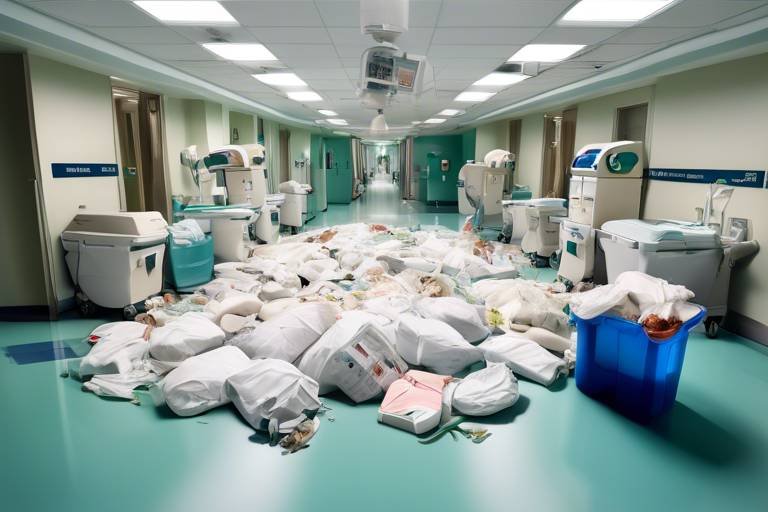
What Happens with Recyclable Items that Aren't Recycled?
When we toss our recyclable items into the bin, we often assume they will be transformed into new products, contributing to a sustainable future. However, the reality is far more complex. Many recyclable materials fail to make it through the recycling process, and understanding this journey is crucial. So, what really happens to those items that don’t get recycled? The fate of these materials can have significant environmental and economic implications.
First, let's visualize the typical journey of a recyclable item. Once we place it in the recycling bin, it is collected by waste management services and transported to a recycling facility. Here, it should ideally be sorted, cleaned, and processed into raw materials for new products. However, this process is fraught with challenges. For instance, contamination from food residues or mixing non-recyclable items with recyclables can lead to entire batches being rejected. When this occurs, these items are often sent to landfills instead of being recycled.
Now, consider the implications of this failure to recycle. When recyclable materials end up in landfills, they contribute to a myriad of environmental issues. For one, they occupy valuable space in landfills, which are already overflowing. Additionally, as these materials decompose, they release harmful greenhouse gases like methane into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change. It’s a vicious cycle where our negligence leads to further environmental degradation.
Moreover, the economic impact of failing to recycle is profound. Local economies suffer when recyclable materials are not processed. Waste management costs rise, as municipalities must pay to dispose of materials that could have been recycled. Furthermore, the recycling industry itself loses out on valuable resources that could create jobs and stimulate economic growth. In fact, studies have shown that recycling creates significantly more jobs than landfilling does, highlighting the missed opportunities when we fail to recycle.
It’s essential to address some common misconceptions about recycling as they play a crucial role in this dilemma. Many people believe that all plastics are recyclable, but in reality, not all types can be processed. This misunderstanding leads to improper sorting and contamination, which ultimately results in more materials being sent to landfills. Educating the public about what can and cannot be recycled is vital for improving recycling rates.
In addition to misconceptions, there are several barriers that hinder effective recycling practices. A lack of education, insufficient recycling facilities, and even the complexity of recycling guidelines can deter individuals from participating in recycling programs. By identifying these challenges, communities can work towards implementing solutions that foster better recycling habits.
Fortunately, innovative recycling solutions are emerging to tackle these issues. New technologies, such as advanced sorting systems and biodegradable materials, are being developed to enhance recycling efforts. Programs that incentivize recycling, like deposit return schemes, are also gaining traction. These initiatives not only divert more materials from landfills but also promote a culture of sustainability.
Community engagement is another critical aspect of effective recycling programs. When communities come together to promote recycling, the impact can be significant. Organizing local clean-up events, educational workshops, and recycling drives can raise awareness and encourage participation. Creating a sense of shared responsibility can motivate individuals to take action and make recycling a priority.
Looking ahead, the future of recycling is promising, but it requires collective effort. Advancements in technology and policy changes will be essential in revolutionizing how we handle recyclable materials. With ongoing innovation and community involvement, we can create a more sustainable future where recycling becomes the norm rather than the exception.
- What types of materials can be recycled? Most paper products, certain plastics, metals, and glass can be recycled, but it’s important to check local guidelines for specifics.
- How can I reduce contamination in my recycling? Rinse containers before recycling, and ensure that only accepted materials are placed in the recycling bin.
- What happens to recycling after it’s collected? Collected recyclables are taken to a facility where they are sorted, cleaned, and processed into new materials.
- Why is recycling important? Recycling conserves resources, reduces landfill waste, and helps lower greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a healthier planet.

The Journey of Recyclables
When we toss our empty soda cans or plastic bottles into the recycling bin, we often feel a sense of accomplishment, believing we're doing our part to save the planet. But have you ever wondered what really happens to those recyclables after they leave your curb? The journey of recyclable materials is not as straightforward as it might seem. In an ideal world, these items would smoothly transition from our homes to recycling facilities, where they would be sorted, processed, and transformed into new products. However, the reality is filled with obstacles that can derail this process.
Initially, recyclables are collected by waste management services and transported to a Materials Recovery Facility (MRF). Here, the real sorting begins. Workers and machines separate materials based on type—plastics, metals, paper, and glass. It sounds efficient, right? But here's where the journey can hit a snag. Contamination is a significant issue; when non-recyclable items are mixed in with recyclables, it complicates the sorting process. For example, a greasy pizza box tossed in with clean cardboard can ruin an entire batch of recyclable materials. This is why it's crucial to properly clean and sort your recyclables before placing them in the bin.
After sorting, the recyclable materials are compacted and baled, making them easier to transport to manufacturers. However, not all materials make it to this stage. According to recent statistics, nearly 35% of recyclable materials end up in landfills due to contamination or improper disposal. This means that while we may believe we're contributing to a sustainable future, a significant portion of our efforts may be going to waste.
Once the materials reach manufacturers, they undergo further processing. This stage varies significantly based on the type of material. For instance, glass can be melted down and reformed into new containers, while plastics might be shredded and reconstituted into new products. However, the quality of the recycled material is often lower than that of virgin materials, which can lead to manufacturers opting for new materials instead. This decision not only impacts the recycling industry but also has broader implications for our environment, as it perpetuates the cycle of resource extraction and waste generation.
So, what can we do to improve this journey? Education is key. By raising awareness about the importance of proper recycling practices, we can reduce contamination rates and ensure more materials make it through the recycling process. Additionally, communities can advocate for better recycling infrastructure, making it easier for residents to recycle effectively.
In summary, the journey of recyclables is a complex path filled with challenges. From the moment we toss an item into the recycling bin to its potential rebirth as a new product, numerous factors can influence its fate. Understanding this journey helps us appreciate the importance of our role in the recycling process and encourages us to take action in our daily lives.

Environmental Consequences
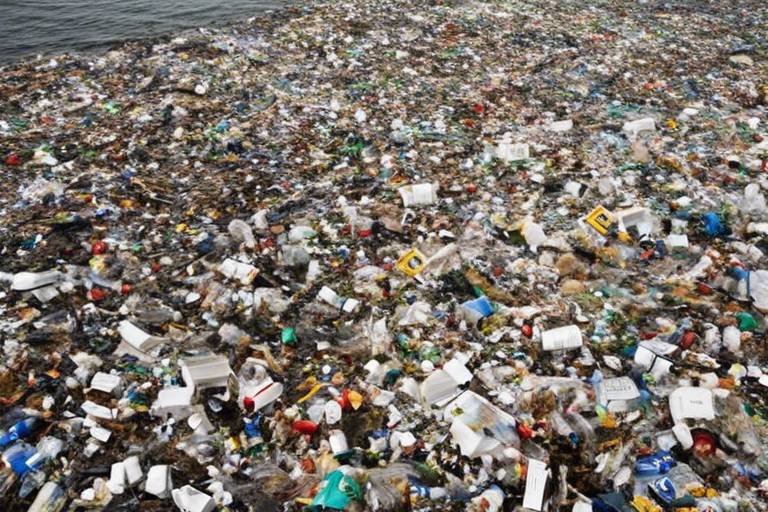
When recyclable items are not recycled, the repercussions ripple through our environment like a stone tossed into a pond. Each piece of plastic, glass, or metal that fails to find its way into the recycling stream contributes to a growing mountain of waste in landfills. This is not just an aesthetic issue; it has profound implications for our planet's health. Imagine a world where natural resources are depleted faster than they can be replenished. The reality is that every unrecycled item represents a missed opportunity to conserve precious resources.
Landfills are not just holes in the ground; they are sources of significant pollution and environmental degradation. As waste decomposes, it releases harmful gases, including methane, a greenhouse gas that is over 25 times more potent than carbon dioxide in terms of its ability to trap heat in the atmosphere. This contributes to climate change, which is one of the most pressing issues we face today. Not to mention, the toxins from decomposing materials can seep into the soil and groundwater, posing serious risks to ecosystems and human health.
Furthermore, the failure to recycle leads to increased resource depletion. Every time we throw away a recyclable item, we are essentially throwing away the energy and raw materials that went into producing it. For instance, recycling aluminum saves up to 95% of the energy required to create new aluminum from raw materials. If we fail to recycle, we are forced to extract more raw materials, which can lead to habitat destruction, increased mining, and more pollution. In essence, not recycling is akin to robbing future generations of their natural heritage.
To illustrate the environmental impact of failing to recycle, consider the following table that highlights the effects of common recyclable materials:
| Material | Environmental Impact of Not Recycling |
|---|---|
| Plastic | Contributes to ocean pollution, harming marine life and ecosystems. |
| Glass | Requires significant energy to produce new glass, leading to increased carbon emissions. |
| Paper | Leads to deforestation and loss of biodiversity as more trees are cut down. |
| Metals | Increases mining activities, which can lead to soil erosion and habitat destruction. |
In conclusion, the environmental consequences of failing to recycle are profound and multifaceted. By not recycling, we are not only contributing to pollution and resource depletion but also jeopardizing the health of our planet for future generations. It’s a cycle that can be broken, but it requires awareness, education, and action from all of us. So, the next time you consider tossing a recyclable item in the trash, think about the long-term effects of that decision. Are we willing to bear the costs of our convenience?
- What can I do to improve my recycling habits? Start by educating yourself on what materials are recyclable in your area and make a conscious effort to sort your waste properly.
- Why is recycling important? Recycling reduces waste, conserves natural resources, saves energy, and minimizes pollution.
- How can communities promote better recycling practices? Communities can engage residents through educational programs, workshops, and by providing convenient recycling facilities.

Economic Implications
When we think about recycling, we often focus on the environmental benefits, but the are equally significant. The failure to recycle not only affects our planet but also has a ripple effect on local economies and job markets. Imagine a bustling recycling facility that processes materials and creates jobs; now picture that same facility closing due to insufficient recyclable materials. This scenario is not just hypothetical; it’s a reality in many communities.
When recyclable materials end up in landfills instead of being processed, local governments face increased costs associated with waste management. Landfills are expensive to maintain, and as more waste accumulates, municipalities must allocate more funds for waste disposal. This can lead to higher taxes or fees for residents, which is an economic burden that no one wants to bear. In fact, studies indicate that for every ton of waste that is recycled, communities can save an average of $30 to $50 in landfill costs.
Moreover, the recycling industry itself is a significant source of employment. According to recent data, the recycling sector supports over 1.1 million jobs in the United States alone. These jobs range from collection and sorting to processing and manufacturing. When we fail to recycle, we not only lose these jobs but also miss out on potential growth in the green economy. The more materials we recycle, the more demand there is for skilled workers in the recycling and manufacturing sectors. It's a win-win situation that we are currently undermining.
Additionally, the economic implications extend to businesses as well. Companies that rely on recycled materials for production can face increased costs if the supply of recyclables diminishes. This may lead to higher prices for consumers, as businesses pass on the costs to maintain their profit margins. In a world where consumers are increasingly conscious of sustainability, businesses that fail to adapt to recycling practices risk losing their competitive edge.
To further illustrate the economic impact, consider the table below, which outlines the costs associated with recycling versus landfilling:
| Action | Cost per Ton |
|---|---|
| Recycling | $30 - $50 |
| Landfilling | $50 - $100 |
As we can see, recycling presents a more cost-effective solution compared to landfilling. However, the benefits of recycling extend beyond just immediate cost savings. By investing in recycling infrastructure and education, communities can create a more sustainable economy that not only conserves resources but also fosters job creation and economic resilience.
In conclusion, the economic implications of failing to recycle are profound. From increased waste management costs to lost job opportunities, the effects are felt across various sectors. To create a sustainable future, it’s crucial that we prioritize recycling efforts and educate our communities about its importance. After all, a thriving economy and a healthy planet go hand in hand.
- What are the main economic benefits of recycling? Recycling reduces waste management costs, creates jobs, and supports local economies.
- How does recycling impact job creation? The recycling industry supports millions of jobs in collection, processing, and manufacturing.
- What costs are associated with landfilling? Landfilling can be significantly more expensive than recycling, often costing municipalities more in maintenance and fees.
- Can businesses benefit from recycling? Yes, businesses can save on raw material costs and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.

Common Misconceptions
When it comes to recycling, many people harbor misconceptions that can hinder effective practices. One of the biggest myths is that all plastics are recyclable. In reality, only certain types of plastics can be processed in standard recycling facilities. For example, while PETE (Polyethylene Terephthalate) and HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) are widely accepted, other plastics like polystyrene (often found in disposable cups and takeout containers) are frequently not recyclable at all. This can lead to confusion and frustration when individuals attempt to sort their waste.
Another common misconception is that rinsing containers before recycling is unnecessary. However, many recycling facilities require that items be clean and free from food residue. This is because leftover food can contaminate entire batches of recyclables, causing them to be rejected and sent to landfills. Think of it this way: if you wouldn't want to eat off a plate that had leftover spaghetti on it, then the same goes for recyclables. Cleanliness is key!
Additionally, some folks believe that if an item has a recycling symbol on it, it can be recycled anywhere. Unfortunately, the recycling symbol can be misleading. Just because something is marked with a recycling symbol doesn't guarantee it will be accepted by local programs. Each municipality has its own rules about what can and cannot be recycled. Therefore, it's essential to check with your local recycling guidelines to avoid confusion.
To further complicate matters, many people think that recycling is a catch-all solution to environmental problems. While recycling is important, it is just one part of the puzzle. The real heroes in the fight against waste are reducing and reusing. Imagine if everyone focused on buying less or choosing products with minimal packaging; the amount of waste generated would significantly decrease, making recycling efforts far more effective.
In light of these misconceptions, education and awareness play crucial roles in improving recycling rates. Communities can benefit from workshops, informational pamphlets, and social media campaigns that clarify what can be recycled and how to properly prepare items for recycling. Engaging the public in discussions about these common myths can create a more informed society that takes recycling seriously.
In summary, addressing and debunking these common misconceptions is vital for improving recycling rates and ensuring that more materials are processed correctly. By understanding the realities of recycling, individuals can contribute to a more sustainable future, making informed choices that benefit both the environment and the economy.
- What types of plastics can be recycled? Only certain types such as PETE and HDPE are widely accepted. Always check local guidelines.
- Do I need to rinse my recyclables? Yes, items should be clean and free from food residue to prevent contamination.
- Is recycling enough to solve environmental issues? No, reducing and reusing are equally important to minimize waste.
- What should I do if I'm unsure about recycling an item? Check with your local recycling program for specific guidelines.

Barriers to Recycling
Recycling is often seen as a straightforward solution to our waste problems, but the reality is much more complex. There are several barriers that prevent effective recycling practices from taking root in our communities. One of the most significant challenges is a lack of education. Many people simply do not understand what can and cannot be recycled. For instance, did you know that greasy pizza boxes and certain types of plastic can confuse the recycling process? Without proper knowledge, recyclable items often end up in the trash instead of the recycling bin.
Another major hurdle is the inadequate facilities available for processing recyclables. In many areas, recycling centers are few and far between, making it difficult for residents to access them. This geographical limitation can lead to lower participation rates in recycling programs. Additionally, some facilities are not equipped to handle the types of materials that are commonly disposed of, resulting in a backlog of recyclable waste that ultimately gets sent to landfills.
Furthermore, inconsistent policies across different municipalities can create confusion. For example, one city might accept glass bottles while another does not. This inconsistency can frustrate residents who want to do the right thing but are unsure of the rules. A
| City | Accepts Glass | Accepts Plastic Bags | Accepts Pizza Boxes |
|---|---|---|---|
| City A | Yes | No | No |
| City B | No | Yes | Yes |
| City C | Yes | No | Yes |
Moreover, the perception of recycling as a low-impact solution can lead to apathy. Some individuals believe that recycling is just a drop in the bucket when it comes to tackling larger environmental issues, such as climate change. This mindset can diminish their motivation to participate in recycling programs. To combat this, it's essential to communicate the tangible benefits of recycling, not only for the environment but also for the economy.
Lastly, economic factors play a significant role in the barriers to recycling. Many recycling programs are underfunded, leading to limited resources for outreach and education. When recycling becomes too costly for municipalities, they may cut back on services or increase fees, discouraging participation. This creates a vicious cycle where less recycling leads to higher costs for waste management, which in turn reduces funding for recycling initiatives.
Addressing these barriers requires a multifaceted approach. Communities need to invest in education and outreach programs that clearly communicate what can be recycled and why it matters. Additionally, improving access to recycling facilities and ensuring consistent policies across regions can help bridge the gap. By tackling these challenges head-on, we can create a more sustainable future where recycling is not just an option, but a norm.
- What are the most common items that can be recycled? Most common recyclable items include paper, cardboard, glass bottles, aluminum cans, and certain plastics. Always check local guidelines for specifics.
- How can I educate myself about recycling in my area? Local government websites often provide resources and guidelines. Additionally, community workshops and online platforms can be helpful.
- What should I do if my city doesn't have a recycling program? Consider advocating for one by contacting local officials or joining community efforts to promote sustainable practices.

Innovative Recycling Solutions
In the quest to tackle the growing waste crisis, innovative recycling solutions are emerging as a beacon of hope. These advancements not only enhance the efficiency of recycling processes but also contribute to a more sustainable future. Imagine a world where every recyclable material is processed effectively, reducing the burden on landfills and conserving precious resources. This vision is becoming increasingly attainable thanks to cutting-edge technologies and creative initiatives.
One of the most exciting developments in recycling is the rise of smart recycling bins. These bins are equipped with sensors and AI technology that can identify and sort recyclable materials automatically. By streamlining the sorting process, these smart bins minimize human error and ensure that more materials are recycled correctly. Picture a neighborhood where residents can simply toss their recyclables into a bin that does all the hard work for them. This not only simplifies the recycling process but also encourages more people to participate.
Another innovative solution is the use of chemical recycling. Unlike traditional recycling methods that often degrade the quality of materials, chemical recycling breaks down plastics into their original monomers, allowing for the creation of new, high-quality products. This method has the potential to revolutionize the way we think about plastic waste. Instead of viewing plastic as a single-use item, we can begin to see it as a valuable resource that can be reused indefinitely. This shift in perspective is crucial for combating plastic pollution.
Furthermore, companies are increasingly adopting closed-loop systems, where the waste generated from a product is used to create new products. For instance, some fashion brands are now using recycled materials to produce new clothing lines. This not only reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills but also encourages consumers to make more environmentally friendly choices. Imagine wearing a shirt made from recycled plastic bottles; it’s not just a fashion statement but a step toward sustainability.
Community engagement plays a vital role in these innovative solutions. Local governments and organizations are launching educational campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of recycling and the technologies available. Programs that involve community members in the recycling process, such as workshops and clean-up events, can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility. When people understand the impact of their actions, they are more likely to participate actively in recycling efforts.
To summarize, the future of recycling is bright, thanks to innovative solutions that are transforming the landscape of waste management. From smart bins and chemical recycling to closed-loop systems and community engagement, these advancements are paving the way for a more sustainable world. However, it’s essential to continue supporting and investing in these technologies to ensure that we can effectively manage our waste and protect our planet for future generations.
- What is chemical recycling? Chemical recycling is a process that breaks down plastics into their original monomers, allowing for the creation of new, high-quality plastic products.
- How do smart recycling bins work? Smart recycling bins use sensors and AI technology to identify and sort recyclable materials automatically, reducing human error and improving recycling rates.
- What are closed-loop systems? Closed-loop systems are processes where waste generated from a product is used to create new products, minimizing waste and promoting sustainability.
- How can communities get involved in recycling efforts? Communities can participate by organizing clean-up events, educational workshops, and campaigns to raise awareness about the importance of recycling.

Community Engagement
When it comes to recycling, community engagement plays a pivotal role in ensuring that recyclable materials are properly sorted, collected, and processed. Think of it like a team sport; every player needs to know their position and play their part for the team to succeed. In this case, the team consists of local residents, businesses, and municipal authorities all working together towards a common goal: reducing waste and promoting sustainability. But how do we get everyone on board?
First and foremost, education is key. Many people simply don’t understand what can and cannot be recycled. A well-informed community is more likely to participate actively in recycling programs. Workshops, informational flyers, and social media campaigns can help bridge this knowledge gap. For instance, consider organizing community events where residents can learn about recycling practices and even bring their recyclables for proper sorting. This not only educates but also fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility among community members.
Moreover, creating a sense of community pride can significantly enhance recycling efforts. When people feel connected to their neighborhood and understand the positive impact of their actions, they are more likely to engage in sustainable practices. Initiatives like community clean-up days, recycling competitions, or even neighborhood rewards programs can ignite that spark. Imagine a friendly competition where the neighborhood that recycles the most earns a community garden or a public art installation. Such initiatives not only promote recycling but also strengthen community bonds.
Another effective strategy is to collaborate with local businesses. By partnering with companies that share a commitment to sustainability, communities can create a ripple effect. For instance, local shops can offer discounts to customers who bring in their own reusable bags or containers. This not only encourages recycling but also promotes a culture of sustainability among consumers. Additionally, businesses can sponsor recycling bins in public spaces, making it easier for residents to dispose of their recyclables correctly.
Furthermore, technology can play a significant role in community engagement. Mobile apps that track recycling habits, provide reminders for collection days, or offer tips on reducing waste can be incredibly effective. Imagine an app that gamifies recycling—where users earn points for recycling correctly and can redeem them for rewards or discounts at local businesses. This approach not only makes recycling fun but also encourages consistent participation.
In conclusion, community engagement is not just about getting people to recycle; it's about creating a culture of sustainability. By educating residents, fostering pride, collaborating with businesses, and leveraging technology, communities can significantly improve their recycling rates. It’s a collective effort that requires everyone to play their part, and the benefits extend far beyond just reducing waste. A more engaged community leads to a healthier environment, economic growth, and a brighter future for all.
- How can I get involved in my community's recycling program? Check with your local government or community center for upcoming events and volunteer opportunities.
- What are some common recyclable items that people often overlook? Items like pizza boxes, glass jars, and certain types of plastics can often be recycled but may be overlooked.
- How can technology improve recycling efforts? Apps that track recycling habits and provide educational resources can encourage participation and proper sorting.

Future of Recycling
The is not just a matter of improving current practices; it's about embracing innovation and rethinking how we handle waste. As environmental concerns continue to mount, the pressure is on industries, governments, and communities to find effective solutions that can significantly reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills. Imagine a world where recycling is not just an option but a seamless part of our daily lives—this vision is becoming increasingly attainable.
One of the most promising developments in the recycling landscape is the advent of advanced sorting technologies. These technologies use artificial intelligence and machine learning to identify and separate recyclable materials more efficiently than ever before. For instance, automated systems can now recognize various types of plastics, metals, and papers, ensuring that more materials are diverted from landfills and sent to recycling facilities. This not only increases recycling rates but also reduces contamination, which is a major hurdle in the recycling process.
Moreover, innovations in materials science are paving the way for new recyclable materials that can replace traditional, less sustainable options. Biodegradable plastics and other eco-friendly materials are being developed to minimize environmental impact. As these materials become more mainstream, they will contribute to a circular economy where resources are reused rather than discarded, ultimately leading to a more sustainable future.
Policy changes also play a critical role in shaping the future of recycling. Governments around the world are implementing stricter regulations on waste management and incentivizing recycling initiatives. For example, some regions are introducing extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws, which hold manufacturers accountable for the entire lifecycle of their products, including disposal. This encourages companies to design products that are easier to recycle and reduces the burden on consumers.
In addition to technological and policy advancements, community engagement remains vital. As we look ahead, fostering a culture of sustainability within communities can drive significant change. Educational programs that inform residents about the importance of recycling and how to do it correctly can lead to higher participation rates. Community-led initiatives, such as local recycling drives or workshops, can empower individuals to take action and make a difference.
As we envision the future of recycling, it’s clear that collaboration will be key. The convergence of technology, policy, and community action will create a robust framework for effective recycling practices. By working together, we can create a world where waste is minimized, resources are conserved, and sustainability is prioritized.
- What are the latest technologies in recycling? Advanced sorting systems using AI, biodegradable materials, and enhanced recycling processes are among the latest innovations.
- How can communities improve recycling rates? By implementing educational programs and engaging residents in local initiatives, communities can significantly boost participation in recycling efforts.
- What role do governments play in recycling? Governments can enact policies that encourage recycling, such as EPR laws and incentives for sustainable practices.
- What is a circular economy? A circular economy is an economic system aimed at eliminating waste and the continual use of resources, promoting sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What happens to recyclable items that aren't recycled?
When recyclable items fail to make it through the recycling process, they often end up in landfills. This not only contributes to increased waste but also leads to pollution and resource depletion. It's like throwing away a perfectly good meal; it just feels wrong!
- Why do some recyclable materials end up in landfills?
There are several reasons why recyclable materials don’t make it to the recycling facilities. Poor sorting at the source, contamination with non-recyclables, and a lack of proper facilities can all play a role. Imagine trying to bake a cake with spoiled ingredients—it just won’t work!
- What are the environmental consequences of not recycling?
Not recycling leads to significant environmental issues, including increased landfill waste, pollution, and higher greenhouse gas emissions. It's like adding more fuel to a fire; the more we throw away, the worse it gets for our planet.
- How does failing to recycle impact the economy?
When recyclable materials are not processed, it can lead to increased costs for waste management and lost opportunities in the recycling industry. Think of it as missing out on a great investment; the potential gains are just tossed away!
- What are some common misconceptions about recycling?
Many people believe that all plastics are recyclable or that rinsing isn’t necessary. In reality, proper sorting and cleaning are crucial to ensure materials can be effectively recycled. It’s like trying to solve a puzzle with missing pieces; it just doesn’t fit!
- What barriers prevent effective recycling practices?
Lack of education, inadequate facilities, and confusion about what can be recycled are significant barriers. Overcoming these challenges is essential for improving recycling rates. It's similar to trying to learn a new sport without proper coaching; you need guidance to succeed!
- Are there innovative solutions to enhance recycling?
Yes! Many new technologies and programs are emerging to improve recycling efforts. From advanced sorting machines to community initiatives, these innovations can help divert more materials from landfills. Think of it as upgrading your tools to build something better!
- How can communities get involved in recycling?
Community engagement is key to successful recycling programs. Strategies like educational campaigns, local recycling events, and partnerships with schools can foster a culture of sustainability. It’s like planting seeds in a garden; with care and attention, they can grow into something beautiful!
- What does the future hold for recycling?
The future of recycling looks promising with advancements in technology and policy changes on the horizon. Innovations could revolutionize how we handle recyclable materials, making the process more efficient and effective. It’s like getting a brand new toolbox—everything becomes easier to manage!