healthier ecosystem. By choosing to grow a diverse array of crops, urban farmers can mimic natural ecosystems, which are typically more resilient and productive than monocultures.
The benefits of promoting biodiversity through urban farming extend beyond just environmental health. They also enhance community well-being by providing educational opportunities and fostering a sense of stewardship among residents. Community members can participate in workshops and volunteer days, learning about the importance of biodiversity and sustainable practices. This engagement not only strengthens community ties but also empowers individuals to take action toward environmental conservation.
In summary, urban farming is not just about food production; it’s a holistic approach to revitalizing urban spaces. By promoting biodiversity, urban farms can create healthier ecosystems, enhance food security, and build stronger communities. As cities continue to grow, the integration of urban agriculture will be vital in ensuring that we maintain a balance between urban development and ecological preservation.
- What is urban farming? Urban farming refers to the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food within urban areas, utilizing small spaces like rooftops, backyards, and community gardens.
- How does urban farming benefit the environment? Urban farming promotes biodiversity, reduces food miles, and enhances air quality, contributing to a healthier urban ecosystem.
- Can urban farming help with food security? Yes, by growing food locally, urban farming can increase access to fresh produce, thereby improving food security in urban communities.
- What are some challenges faced by urban farmers? Urban farmers often encounter challenges such as land access, regulatory hurdles, and financial sustainability.
- What innovative techniques are used in urban farming? Techniques such as vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics are commonly employed to maximize space and resources in urban settings.

Community Engagement and Education
Urban farming is not just about growing food; it's a vibrant movement that brings communities together and fosters a deeper understanding of our food systems. Imagine stepping into a local urban farm and being greeted by the rich smell of fresh herbs and the sight of children learning to plant seeds. This is the essence of community engagement in urban agriculture. By involving local residents in farming initiatives, urban farms become hubs of education and interaction, where people from diverse backgrounds can share knowledge, skills, and experiences.
One of the most exciting aspects of urban farming is its ability to educate the community about sustainable practices. Workshops and hands-on activities often take place on these farms, teaching participants about everything from composting to crop rotation. For instance, a community garden might host a workshop on how to create a compost bin, which not only reduces waste but also enriches the soil for future crops. This type of education empowers individuals to take control of their food sources, making them more conscious consumers.
Moreover, urban farms often collaborate with schools, offering educational programs that integrate farming into the curriculum. Students can learn about biology, ecology, and nutrition in a practical setting. Such programs can ignite a passion for environmental stewardship among young people, encouraging them to think critically about their food choices and the impact of agriculture on the planet.
Urban farming initiatives also promote social cohesion. They create spaces where neighbors can interact, share stories, and build relationships. These farms can serve as community gathering spots, where people come together not just to work the land but to celebrate local culture and foster a sense of belonging. By participating in communal farming efforts, residents develop a shared responsibility for their environment, leading to a more engaged and informed community.
In summary, urban farming plays a vital role in community engagement and education. It transforms urban landscapes into interactive learning environments, promotes sustainable practices, and strengthens community ties. As cities continue to grow, the importance of these initiatives cannot be overstated. They are essential for building resilient communities that are equipped to face the challenges of the future.
- What is urban farming?
Urban farming refers to the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas. It includes a variety of activities, from community gardens to rooftop farms. - How does urban farming benefit the community?
Urban farming enhances food security, promotes sustainability, provides educational opportunities, and fosters community engagement. - What are some challenges faced by urban farmers?
Challenges include land access, regulatory barriers, and the need for financial sustainability. - How can I get involved in urban farming?
You can participate by volunteering at local farms, joining community gardening initiatives, or even starting your own urban garden at home.

Challenges Facing Urban Farming
While urban farming holds immense promise for the future of food production, it is not without its fair share of challenges. One of the most pressing issues is land access. In bustling cities, where real estate prices soar, finding affordable land for farming can feel like searching for a needle in a haystack. Urban farmers often find themselves competing with developers, businesses, and even residential projects for prime plots of land. This competition can lead to a frustrating cycle where potential urban farmers are left with few options, pushing them to the outskirts of the city or making them rely on temporary spaces that lack stability.
Another significant hurdle is the complex web of regulatory barriers that urban farmers must navigate. Local governments often have outdated policies that do not accommodate innovative farming practices. Zoning laws may restrict agricultural activities in certain areas, and obtaining the necessary permits can be a daunting task. These regulations can stifle creativity and hinder the growth of urban farming initiatives. Farmers may spend months, if not years, trying to get the green light to operate, which can drain financial resources and enthusiasm.
Furthermore, the issue of financial sustainability looms large over urban farming ventures. Many urban farmers start with limited capital and face high operational costs, from purchasing seeds and equipment to maintaining their crops. Without proper funding or access to grants, many of these initiatives struggle to stay afloat. The need for innovative business models that can generate consistent revenue is critical. For instance, some urban farms have turned to community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs, where local residents pay upfront for a share of the harvest. This not only helps with cash flow but also fosters a sense of community ownership.
Despite these challenges, urban farming continues to evolve. Farmers are finding creative solutions to overcome obstacles, such as forming cooperatives to share resources, advocating for policy changes, and utilizing technology to enhance productivity. By embracing collaboration and innovation, urban farmers can pave the way for a more sustainable future.
- What is urban farming? Urban farming refers to the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas. It can take many forms, including community gardens, rooftop farms, and vertical farming.
- What are the benefits of urban farming? Urban farming promotes food security, reduces carbon footprints, enhances community engagement, and improves access to fresh produce.
- What challenges do urban farmers face? Urban farmers often encounter challenges such as land access, regulatory barriers, and financial sustainability issues.
- How can urban farming be made more sustainable? By adopting innovative techniques like vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics, urban farmers can maximize productivity while minimizing environmental impacts.

Land Access Issues
Securing land for urban farming is akin to trying to find a needle in a haystack—especially in bustling cities where real estate prices soar and space is at a premium. Urban farmers often face a myriad of challenges when it comes to accessing suitable land for their operations. The competition for land is fierce, with developers and businesses vying for the same parcels that could otherwise be transformed into vibrant green spaces. This scenario creates a daunting landscape for aspiring urban farmers who are passionate about cultivating local produce.
One major hurdle is the high cost of land. In many urban areas, the price per square foot can be astronomical, making it nearly impossible for small-scale farmers to afford a piece of land. This financial barrier can deter individuals from pursuing urban farming altogether, limiting the diversity of food sources available in cities. Moreover, even if land is available, it may come with restrictions that complicate the farming process. Zoning laws and land use regulations can make it difficult for urban farmers to establish their operations legally.
Another challenge is the competition with other land uses. As cities continue to grow, the demand for housing, commercial space, and infrastructure increases, pushing agricultural land further out of reach. Urban farmers often find themselves negotiating with city planners and developers, who may not prioritize agriculture in their plans. This can lead to a situation where urban farming is seen as an afterthought rather than an integral part of the urban landscape.
Additionally, many urban farmers face issues related to accessibility and infrastructure. Even if they secure land, they may struggle with inadequate access to water, transportation, and other essential resources necessary for successful farming. For instance, without reliable water sources, maintaining crops can become an uphill battle. Urban farmers must often be innovative, seeking alternative solutions such as rainwater harvesting or utilizing community resources to overcome these obstacles.
To provide a clearer picture, let’s take a look at a table that outlines some of the common land access issues faced by urban farmers:
| Issue | Description |
|---|---|
| High Land Costs | Urban land prices can be prohibitively expensive, making it difficult for small-scale farmers to acquire land. |
| Regulatory Restrictions | Complex zoning laws and land use regulations can hinder the establishment of urban farms. |
| Competing Interests | Developers and businesses often compete for the same land, sidelining agricultural initiatives. |
| Infrastructure Challenges | Lack of access to essential resources like water and transportation can impede farming efforts. |
In summary, while urban farming holds incredible potential for enhancing food security and sustainability in cities, the present significant barriers that need to be addressed. Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration between urban farmers, city planners, and community stakeholders to create a more favorable environment for local food production. As cities evolve, it’s crucial to recognize the value of integrating agriculture into urban planning, ensuring that future generations can enjoy the benefits of fresh, locally grown food.
- What are the main challenges urban farmers face? Urban farmers often struggle with high land costs, regulatory restrictions, competition for land, and infrastructure challenges.
- How can cities support urban farming? Cities can support urban farming by implementing favorable zoning laws, providing financial incentives, and creating community partnerships.
- What innovative techniques are being used in urban farming? Techniques like vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics are gaining traction as efficient methods for urban food production.

Regulatory Barriers
Urban farming is not just about planting seeds and harvesting crops; it’s also about navigating a complex web of that can stifle innovation and growth. As cities embrace the concept of urban agriculture, they often find themselves grappling with outdated policies that were never designed to accommodate this modern movement. This can lead to a frustrating experience for urban farmers who are eager to contribute to their communities and the environment.
One of the primary challenges is the zoning laws that dictate what can be built and where. Many urban areas have strict zoning regulations that classify land use in ways that can exclude farming activities. For instance, a vacant lot might be zoned for commercial development, leaving aspiring urban farmers without a place to grow their crops. This not only limits the available space for farming but also places additional pressure on urban farmers to advocate for changes in local legislation.
Moreover, health and safety regulations can pose significant hurdles. Urban farms often face scrutiny regarding food safety standards that are typically applied to large-scale agricultural operations. These regulations can be overwhelming, especially for small-scale farmers who may lack the resources to comply. For example, requirements for sanitation, pest control, and waste management can be daunting, leading many potential farmers to abandon their ambitions altogether.
In addition to zoning and health regulations, licensing requirements can also create obstacles. Urban farmers may need multiple permits to operate legally, which can be time-consuming and costly. The bureaucratic process can deter newcomers from entering the market, thereby limiting the diversity and resilience of urban agriculture. To illustrate this point, consider a small urban farm that wants to sell its produce at a local farmer's market. The owner must navigate a series of permits and licenses, which can often take months to obtain, delaying their ability to bring fresh produce to the community.
Despite these challenges, there is hope on the horizon. Many cities are beginning to recognize the value of urban agriculture and are actively working to reform these regulatory barriers. Initiatives to streamline the permitting process, revise zoning laws, and provide resources for compliance are gaining traction. As urban farming continues to grow, it is essential for stakeholders—including local governments, community organizations, and farmers—to collaborate and advocate for policies that support sustainable food production in urban settings.
Ultimately, addressing these regulatory barriers is crucial for the future of urban farming. By creating a more supportive environment, cities can unlock the potential of urban agriculture to enhance food security, promote sustainability, and foster community engagement. It’s a win-win situation that not only benefits farmers but also enriches urban life.
- What are the main regulatory barriers faced by urban farmers? Urban farmers often encounter zoning laws, health and safety regulations, and complex licensing requirements that can hinder their operations.
- How can cities support urban farming? Cities can support urban farming by revising zoning regulations, streamlining the permitting process, and providing resources for compliance.
- Why is urban farming important? Urban farming is important for enhancing food security, reducing environmental impact, and fostering community engagement.

Innovative Urban Farming Techniques
In the quest to transform our cities into sustainable food hubs, are leading the charge. As urban populations continue to swell, traditional farming methods simply won’t cut it in the concrete jungle. Enter techniques such as vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics, which are not just buzzwords but game-changers in how we think about food production in urban settings. These methods not only maximize space but also enhance efficiency, making them vital in addressing the challenges of urban agriculture.
Let’s start with vertical farming. Imagine a skyscraper, but instead of offices or apartments, it’s filled with lush greenery and crops stacked in layers. This technique allows farmers to grow a significant amount of produce in a limited footprint, utilizing advanced technologies like LED lighting and climate control systems. Vertical farms can produce up to 100 times more food per square meter compared to traditional farms, and they can be located right in the heart of cities, minimizing transportation costs and time. This is particularly crucial as we strive to reduce our carbon footprint.
Next up is hydroponics. This method involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water rather than soil. Hydroponics can be implemented in various settings, from small home systems to large commercial operations. The beauty of hydroponics lies in its efficiency; it uses up to 90% less water than traditional farming methods and allows for year-round crop production. Urban farmers can grow everything from leafy greens to tomatoes, all while conserving precious resources. Imagine biting into a fresh, juicy tomato that was grown just a few blocks away!
Then we have aquaponics, which takes hydroponics a step further by integrating fish farming into the system. In this symbiotic relationship, fish waste provides an organic nutrient source for the plants, while the plants help filter and clean the water for the fish. This closed-loop system not only maximizes space but also creates a sustainable ecosystem that can yield both fish and vegetables. Urban aquaponics can be a fantastic solution for food deserts, providing fresh produce and protein to communities that need it the most.
| Technique | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Vertical Farming | Growing crops in stacked layers, often in controlled environments. | Maximizes space, reduces food miles, and increases yield. |
| Hydroponics | Growing plants in nutrient-rich water without soil. | Uses less water, allows for year-round production, and conserves resources. |
| Aquaponics | Combining fish farming with hydroponics in a symbiotic environment. | Produces both fish and vegetables, creates a sustainable ecosystem. |
These innovative techniques not only redefine how we grow food but also serve as a beacon of hope for urban sustainability. The integration of technology and nature in urban farming practices is paving the way for a future where cities can be self-sufficient in food production. But it doesn’t stop here; as urban farming continues to evolve, who knows what other groundbreaking methods will emerge? The potential is as vast as the skies above our cities!
- What is urban farming? Urban farming is the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas.
- How does vertical farming work? Vertical farming utilizes stacked layers of crops grown in controlled environments, often using hydroponic or aeroponic systems.
- What are the benefits of hydroponics? Hydroponics uses significantly less water than traditional farming, allows for faster growth, and can be done indoors or in limited spaces.
- Can aquaponics be done at home? Yes, many people set up small aquaponics systems at home to grow vegetables and raise fish.

Vertical Farming
Imagine a world where fresh produce is just an elevator ride away! is revolutionizing the way we think about agriculture, especially in urban areas where space is at a premium. By stacking crops in layers, vertical farms can produce a substantial amount of food without requiring vast expanses of land. This innovative approach not only maximizes space but also allows for year-round cultivation, regardless of the weather outside. Think of it like a skyscraper, but instead of offices, it's filled with vibrant greens and juicy tomatoes!
One of the most exciting aspects of vertical farming is its ability to reduce the environmental impact of food production. Traditional farming often involves extensive land use, which can lead to habitat destruction and biodiversity loss. In contrast, vertical farms can be set up in repurposed buildings, warehouses, or even shipping containers, making them a sustainable alternative. Plus, these farms utilize advanced technologies such as LED lighting and automated nutrient delivery systems, which not only optimize growth but also conserve resources.
However, you might be wondering about the cost and energy consumption associated with vertical farming. While initial setup costs can be high, the long-term benefits often outweigh the expenses. For instance, vertical farms can significantly cut down on transportation costs since they are located closer to urban consumers. Additionally, many vertical farms are now incorporating renewable energy sources, such as solar panels, to power their operations, further enhancing their sustainability.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the key benefits of vertical farming:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Space Efficiency | Utilizes limited urban space by stacking crops vertically. |
| Year-Round Production | Enables continuous crop cultivation regardless of climate. |
| Reduced Transportation Costs | Located near consumers, minimizing food miles. |
| Resource Conservation | Efficient use of water and nutrients through controlled systems. |
In addition to these benefits, vertical farming also opens up opportunities for urban communities to engage in food production. Imagine local residents participating in workshops to learn about hydroponics and aquaponics, or even managing their own small vertical gardens! This community involvement not only fosters a sense of ownership but also educates individuals about sustainable practices and healthy eating.
As we look toward the future, it’s clear that vertical farming holds immense potential to transform urban landscapes. By integrating technology with agriculture, we can create a more resilient food system that not only feeds our growing populations but also protects our planet. So, the next time you bite into a crisp salad or enjoy a fresh herb, consider the possibility that it might have been grown just a few floors above you!
- What is vertical farming? - Vertical farming is an innovative method of growing crops in vertically stacked layers, often using controlled-environment agriculture technology.
- How does vertical farming benefit the environment? - It minimizes land use, reduces transportation emissions, and can utilize renewable energy sources.
- Is vertical farming cost-effective? - While the initial investment can be high, the long-term savings on transportation and resources often make it financially viable.
- Can vertical farms grow all types of crops? - Vertical farms are particularly suited for leafy greens, herbs, and some fruits, but ongoing research is expanding the range of crops that can be cultivated.

Hydroponics and Aquaponics
When it comes to urban farming, hydroponics and aquaponics are two innovative techniques that are turning heads and reshaping the way we think about food production. Imagine growing vibrant, fresh vegetables without the need for traditional soil. Sounds like magic, right? But it’s not! These methods leverage technology and nature’s own processes to create sustainable food systems right in the heart of our cities.
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants in a nutrient-rich water solution. This technique allows plants to absorb nutrients directly through their roots, leading to faster growth rates and higher yields compared to traditional farming methods. In urban settings where space is a premium, hydroponics can be particularly advantageous. For instance, a hydroponic system can be set up in a small apartment, a rooftop, or even in a warehouse, making fresh produce accessible to city dwellers.
On the other hand, aquaponics takes things a step further by combining hydroponics with aquaculture—the cultivation of fish. In this symbiotic system, fish waste provides an organic nutrient source for the plants, while the plants help filter and purify the water for the fish. This closed-loop system not only maximizes space but also minimizes waste, creating a sustainable ecosystem that benefits both plants and aquatic life. Urban aquaponics can be a game-changer, providing a dual source of nutrition—fresh vegetables and fish—right where they are needed most.
Let’s break down some of the key advantages of hydroponics and aquaponics:
- Space Efficiency: Both systems can be designed to fit into small areas, making them ideal for urban environments.
- Water Conservation: Hydroponics and aquaponics use significantly less water than traditional farming—up to 90% less in some cases.
- Pesticide-Free Produce: These systems often eliminate the need for harmful pesticides, resulting in healthier food options.
- Year-Round Production: Controlled environments allow for continuous growth cycles, providing fresh produce regardless of the season.
While the benefits are clear, it’s important to recognize that starting a hydroponic or aquaponic system requires an initial investment in equipment and technology. However, the long-term gains in food production and sustainability can far outweigh these upfront costs. As urban populations continue to grow, the demand for innovative food solutions like hydroponics and aquaponics will only increase.
In conclusion, hydroponics and aquaponics are not just trends; they represent a fundamental shift in how we can approach food production in urban areas. By embracing these technologies, we can create greener cities, enhance food security, and pave the way for a more sustainable future.
Q: What is hydroponics?
A: Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil, using a nutrient-rich water solution instead.
Q: How does aquaponics work?
A: Aquaponics combines fish farming with hydroponics, where fish waste provides nutrients for the plants, and the plants help purify the water for the fish.
Q: Can I start a hydroponic or aquaponic system at home?
A: Yes! Many systems are designed for home use and can be set up in small spaces like balconies or kitchens.
Q: What are the main benefits of these systems?
A: They are space-efficient, conserve water, produce pesticide-free food, and allow for year-round cultivation.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is urban farming?
Urban farming refers to the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in or around urban areas. It can include community gardens, rooftop farms, and even vertical farming systems. Essentially, it’s a way to grow food where people live, making it fresher and more accessible.
- Why is urban farming gaining popularity?
The rise in urban farming is largely due to the growing need for sustainable food sources as city populations increase. People are becoming more aware of where their food comes from and are seeking local, fresh options. Urban farming also addresses issues like food deserts and promotes community engagement.
- What are the environmental benefits of urban farming?
Urban farming has several environmental advantages, including reducing carbon footprints by cutting down on food miles, promoting biodiversity, and improving air quality. By growing food locally, urban farms help create green spaces that support various plant and animal species, contributing to a healthier urban ecosystem.
- What challenges do urban farmers face?
Urban farmers encounter various challenges, such as high land prices, regulatory barriers, and financial sustainability concerns. Securing land for farming can be particularly tough in densely populated areas, and navigating complex regulations can hinder their operations.
- What innovative techniques are used in urban farming?
To overcome challenges, urban farmers are turning to innovative techniques like vertical farming, hydroponics, and aquaponics. Vertical farming allows for growing crops in stacked layers, maximizing limited space, while hydroponics and aquaponics offer efficient, soil-less methods of cultivation that can thrive in urban settings.
- How can I get involved in urban farming?
Getting involved in urban farming can be as simple as joining a local community garden, volunteering at an urban farm, or starting your own small-scale garden at home. Many cities also offer workshops and educational programs to help you learn about sustainable practices and food production.



















