Oil Apocalypse: The Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill and Its Aftermath
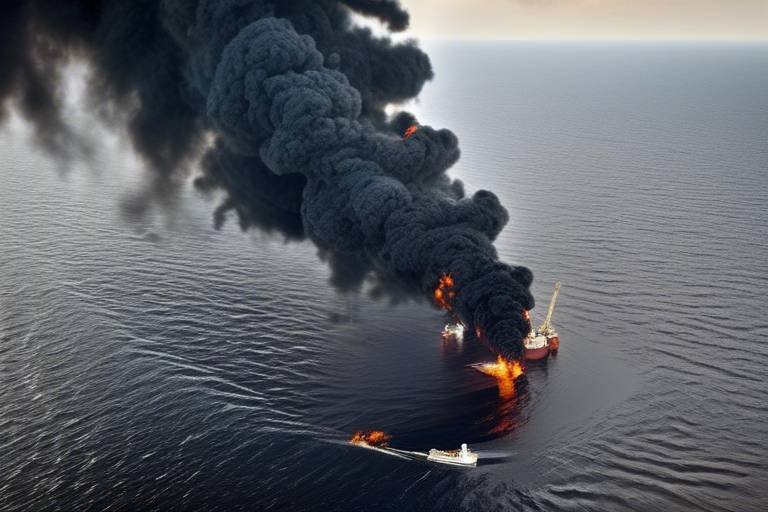
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill, which occurred in April 2010, is often described as one of the most devastating environmental disasters in history. It was more than just an unfortunate event; it was a wake-up call for humanity about the perils of our reliance on fossil fuels. Imagine a vast expanse of ocean, teeming with life, suddenly choked by millions of gallons of crude oil. The spill not only wreaked havoc on marine ecosystems but also highlighted the fragility of our environment and the dire consequences of human negligence. This article delves into the catastrophic Deepwater Horizon oil spill, exploring its causes, immediate impacts, long-term environmental consequences, and the ongoing recovery efforts that highlight the complexities of oil dependency and environmental stewardship.
Understanding the technical and managerial failures that led to the Deepwater Horizon disaster is crucial. The spill was not merely an accident; it was the result of a series of poor decisions and oversights. A combination of factors contributed to this calamity, including inadequate safety measures, rushed operations, and a culture that prioritized profit over safety. For instance, the lack of proper blowout preventers and the failure to heed warning signs were pivotal in allowing the disaster to unfold. These oversights serve as a stark reminder of the importance of rigorous safety protocols and the potential consequences when they are ignored.
The immediate aftermath of the spill caused unprecedented damage to marine ecosystems. The Gulf of Mexico, a vibrant and diverse habitat, was transformed into a toxic wasteland. Oil covered beaches, smothered marine life, and disrupted the delicate balance of this unique environment. The effects were felt almost instantly, with reports of dead fish, birds, and other wildlife emerging in the days following the spill. The region's biodiversity, which had taken millions of years to develop, was suddenly under siege.
The spill significantly affected various marine species, from fish to birds. In the short term, the immediate effects included the death of countless organisms, as oil infiltrated their habitats. Long-term consequences, however, are more insidious. The oil disrupted food chains, leading to declines in fish populations and affecting species that rely on them for survival. The ripple effects of this disaster are still being felt today, with some species struggling to recover. The Gulf's once-thriving ecosystems are now a shadow of their former selves, raising questions about biodiversity and the future of marine life in the region.
The fishing industry faced severe disruptions due to contamination. Local fisheries, which had been the lifeblood of coastal communities, were devastated. The economic impact was staggering, as fishermen found their livelihoods threatened by closed fishing areas and contaminated waters. The spill not only harmed marine life but also dealt a heavy blow to the economy, leading to job losses and economic instability for many families. The long-term ramifications for local fisheries and fishing communities are still being assessed, as recovery remains an uphill battle.
Coastal ecosystems, such as marshes and mangroves, suffered extensive damage. These critical habitats play a vital role in protecting shorelines, filtering pollutants, and providing shelter for numerous species. The oil spill disrupted these ecosystems, leading to erosion, loss of vegetation, and a decline in wildlife populations. The effects on these habitats are not just environmental; they have social and economic implications for communities that rely on them for sustenance and protection against storms.
The spill raised significant health concerns for local populations. Workers involved in the cleanup and residents living in proximity to the affected areas faced exposure to toxic substances, leading to a range of health issues. Reports of respiratory problems, skin conditions, and psychological stress emerged in the aftermath of the disaster. The long-term health effects are still being studied, but the incident serves as a grim reminder of the human cost of environmental disasters.
The Deepwater Horizon spill left lasting scars on the environment, with ongoing ecological challenges. The long-term effects on ecosystems, species recovery, and habitat restoration efforts are complex and multifaceted. While some areas are showing signs of recovery, others continue to struggle with the aftermath of the spill. The ecological balance of the Gulf of Mexico has been altered, and the road to recovery is fraught with challenges.
Efforts to restore the affected areas are ongoing. Numerous initiatives and strategies have been implemented to rehabilitate ecosystems and support local communities in recovery. From habitat restoration projects to economic support for displaced fishermen, these efforts highlight the resilience of both nature and humanity. However, the road to recovery is long, and the full extent of the damage is still being assessed. The importance of community involvement and sustainable practices cannot be overstated in these restoration efforts.
The spill prompted widespread discussions on oil drilling safety and regulations. In the wake of such a disaster, it is imperative to reflect on the lessons learned. Stricter regulations, improved safety protocols, and a renewed focus on environmental stewardship have emerged as critical components to prevent future disasters. The Deepwater Horizon spill serves as a cautionary tale, emphasizing the need for vigilance in the face of our reliance on fossil fuels.
The Deepwater Horizon disaster has sparked a critical examination of our reliance on fossil fuels. As we grapple with the implications for energy policy, the push towards renewable alternatives has gained momentum. The urgency to transition to sustainable energy sources is more pressing than ever, as we seek to avoid repeating the mistakes of the past. The future of our planet hinges on our ability to adapt and embrace cleaner, safer energy solutions.
- What caused the Deepwater Horizon oil spill?
The spill was caused by a combination of technical failures and managerial oversights, including inadequate safety measures and equipment failures. - How did the spill affect marine life?
The spill resulted in the death of numerous marine species and disrupted food chains, leading to long-term ecological consequences. - What efforts are being made to restore the affected areas?
Restoration efforts include habitat rehabilitation, economic support for affected communities, and ongoing research to monitor environmental recovery. - What lessons have been learned from the disaster?
The disaster highlighted the need for stricter safety regulations and a renewed focus on environmental stewardship in the oil industry. - How does the spill impact human health?
Local populations faced significant health risks due to exposure to toxic substances, leading to various health issues.

Causes of the Deepwater Horizon Spill
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill, which occurred on April 20, 2010, serves as a stark reminder of the vulnerabilities inherent in offshore drilling. Understanding the technical and managerial failures that led to this disaster is essential for grasping its catastrophic consequences. The incident was not merely a result of a single failure but rather a series of decisions and oversights that compounded over time, ultimately culminating in one of the worst environmental crises in history.
At the heart of this disaster was the blowout preventer, a critical safety device designed to seal off the well in the event of an emergency. Unfortunately, a combination of mechanical failures and human errors rendered this device ineffective. Investigations revealed that the blowout preventer had numerous issues, including faulty components and a lack of proper maintenance. This situation was exacerbated by the pressure to cut costs and expedite drilling operations, which led to a culture of neglect regarding safety protocols.
Moreover, the decisions made by BP and its partners were influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Cost-cutting measures: Companies often prioritize profits over safety, leading to inadequate risk assessments.
- Lack of oversight: Regulatory agencies failed to enforce existing safety standards, allowing companies to operate with minimal scrutiny.
- Inadequate training: Workers on the rig were not sufficiently trained to handle emergencies, which contributed to the chaos during the blowout.
These factors culminated in a tragic sequence of events that could have been prevented. As the rig was drilling into the Macondo Prospect, a series of miscalculations regarding pressure and cement integrity led to an explosion that claimed the lives of 11 crew members and resulted in the uncontrolled release of oil into the Gulf of Mexico. The situation was further aggravated by poor communication among the various stakeholders involved, which hindered effective response efforts in the critical moments following the blowout.
In addition to the immediate technical failures, the Deepwater Horizon spill raises questions about the broader implications of our reliance on fossil fuels. The disaster highlighted systemic issues within the oil industry, including the need for stricter regulations and improved safety measures. The fallout from this incident serves as a cautionary tale, reminding us that the pursuit of energy must be balanced with a commitment to environmental stewardship and public safety.
In conclusion, the causes of the Deepwater Horizon spill are a complex web of technical failures, human errors, and systemic issues within the oil industry. Understanding these causes is crucial for preventing future disasters and ensuring that our energy practices are both safe and sustainable.

Immediate Environmental Impact
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill, which occurred in April 2010, unleashed approximately 4.9 million barrels of crude oil into the Gulf of Mexico. This catastrophic event caused an immediate and devastating impact on the marine environment, affecting everything from the tiniest plankton to the majestic dolphins swimming in the Gulf's waters. The sheer volume of oil released created a slick that spread across vast distances, leading to a complex web of ecological consequences that are still being felt today.
One of the most alarming aspects of the spill was its effect on the marine ecosystems. The Gulf of Mexico is home to a rich diversity of life, including sensitive habitats such as coral reefs, seagrass beds, and marshlands. The oil infiltrated these habitats, coating marine organisms and disrupting their natural behaviors. For instance, fish and shellfish experienced acute toxicity from the oil, leading to immediate mortality and long-term health issues.
The spill's impact on marine life was profound and multifaceted. Various species, including sea turtles, marine mammals, and numerous fish species, faced immediate threats. The oil not only suffocated marine organisms but also contaminated their food sources, leading to a ripple effect throughout the food chain. For example, the oil's toxic components affected the reproductive systems of fish, leading to decreased populations over time.
The fishing industry, a vital part of the Gulf's economy, was severely disrupted. Fishermen found their livelihoods jeopardized as waters became polluted and fishing areas were closed to prevent contaminated catches from entering the market. The economic ramifications were staggering, with local communities facing job losses and decreased income. According to estimates, the fishing industry suffered losses of around $2.5 billion, which underscores the spill's far-reaching consequences.
Coastal habitats, such as marshes and mangroves, were not spared from the disaster's wrath. These ecosystems serve as critical buffers against storms and provide essential services, including water filtration and habitat for wildlife. The oil coated the vegetation, leading to die-offs and a decline in plant health. The long-term effects on these habitats are concerning, as they play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting biodiversity.
In addition to the environmental toll, the spill raised significant health concerns for local populations. Workers involved in cleanup efforts faced exposure to toxic substances, while residents living near the coast reported respiratory issues and other health problems. The psychological impact of the disaster also cannot be ignored, as communities grappled with the loss of their livelihoods and the threat to their environment.
In conclusion, the immediate environmental impact of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill was catastrophic, affecting marine life, coastal ecosystems, and human health. The consequences of this disaster serve as a stark reminder of the fragility of our environment and the urgent need for responsible stewardship of our natural resources.
- What caused the Deepwater Horizon oil spill?
The spill was caused by a blowout during drilling operations, leading to a catastrophic explosion and the release of millions of barrels of oil into the Gulf of Mexico. - How long did the oil spill last?
The spill continued for 87 days, from April 20 to July 15, 2010, before the well was successfully capped. - What were the long-term effects of the spill on marine life?
Many species experienced population declines, reproductive issues, and long-term health problems due to exposure to oil and its toxic components. - Are the ecosystems in the Gulf of Mexico recovering?
While some areas have shown signs of recovery, many ecosystems are still struggling, and restoration efforts are ongoing.

Impact on Marine Life
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill unleashed a wave of devastation upon marine life, creating a ripple effect that would be felt for years to come. Imagine a vibrant underwater world, teeming with life, suddenly engulfed in a thick, toxic blanket of oil. This catastrophic event did not just affect the immediate vicinity of the spill; it sent shockwaves through the entire Gulf of Mexico ecosystem. The impact on marine life was both immediate and profound, affecting everything from the smallest plankton to the largest marine mammals.
One of the most alarming consequences of the spill was the direct harm to fish populations. Species such as redfish, tuna, and mackerel faced significant mortality rates due to the oil's toxicity. Fish are not just important for biodiversity; they are a crucial part of the food web. When fish populations decline, the entire ecosystem suffers. Moreover, the long-term exposure to oil can lead to genetic mutations and reproductive issues, further threatening the survival of these species.
Additionally, the spill had devastating effects on marine mammals and birds. Species like dolphins and sea turtles, which are already vulnerable, faced heightened risks. The oil contaminated their habitats and food sources, leading to increased mortality rates. For instance, the bottlenose dolphin population saw a marked increase in deaths, with many of the survivors suffering from illnesses linked to oil exposure. The effects on birds were equally dire, as oil-coated feathers lose their waterproofing, leading to hypothermia and death. Birds that rely on the coastal habitats for nesting and feeding were also significantly impacted.
To illustrate the extent of the damage, consider the following table that summarizes the impact on various marine species:
| Marine Species | Immediate Impact | Long-term Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Fish (e.g., Redfish, Tuna) | Increased mortality rates | Genetic mutations, reproductive issues |
| Dolphins | Heightened mortality, illness | Population decline, long-term health issues |
| Sea Turtles | Habitat contamination | Decreased nesting success, population threats |
| Birds (e.g., Pelicans) | Feather contamination, hypothermia | Nesting failures, population decline |
The complex interdependencies within marine ecosystems mean that the effects of the oil spill extend far beyond the immediate casualties. For instance, the decline of fish populations affects not only the species that prey on them but also the fishermen who rely on these fish for their livelihoods. The ripple effect is a stark reminder of how interconnected our ecosystems are and how a single event can disrupt the delicate balance of life.
In conclusion, the Deepwater Horizon oil spill serves as a grim reminder of the fragility of marine ecosystems. The impacts on marine life are a clarion call for better environmental stewardship and a reevaluation of our relationship with fossil fuels. As we continue to grapple with the aftermath of this disaster, it is essential to remember that the health of our oceans is inextricably linked to the health of our planet.
- What caused the Deepwater Horizon oil spill? The spill was primarily caused by a blowout during drilling operations, leading to the release of millions of barrels of oil into the Gulf of Mexico.
- How did the spill affect marine life? The spill caused immediate harm to fish, marine mammals, and birds, leading to increased mortality rates and long-term ecological consequences.
- What are the ongoing recovery efforts? Restoration efforts include habitat rehabilitation, monitoring of affected species, and community support initiatives to help local economies recover.
- What lessons have been learned from the disaster? The spill highlighted the need for stricter safety regulations in oil drilling and a critical reevaluation of our reliance on fossil fuels.

Effects on Fisheries
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill unleashed a wave of devastation that rippled through the fishing industry in the Gulf of Mexico. Imagine waking up one day to find your livelihood in jeopardy, your nets empty, and your waters tainted. For many local fishermen and their families, this was not just a nightmare—it was a harsh reality. The spill contaminated vast stretches of water, leading to immediate closures of fishing areas and creating a significant economic burden on communities that relied heavily on this industry.
In the immediate aftermath, the closure of fishing grounds was one of the most drastic measures taken to safeguard public health and the environment. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) reported that over 88,000 square miles of ocean were closed to fishing at the height of the crisis. This not only affected the availability of seafood but also disrupted the intricate web of life that thrives in these waters.
The impact on fisheries can be broken down into several key areas:
- Decline in Fish Populations: The toxic substances released into the water created an unfavorable environment for many fish species. Studies indicated a significant decline in populations of commercially important species such as shrimp, oysters, and blue crabs.
- Contamination of Seafood: Concerns over the safety of seafood led to extensive testing and monitoring. Many consumers hesitated to purchase seafood from the Gulf, fearing contamination, which further exacerbated the economic struggles of local fishermen.
- Long-Term Ecological Effects: The spill disrupted breeding cycles and habitats, leading to long-term declines in fish stocks. The ripple effects of this disruption can take years, if not decades, to fully understand.
Moreover, the economic ramifications were staggering. In 2010 alone, the fishing industry in the Gulf suffered losses estimated at around $2.5 billion. Fishermen faced not only immediate income loss but also long-term uncertainties about the viability of their businesses. Many were forced to seek alternative employment or leave the industry altogether, leading to a loss of traditional knowledge and skills that had been passed down through generations.
As recovery efforts began, the focus shifted towards not just restoring fish populations but also rebuilding the fishing communities that had been devastated. Initiatives were launched to provide financial assistance to affected fishermen, and efforts were made to monitor and rehabilitate fish habitats. However, the road to recovery is long and fraught with challenges, as the scars of the spill remain evident in both the ecosystem and the economy.
In conclusion, the effects of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill on fisheries serve as a stark reminder of the fragility of our marine ecosystems and the communities that depend on them. The incident not only highlighted the immediate consequences of environmental disasters but also underscored the importance of sustainable practices and responsible stewardship of our natural resources.
- What caused the Deepwater Horizon oil spill? The spill was primarily caused by a blowout during drilling operations, which led to the release of millions of barrels of oil into the Gulf of Mexico.
- How did the spill affect local fisheries? The spill led to the closure of fishing areas, a decline in fish populations, and economic losses for local fishermen.
- Are seafood from the Gulf safe to eat now? Extensive testing has been conducted to ensure seafood safety, but caution is still advised, especially in areas heavily impacted by the spill.

Impact on Coastal Habitats
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill unleashed a wave of devastation across the coastal habitats of the Gulf of Mexico, impacting ecosystems that are vital to both wildlife and local communities. Imagine a vibrant tapestry of marshes, mangroves, and wetlands, each thread representing a unique species and its role in the ecosystem. The spill disrupted this intricate web, leaving behind a stark reminder of our vulnerability to environmental disasters. The immediate effects were catastrophic; oil slicks coated the shores, smothering plants and choking the life out of these crucial habitats.
Coastal ecosystems serve as protective buffers against storms and erosion, and they provide critical nurseries for many marine species. However, the oil spill altered the delicate balance of these environments. For instance, marshes, which are often the first line of defense against storm surges, became inundated with toxic substances. The oil penetrated the soil, affecting not just the surface but also the root systems of grasses and other vegetation that thrive in these areas. This led to a decline in plant health, which in turn affected the species that rely on these plants for food and shelter.
Furthermore, the impact on mangroves was equally alarming. These trees, which thrive in brackish waters, play a crucial role in stabilizing coastlines and providing habitat for various marine animals. The oil contamination led to a decline in mangrove health, reducing their ability to support biodiversity. Affected areas saw a decrease in the populations of birds, fish, and other wildlife that depend on these habitats. As a result, the food chain was disrupted, leading to broader implications for the entire ecosystem.
To illustrate the extent of the damage, consider the following table that summarizes the key impacts on coastal habitats:
| Habitat Type | Impact | Long-term Effects |
|---|---|---|
| Marshes | Oil contamination, reduced plant health | Loss of biodiversity, increased erosion |
| Mangroves | Decline in tree health, habitat loss | Reduced wildlife populations, compromised coastal protection |
| Wetlands | Inundation with oil, habitat degradation | Altered water quality, diminished ecosystem services |
In addition to the ecological damage, the spill had significant socio-economic repercussions for communities that depend on these habitats for their livelihoods. Fishermen and local businesses faced a steep decline in resources as fish populations dwindled and tourism suffered due to the negative perception of the affected areas. The loss of these habitats not only affected the local economy but also diminished the cultural and recreational value of the Gulf Coast.
In conclusion, the impact of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill on coastal habitats is a stark reminder of the fragility of our ecosystems. The long-term recovery of these environments will require sustained efforts and a commitment to restoring not just the physical landscape but also the intricate relationships that define these vital ecosystems.
- What caused the Deepwater Horizon oil spill? The spill was primarily caused by a blowout during drilling operations, which led to a catastrophic failure of the rig.
- How did the oil spill affect local wildlife? The spill had severe impacts on various marine species, leading to declines in populations and disrupted food chains.
- What are the long-term effects on coastal habitats? Long-term effects include habitat degradation, loss of biodiversity, and increased vulnerability to storms and erosion.
- What restoration efforts are being implemented? Restoration efforts include habitat rehabilitation, water quality monitoring, and community support initiatives to recover from the spill's impacts.

Human Health Concerns
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill, which occurred in April 2010, was not just an environmental disaster; it was also a profound human health crisis. As millions of gallons of crude oil gushed into the Gulf of Mexico, the immediate and long-term health implications for local communities became a pressing concern. Residents, fishermen, and cleanup workers were exposed to a cocktail of toxic substances, leading to a myriad of health issues that raised alarms across the region.
One of the most alarming aspects of the spill was the exposure to volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are released during the oil extraction and refining processes. These compounds can lead to serious health problems, including:
- Respiratory Issues: Many individuals reported respiratory symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath, which were exacerbated by inhaling fumes from the oil and dispersants used in cleanup efforts.
- Neurological Effects: Prolonged exposure to toxic chemicals can lead to neurological issues, including headaches, dizziness, and cognitive impairments.
- Skin Irritations: Direct contact with oil and dispersants resulted in skin rashes and other dermatological conditions among cleanup workers and residents.
Moreover, the psychological impact of the disaster cannot be overlooked. The fear of contamination and the uncertainty about the long-term effects on health created a climate of anxiety and stress among the affected populations. Many residents experienced symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), as the spill disrupted their lives and livelihoods. The fishing industry, a cornerstone of the local economy, faced uncertainties that left families in financial distress, further compounding mental health issues.
In the aftermath of the spill, health studies were initiated to assess the impacts on the local population. The findings were concerning. Research indicated an increase in reports of chronic illnesses, including respiratory diseases and mental health disorders. Furthermore, the long-term consequences of exposure to oil and its components are still being studied, as scientists seek to understand the full scope of health risks associated with such environmental disasters.
As cleanup operations progressed, health monitoring programs were established to track the health of workers and residents. These programs aimed to provide medical assistance and information about potential health risks, emphasizing the importance of ongoing health surveillance in the wake of such disasters. The need for comprehensive health strategies and support systems became evident as communities grappled with the aftermath of the spill.
In conclusion, the Deepwater Horizon oil spill serves as a stark reminder of the interconnectedness of environmental health and human health. As we continue to depend on fossil fuels, it is crucial to prioritize safety measures and health monitoring to protect vulnerable populations from the adverse effects of oil spills and other environmental catastrophes.
- What were the main health concerns after the Deepwater Horizon oil spill?
The main health concerns included respiratory issues, neurological effects, skin irritations, and psychological impacts such as PTSD. - How did the spill affect local communities' mental health?
The spill caused significant anxiety and stress among residents due to fears of contamination and economic instability, leading to increased reports of mental health disorders. - Are there ongoing health studies related to the spill?
Yes, health studies are still being conducted to understand the long-term effects of exposure to oil and its components on local populations.

Long-term Environmental Consequences
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill was not just a fleeting disaster; it has left a profound and lasting impact on the environment that continues to be felt today. While the immediate effects were devastating, the long-term consequences have proven to be equally, if not more, alarming. The ecosystems that once thrived in the Gulf of Mexico now face a myriad of challenges that threaten their survival. This section aims to dissect these ongoing ecological issues, highlighting the resilience of nature while acknowledging the scars left behind by this catastrophic event.
One of the most significant long-term consequences of the spill is the disruption of biodiversity. Marine species, including fish, sea turtles, and various bird populations, have struggled to recover from the initial shock of the spill. The oil not only contaminated their habitats but also introduced toxic substances into the food chain. For instance, studies have shown that certain fish species, such as redfish and mackerel, have experienced deformities and decreased populations due to prolonged exposure to oil and chemical dispersants used during cleanup efforts. This has raised concerns about the overall health of marine ecosystems, as these species play crucial roles in maintaining the balance of marine life.
Furthermore, the spill has had a devastating impact on fisheries. The fishing industry, a vital part of the Gulf's economy, has faced severe disruptions. Many fishing grounds were closed immediately after the spill, leading to significant economic losses for local fishermen and communities. Even years later, the stigma associated with contaminated seafood has made it difficult for the industry to recover fully. The long-term effects on fish populations mean that not only are fishermen affected, but entire communities that rely on these resources for their livelihoods are at risk. The following table illustrates the economic impact on key fish species in the Gulf region post-spill:
| Fish Species | Population Decline (%) | Economic Impact (Million $) |
|---|---|---|
| Redfish | 30% | 150 |
| Mackerel | 25% | 100 |
| Grouper | 40% | 200 |
In addition to the impact on marine life and fisheries, the spill has wreaked havoc on coastal habitats. Critical ecosystems such as marshes and mangroves, which serve as natural barriers against storms and provide essential breeding grounds for various species, have suffered extensive damage. The oil infiltrated these delicate environments, leading to a decline in plant life and the species that depend on them. The loss of these habitats not only affects wildlife but also increases the vulnerability of coastlines to erosion and storm surges, posing a significant risk to human settlements along the Gulf.
Moreover, the health of local populations has been a growing concern. The spill raised significant health issues for those living in proximity to the affected areas. Residents and workers exposed to the toxic substances released during the spill have reported a range of health problems, including respiratory issues, skin ailments, and psychological effects stemming from the disaster's aftermath. The long-term health repercussions are still being studied, but the initial findings paint a concerning picture of the spill's impact on human health.
As we reflect on the long-term environmental consequences of the Deepwater Horizon disaster, it becomes clear that recovery is a complex and ongoing process. Efforts to restore affected ecosystems are underway, but the road to healing is long and fraught with challenges. The resilience of nature is remarkable, yet the scars left by this catastrophe serve as a stark reminder of the fragility of our environment and the importance of responsible stewardship.
- What caused the Deepwater Horizon oil spill? The spill was primarily caused by a blowout during drilling operations, leading to the release of millions of barrels of oil into the Gulf of Mexico.
- How has the spill affected marine life? The spill has resulted in population declines, deformities, and long-term health issues for various marine species.
- What are the ongoing recovery efforts? Restoration initiatives include habitat rehabilitation, monitoring of wildlife populations, and support for affected communities.
- What lessons have been learned from the disaster? The spill highlighted the need for improved safety regulations and practices in the oil industry to prevent future disasters.
Restoration Efforts
The aftermath of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill was not just a wake-up call; it was a clarion call for action. Communities, scientists, and environmentalists rallied together to address the extensive damage inflicted on the Gulf Coast. Restoration efforts have been ongoing and multifaceted, aiming not only to rehabilitate the affected ecosystems but also to restore the livelihoods of those who depend on them. The complexity of these initiatives is akin to piecing together a massive jigsaw puzzle, where each piece represents a different aspect of recovery.
One of the primary focuses of the restoration efforts has been on the rehabilitation of marine and coastal habitats. This includes initiatives to restore critical ecosystems such as marshes, mangroves, and seagrasses, which play vital roles in protecting shorelines and providing habitats for countless species. For instance, organizations like the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and various local NGOs have been instrumental in implementing restoration projects that aim to enhance the resilience of these ecosystems to future environmental stressors.
Furthermore, the restoration efforts are not limited to ecological aspects alone; they also encompass community engagement and economic recovery. The fishing industry, which suffered immensely due to the spill, has seen initiatives aimed at revitalizing local fisheries. This includes:
- Restoration of fish populations through hatchery programs.
- Implementation of sustainable fishing practices.
- Support for local fishermen through grants and training programs.
In addition to these measures, a significant portion of the restoration funding has been directed toward scientific research and monitoring. Understanding the long-term impacts of the oil spill on marine life is crucial for informing future conservation strategies. Scientists have been conducting extensive studies to track the recovery of various species and to assess the overall health of the Gulf ecosystem. This ongoing research is vital, as it not only sheds light on the current state of the environment but also helps to guide future restoration efforts.
Moreover, the restoration initiatives are backed by a robust framework of legislation and funding. The RESTORE Act, enacted in 2012, allocates 80% of the penalties from the spill to Gulf Coast restoration projects. This has resulted in billions of dollars being invested in various restoration programs, highlighting a commitment to healing the wounds inflicted by the disaster.
However, the journey to recovery is far from over. The restoration efforts are a marathon, not a sprint. It requires continuous collaboration among various stakeholders, including government agencies, non-profits, and local communities. As we look to the future, it’s essential to recognize that the lessons learned from the Deepwater Horizon spill can guide us in creating a more sustainable and resilient environment. The commitment to restoration is not just about fixing what was broken; it’s about building a better future for both the ecosystem and the communities that rely on it.
- What are the main goals of the restoration efforts following the Deepwater Horizon spill?
The main goals include rehabilitating damaged ecosystems, supporting local communities, and ensuring the long-term recovery of marine life and habitats. - How is the restoration funded?
Funding primarily comes from penalties imposed under the RESTORE Act, which allocates a significant portion of the fines from the spill to Gulf Coast restoration projects. - Are local communities involved in the restoration process?
Yes, local communities play a crucial role in the restoration process, participating in decision-making and benefiting from initiatives aimed at economic recovery. - What types of habitats are being restored?
Key habitats being restored include marshes, mangroves, and seagrasses, which are vital for marine biodiversity and coastal protection.

Lessons Learned
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill was not just a tragic event; it was a wake-up call for the entire oil industry and environmental regulators. The magnitude of this disaster highlighted serious flaws in safety protocols and regulatory oversight. It’s almost like a movie where the protagonist ignores the warnings until it’s too late. So, what exactly did we learn from this catastrophe? Let’s explore the key takeaways that emerged from the ashes of this environmental tragedy.
First and foremost, the spill underscored the importance of rigorous safety standards. Before the disaster, many companies operated under a false sense of security, believing that their safety measures were foolproof. However, the reality is that even the most advanced technologies can fail if not properly managed. This led to a renewed emphasis on creating and enforcing stricter safety regulations. Companies are now required to conduct more thorough risk assessments and ensure that all safety protocols are not just in place, but actively practiced.
Moreover, the spill revealed the need for greater transparency in the oil industry. In the past, companies often kept their safety records and operational practices under wraps, which made it difficult for regulators and the public to hold them accountable. Now, there’s a growing demand for openness. Stakeholders, including local communities, want to know what companies are doing to minimize risks and protect the environment. This shift towards transparency has led to the implementation of mandatory reporting on safety measures and environmental impacts.
Another significant lesson was the importance of emergency preparedness. The response to the Deepwater Horizon spill was criticized for being slow and inadequate. This has prompted the industry to rethink its emergency response strategies. Companies are now investing in better training programs for their personnel and developing more effective contingency plans. They are also collaborating with local and federal agencies to ensure that everyone involved knows their roles in case of an emergency. The goal is to create a well-oiled machine that can respond quickly and efficiently to future spills.
Furthermore, the disaster raised questions about corporate responsibility. Many people began to wonder whether oil companies should be held accountable not just for the immediate impacts of spills but also for the long-term environmental damage they cause. This has sparked discussions about environmental liability and the need for companies to invest in sustainable practices. It’s no longer enough to simply clean up after a disaster; companies are now expected to take proactive steps to prevent future spills and mitigate their environmental impact.
In essence, the Deepwater Horizon spill served as a catalyst for change in the oil industry. It forced stakeholders to confront uncomfortable truths about safety, transparency, and corporate responsibility. While we can’t undo the damage that was done, we can certainly learn from it and strive to create a safer, more sustainable future. The lessons learned from this tragedy are crucial not just for the oil industry, but for all sectors that impact our environment.
- What were the primary causes of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill?
The spill was primarily caused by a blowout during drilling operations, which was exacerbated by a series of technical and managerial failures. - How did the oil spill impact marine life?
The spill had devastating effects on marine ecosystems, leading to declines in fish populations, bird mortality, and long-term disruptions to food chains. - What measures have been taken to prevent future oil spills?
Increased safety regulations, mandatory reporting, and improved emergency preparedness have been implemented to reduce the risk of future disasters. - What role does corporate responsibility play in the oil industry?
Corporate responsibility is now a critical factor, with companies expected to not only respond to spills but also take proactive measures to protect the environment.

The Future of Oil Dependency
The Deepwater Horizon disaster has not only left an indelible mark on our environment but has also ignited a crucial conversation about our dependency on fossil fuels. As we stand at a crossroads, it’s essential to examine the implications of our current energy policies and the urgent need for a shift towards more sustainable alternatives. The question looms large: can we break free from our oil addiction, or are we doomed to repeat the mistakes of the past?
Our reliance on oil is akin to a double-edged sword. On one side, it fuels our economies and powers our daily lives, but on the other, it poses significant risks to our planet and health. The catastrophic spill in the Gulf of Mexico serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences of our fossil fuel dependency. It’s as if we’ve been playing with fire, and now we’re left to reckon with the ashes. The future demands that we explore renewable energy sources and rethink our energy strategies.
As we delve into the alternatives, we find a plethora of options that could pave the way for a greener future. Renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power are not just buzzwords; they are viable solutions that can significantly reduce our carbon footprint. For instance, consider the following benefits of transitioning to renewable energy:
- Environmental Protection: Reducing greenhouse gas emissions and minimizing ecological disasters.
- Energy Independence: Decreasing reliance on foreign oil and boosting local economies.
- Sustainable Jobs: Creating new employment opportunities in the green energy sector.
Moreover, the global push towards sustainability is gaining momentum. Countries around the world are setting ambitious targets to reduce carbon emissions and invest in clean energy technologies. For example, the European Union aims to become climate-neutral by 2050, while the United States has rejoined the Paris Agreement, signaling a renewed commitment to combating climate change. These initiatives reflect a growing recognition that the status quo is no longer acceptable.
However, transitioning from oil dependency is not without its challenges. The infrastructure required for renewable energy production and distribution needs significant investment and time to develop. Furthermore, vested interests in the fossil fuel industry often resist change, fearing economic repercussions. It’s a complex web of politics, economics, and environmental ethics that we must navigate carefully. The key lies in fostering collaboration between governments, businesses, and communities to create a unified front for change.
In conclusion, the future of oil dependency is at a pivotal point. The Deepwater Horizon oil spill serves as a wake-up call, urging us to reconsider our energy choices and their implications for future generations. As we shift our focus towards sustainable alternatives, we must remain vigilant in our efforts to protect our planet and ensure a healthier, more resilient future. It's not just about avoiding disasters but actively working towards a world where energy is clean, abundant, and accessible to all.
Q1: What are the main alternatives to oil?
A1: The main alternatives include solar energy, wind energy, hydroelectric power, and geothermal energy. Each of these sources has its unique advantages and can contribute to reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.
Q2: How can individuals contribute to reducing oil dependency?
A2: Individuals can contribute by using public transportation, carpooling, adopting energy-efficient appliances, and supporting renewable energy initiatives in their communities.
Q3: What are the economic impacts of transitioning to renewable energy?
A3: Transitioning to renewable energy can lead to job creation in new sectors, reduce energy costs over time, and decrease reliance on imported fuels, ultimately benefiting local economies.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What caused the Deepwater Horizon oil spill?
The Deepwater Horizon oil spill was primarily caused by a series of technical and managerial failures. These included poor decision-making, inadequate safety measures, and a lack of proper oversight. The blowout preventer, a critical safety device, failed to function as intended, leading to the catastrophic blowout.
- What were the immediate environmental impacts of the spill?
The immediate aftermath of the spill was devastating, causing extensive damage to marine ecosystems. Thousands of marine animals, including fish and birds, were affected. The spill released millions of barrels of oil into the Gulf of Mexico, disrupting the delicate balance of the region's habitats.
- How did the spill affect marine life?
The spill had both short-term and long-term consequences for marine life. Many species experienced immediate mortality, while others suffered from chronic health issues due to prolonged exposure to toxins. The spill disrupted food chains, affecting not just individual species but entire ecosystems.
- What impact did the spill have on local fisheries?
Local fisheries faced severe disruptions due to contamination from the spill. Many fishing areas were closed, leading to significant economic losses for fishing communities. The long-term health of fish populations and the overall fishing industry was jeopardized, creating ongoing challenges for recovery.
- Were there any human health concerns related to the spill?
Yes, the spill raised significant health concerns for local populations. Workers involved in the cleanup and residents living near the coast were exposed to toxic substances, leading to potential health risks. Ongoing monitoring and health studies have been essential in addressing these concerns.
- What are the long-term environmental consequences of the spill?
The Deepwater Horizon spill left lasting scars on the environment. Many ecosystems continue to face challenges in recovery, with ongoing issues related to species population declines and habitat degradation. Restoration efforts are crucial to mitigate these long-term impacts.
- What restoration efforts have been implemented?
Restoration efforts include various initiatives aimed at rehabilitating affected ecosystems and supporting local communities. These efforts focus on habitat restoration, species recovery programs, and monitoring to ensure the health of marine and coastal environments.
- What lessons were learned from the Deepwater Horizon disaster?
The spill prompted a reevaluation of oil drilling safety and regulations. Key lessons include the importance of rigorous safety protocols, better risk management practices, and the need for enhanced regulatory oversight to prevent similar disasters in the future.
- How has the spill influenced discussions about oil dependency?
The Deepwater Horizon disaster sparked critical conversations about our reliance on fossil fuels. It has encouraged policymakers and the public to consider renewable energy alternatives and the importance of sustainability in energy policy moving forward.



















