Land Management and Its Impact on Biodiversity
Land management is not just a technical term thrown around in environmental circles; it’s a crucial aspect of how we interact with our planet. Picture this: every time we decide how to use the land—be it for agriculture, urban development, or conservation—we are making choices that ripple through ecosystems, affecting countless species and the very fabric of biodiversity itself. The choices we make today will shape the world of tomorrow, and understanding the profound relationship between land management practices and biodiversity is essential for creating a sustainable future.
Biodiversity, which refers to the variety of life on Earth, is like a complex web, where each strand is interconnected. It provides essential services such as pollination, water purification, and climate regulation. When we lose biodiversity, we not only harm the environment but also jeopardize our own well-being. Hence, the way we manage land is pivotal. It’s not just about maximizing yields or urban sprawl; it’s about finding a balance where both human needs and ecological health can thrive together.
Now, let’s dive deeper into the types of land management practices that are out there. From sustainable agriculture to forestry management and urban planning, each practice has its unique impacts on biodiversity. Understanding these impacts allows us to identify opportunities for improvement. For instance, sustainable agricultural practices can minimize chemical use, preserve natural habitats, and enhance soil health. Techniques like crop rotation and agroforestry can foster a more balanced ecosystem. Imagine a farm where crops are rotated seasonally to prevent soil depletion and pests, allowing the land to rejuvenate and support a variety of plant and animal life.
In the realm of forestry, sustainable logging and reforestation efforts can significantly influence forest biodiversity. When trees are harvested responsibly and new ones are planted, we can maintain the delicate balance of forest ecosystems, providing habitats for wildlife while still meeting human demands for timber and other resources. This dual approach not only helps in preserving biodiversity but also ensures that forests can continue to provide vital ecosystem services for generations to come.
Urban land management presents its own set of challenges. As cities expand, they often encroach on natural habitats, threatening local biodiversity. However, by incorporating green spaces and wildlife corridors into urban planning, we can create environments that support both human life and local ecosystems. Think of parks, green roofs, and urban forests as urban oases—places where nature can flourish amidst concrete and steel. These green infrastructures not only enhance biodiversity but also improve the quality of life for city dwellers, offering recreational spaces and cleaner air.
Community involvement is another key component of effective land management. When local communities engage in decision-making processes, they foster a sense of stewardship and responsibility towards their environment. Collaborative initiatives can lead to innovative solutions that benefit both people and nature. For example, community-led conservation projects can help restore degraded lands, create wildlife habitats, and promote sustainable practices that align with local needs.
In conclusion, the relationship between land management and biodiversity is intricate and profound. By adopting sustainable practices across various sectors—agriculture, forestry, and urban planning—we can enhance ecological health while meeting human needs. It’s a delicate balance, but one that is absolutely necessary for a thriving planet. After all, our well-being is intricately tied to the health of our ecosystems.
- What is biodiversity? Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including the diversity of species, ecosystems, and genetic variations within species.
- Why is biodiversity important? Biodiversity is crucial for ecosystem resilience, providing essential services like pollination, water purification, and climate regulation.
- How can land management practices affect biodiversity? Different land management practices, such as agriculture and urban planning, can either harm or enhance biodiversity depending on how they are implemented.
- What are some sustainable land management practices? Sustainable agriculture, forestry management, and the incorporation of green spaces in urban planning are examples of practices that can promote biodiversity.
- How can communities get involved in land management? Communities can engage in land management by participating in decision-making processes, initiating conservation projects, and promoting sustainable practices locally.

The Importance of Biodiversity
Biodiversity is often described as the variety of life on Earth, encompassing the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms, as well as the ecosystems they form. It plays a critical role in maintaining the health of our planet. Imagine a grand orchestra where each instrument plays a unique part; if one instrument goes silent, the harmony is disrupted. Similarly, when biodiversity is lost, the delicate balance of our ecosystems is thrown off, leading to consequences that can affect us all.
Why is biodiversity so important, you ask? Well, it provides a multitude of ecosystem services that are vital for human survival and well-being. Here are some key services that biodiversity offers:
- Pollination: Many crops depend on pollinators like bees and butterflies. Without them, our food supply would dwindle.
- Water Purification: Diverse ecosystems, such as wetlands, filter pollutants and help maintain clean water sources.
- Climate Regulation: Forests and oceans play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide, helping to mitigate climate change.
- Soil Fertility: A rich variety of organisms contributes to soil health, enhancing its ability to support plant life.
- Medicinal Resources: Many modern medicines are derived from natural compounds found in diverse species.
Understanding these essential services helps frame the conversation around land management and conservation efforts. Biodiversity is not just a luxury; it is a necessity for our survival. The loss of biodiversity can lead to a cascade of negative effects, including increased vulnerability to natural disasters, reduced resilience to climate change, and the potential collapse of food systems. Just as a chain is only as strong as its weakest link, our ecosystems are only as resilient as their biodiversity.
Moreover, biodiversity contributes to cultural and recreational values. Many communities around the world derive their identity and livelihoods from the natural world. From ecotourism to traditional practices, these connections highlight the intrinsic value of preserving diverse ecosystems. When we protect biodiversity, we are not only safeguarding the environment; we are also preserving cultural heritage and ensuring that future generations can enjoy the beauty and benefits of nature.
In summary, the importance of biodiversity cannot be overstated. It is the backbone of our ecosystems, providing essential services that sustain life on Earth. As we navigate the challenges of land management, recognizing and enhancing biodiversity should be at the forefront of our efforts. By doing so, we can create a sustainable future that benefits both people and the planet.
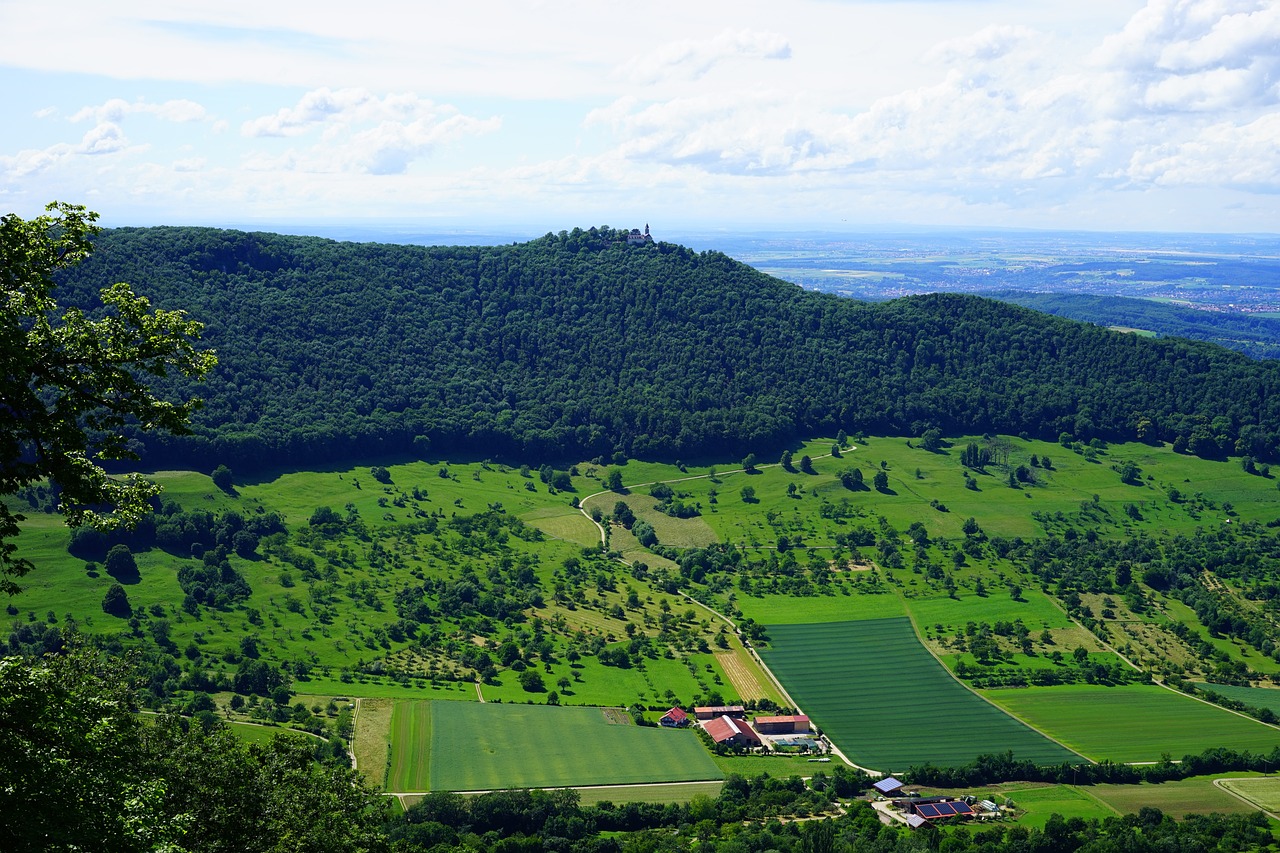

Types of Land Management Practices
When we think about land management practices, it's essential to recognize that these methods can either nurture or hinder biodiversity. Different practices have unique impacts, and understanding these can help us make informed decisions that benefit both the environment and human needs. For instance, agriculture, forestry, and urban planning each come with their own sets of challenges and opportunities. By analyzing these practices, we can uncover ways to improve them and promote sustainable development.
In the realm of agriculture, traditional methods often lead to soil degradation and habitat loss. However, innovative approaches like sustainable agriculture are emerging. These practices aim to minimize chemical usage, preserve natural habitats, and enhance soil health. Techniques such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and agroforestry are not just buzzwords; they represent a shift towards a more balanced ecosystem. Imagine a farm where diverse crops flourish alongside natural vegetation, creating a vibrant tapestry of life rather than a monoculture desert.
Similarly, forestry management plays a pivotal role in maintaining biodiversity. Unsustainable logging practices can devastate forest ecosystems, leading to the extinction of species and the disruption of ecological processes. However, sustainable logging and reforestation efforts can help maintain ecosystem services while providing timber and other resources. It's like a delicate dance where every step must be carefully considered to ensure that both nature and industry can thrive together.
Urban areas present a unique challenge for biodiversity. With rapid urbanization, many natural habitats are lost, leading to a decline in wildlife. But fear not! Effective land management strategies can mitigate these impacts. For example, incorporating green spaces and wildlife corridors into urban planning can create vital habitats for various species. Think of cities as bustling ecosystems where parks and green roofs serve as oases of life amidst concrete jungles.
Moreover, the concept of green infrastructure is gaining traction in urban land management. By integrating natural elements into cityscapes, we can enhance biodiversity while improving the quality of life for residents. Parks, urban forests, and green roofs not only provide habitats but also offer recreational spaces for people. It’s a win-win situation where nature and urban living coexist harmoniously.
Lastly, engaging local communities in land management decisions is crucial. When communities are involved, they become stewards of their environment, fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility. Collaborative initiatives can lead to innovative solutions that benefit both people and nature. After all, who knows the land better than those who live on it? By working together, we can create a sustainable future that respects both human needs and ecological health.
- What is sustainable agriculture? Sustainable agriculture focuses on producing food while minimizing environmental impact, preserving resources for future generations.
- How does urbanization affect biodiversity? Urbanization leads to habitat loss, pollution, and fragmentation, which can threaten various species and reduce biodiversity.
- What are green spaces? Green spaces are areas in urban environments that are covered with vegetation, such as parks, gardens, and green roofs, which support biodiversity and improve quality of life.
- Why is community involvement important in land management? Community involvement fosters stewardship, enhances conservation efforts, and leads to more effective and innovative land management solutions.

Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is like a symphony where every instrument plays its part to create a harmonious relationship between farming and the environment. It’s not just about growing food; it’s about nurturing the land, the ecosystem, and ultimately, our health. By adopting practices that are mindful of ecological balance, we can enhance biodiversity while still meeting the food demands of a growing population. Imagine a farm that not only produces crops but also serves as a habitat for various species—this is the essence of sustainable agriculture.
One of the key principles of sustainable agriculture is the reduction of chemical inputs. Traditional farming often relies heavily on synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which can lead to soil degradation, water contamination, and a decline in biodiversity. In contrast, sustainable practices prioritize natural alternatives that encourage a thriving ecosystem. For instance, farmers might use integrated pest management (IPM), which combines biological control methods with minimal chemical use, creating a healthier environment for both crops and wildlife.
Furthermore, sustainable agriculture emphasizes the importance of crop rotation and agroforestry. These techniques not only improve soil health but also promote a diverse range of plant and animal species. Crop rotation prevents soil depletion and reduces the risk of pest outbreaks, while agroforestry integrates trees into agricultural landscapes, providing shade, habitat, and additional resources. Together, these methods create a more balanced ecosystem that can withstand environmental stresses better than monoculture systems.
To illustrate the positive impact of sustainable agricultural practices, consider the following table that summarizes the benefits of these methods compared to conventional farming:
| Practice | Benefits | Impact on Biodiversity |
|---|---|---|
| Crop Rotation | Improves soil health, reduces pests | Encourages diverse plant species |
| Agroforestry | Enhances habitat, prevents erosion | Supports wildlife and plant diversity |
| Organic Farming | Reduces chemical exposure, promotes health | Encourages a variety of organisms |
In addition to these practices, sustainable agriculture also promotes community engagement. Farmers who collaborate with local communities can share knowledge, resources, and strategies that enhance biodiversity. This partnership not only strengthens local economies but also fosters a sense of stewardship for the land. When people feel connected to their food sources, they are more likely to support sustainable practices and advocate for policies that protect biodiversity.
In conclusion, sustainable agriculture stands as a beacon of hope in the quest to balance human needs with ecological health. By embracing practices that minimize harm and maximize benefits for both the environment and society, we can cultivate a future where biodiversity thrives alongside our agricultural systems. The journey may be challenging, but the rewards—healthier ecosystems, thriving communities, and abundant food—are well worth the effort.
- What is sustainable agriculture? Sustainable agriculture refers to farming practices that prioritize environmental health, economic profitability, and social equity.
- How does sustainable agriculture benefit biodiversity? It promotes diverse ecosystems by minimizing chemical inputs, enhancing soil health, and preserving habitats.
- What are some examples of sustainable agricultural practices? Examples include crop rotation, agroforestry, organic farming, and integrated pest management.
- Can sustainable agriculture feed the growing population? Yes, by implementing efficient practices and technologies, sustainable agriculture can meet food demands while protecting the environment.

Organic Farming
Organic farming is more than just a trend; it’s a revolution in how we approach agriculture. This method avoids synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which are notorious for harming not only the environment but also human health. Instead, organic farming relies on natural processes, promoting a diverse range of plant and animal species. Imagine a vibrant ecosystem where crops thrive alongside beneficial insects and wildlife; that’s the beauty of organic farming!
One of the key benefits of organic farming is its ability to enhance biodiversity. By fostering a variety of species, organic farms create a balanced ecosystem that is more resilient to pests and diseases. For instance, when farmers use crop rotation—a practice where different crops are planted in succession on the same land—they can naturally disrupt pest cycles and improve soil health. This not only leads to healthier crops but also minimizes the need for chemical interventions.
Moreover, organic farming practices often include techniques such as cover cropping and intercropping, which help maintain soil fertility and prevent erosion. Cover crops, like clover or rye, are planted during off-seasons to protect and enrich the soil, while intercropping involves growing two or more crops in proximity for mutual benefits. These practices create a symbiotic relationship between plants, enhancing biodiversity and contributing to a more sustainable agricultural system.
But the impact of organic farming goes beyond just the fields. It can also have significant positive effects on local communities. When farmers adopt organic methods, they often engage with their communities to promote sustainable practices, leading to a greater awareness of environmental issues. This community involvement not only strengthens local economies but also fosters a collective effort towards conservation and biodiversity preservation.
In summary, organic farming is a vital part of the solution to many environmental challenges we face today. By prioritizing biodiversity and sustainability, organic farmers are paving the way for a healthier planet. As consumers, supporting organic products can amplify this positive impact, encouraging more farmers to adopt these practices. So, the next time you reach for that organic apple, remember, you’re not just making a healthier choice for yourself; you’re also contributing to a more vibrant and biodiverse world!
- What is organic farming? Organic farming is an agricultural practice that avoids synthetic chemicals, focusing instead on natural processes to grow crops and raise livestock.
- How does organic farming benefit biodiversity? By promoting diverse plant and animal species, organic farming creates balanced ecosystems that are more resilient to pests and diseases.
- Can organic farming be profitable? Yes, many organic farms can be profitable due to the increasing demand for organic products and the premium prices they often command.
- What are some common organic farming practices? Common practices include crop rotation, cover cropping, intercropping, and the use of natural pest control methods.

Permaculture
Permaculture is more than just a farming method; it's a holistic approach to land management that seeks to create sustainable and self-sufficient agricultural ecosystems. Imagine a garden that works in harmony with nature, where each element supports the others in a delicate balance—this is the essence of permaculture. By mimicking natural ecosystems, permaculture promotes biodiversity and resilience, making it a powerful tool in the quest for sustainable land use.
At its core, permaculture is about observing and understanding the relationships within the environment. It encourages us to ask questions like, "How can we design our landscapes to work with nature rather than against it?" and "What can we learn from natural ecosystems that can be applied to our agricultural practices?" This mindset fosters a sense of stewardship and responsibility towards the land, leading to practices that enhance biodiversity.
One of the key principles of permaculture is the design of polycultures—growing multiple crops in the same space. This contrasts sharply with traditional monoculture farming, which often leads to soil depletion and increased vulnerability to pests and diseases. In a permaculture system, diverse plant species coexist, creating a more resilient ecosystem. For instance, planting nitrogen-fixing legumes alongside fruit trees not only improves soil health but also provides shade and habitat for beneficial insects.
Permaculture also emphasizes the importance of water management. Techniques such as swales, which are shallow channels designed to capture and retain water, help to minimize erosion and improve soil moisture. By slowing down and spreading out water flow, these systems promote healthy plant growth and reduce the need for irrigation. This is particularly crucial in areas prone to drought, where every drop of water counts.
Furthermore, permaculture practices often incorporate animal husbandry in a way that benefits both the animals and the land. Chickens, for example, can be integrated into a garden system to help control pests while providing natural fertilizer. This symbiotic relationship not only boosts productivity but also enhances the overall health of the ecosystem.
In summary, permaculture is a transformative approach to land management that champions biodiversity through thoughtful design and natural principles. By creating systems that are not only productive but also resilient, we can ensure that our agricultural practices contribute positively to the environment and future generations. It’s about creating a legacy of sustainability, where the land thrives alongside its caretakers.
- What is permaculture? Permaculture is a design philosophy that seeks to create sustainable and self-sufficient agricultural ecosystems by mimicking natural processes.
- How does permaculture promote biodiversity? By utilizing polycultures, water management techniques, and integrating animals into farming systems, permaculture enhances the variety of life within an ecosystem.
- Can permaculture be applied in urban areas? Yes! Permaculture principles can be adapted for urban gardening, rooftop gardens, and community green spaces, promoting biodiversity even in city environments.

Forestry Management
Forestry management is a critical component in the conversation about biodiversity. It encompasses a variety of practices that directly affect the health and diversity of forest ecosystems. When managed sustainably, forests can serve as vital habitats for countless species, while also providing essential resources for human use. However, the challenge lies in balancing the demand for timber and other forest products with the need to preserve these ecosystems. Unsustainable practices, such as clear-cutting and overharvesting, can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and a significant decline in biodiversity.
To ensure that forests continue to thrive, it's essential to adopt sustainable forestry practices. These can include selective logging, which minimizes the impact on the surrounding environment, and reforestation efforts that restore tree cover and promote biodiversity. For instance, when a tree is harvested, planting new trees of various species can help maintain the ecological balance and provide habitats for different wildlife. Additionally, implementing buffer zones around water bodies within forested areas can protect aquatic ecosystems and enhance overall biodiversity.
Moreover, the role of indigenous knowledge in forestry management cannot be overlooked. Many indigenous communities have developed sustainable practices over centuries, understanding the intricate relationships between species and their habitats. By incorporating this knowledge into modern forestry management, we can create a more holistic approach that respects both the environment and cultural heritage.
To illustrate the importance of sustainable forestry management, consider the following table that outlines the differences between traditional and sustainable practices:
| Aspect | Traditional Forestry Practices | Sustainable Forestry Practices |
|---|---|---|
| Logging Method | Clear-cutting | Selective logging |
| Impact on Biodiversity | High | Low |
| Soil Erosion | Increased | Minimized |
| Community Involvement | Low | High |
In conclusion, effective forestry management is not just about extracting resources; it's about fostering a sustainable relationship with our forests. By prioritizing practices that enhance biodiversity, we can ensure that these ecosystems continue to provide benefits for generations to come. This involves not only the implementation of sustainable practices but also a commitment to ongoing education and community engagement in forestry management decisions.
- What is sustainable forestry? Sustainable forestry refers to the management of forest resources in a way that maintains their biodiversity, productivity, and ecological processes while meeting current and future human needs.
- How does forestry management impact biodiversity? Forestry management practices can either harm or enhance biodiversity, depending on whether they are sustainable or exploitative. Sustainable practices help maintain habitats and ecosystem health.
- Can local communities contribute to forestry management? Yes, local communities play a crucial role in sustainable forestry management by sharing traditional knowledge and engaging in conservation efforts.

Urban Land Management
Urbanization is a double-edged sword; it brings economic growth and development, but it also poses significant challenges to biodiversity. As cities expand, natural habitats are often destroyed, leading to a decline in wildlife populations and ecosystem services. However, with thoughtful and effective land management strategies, we can mitigate these impacts and create urban environments that support both human needs and ecological health.
One of the key aspects of urban land management is the integration of green spaces into city planning. These areas, which include parks, gardens, and natural reserves, provide essential habitats for various species while also offering recreational spaces for residents. Imagine stepping out of your apartment and into a lush park filled with trees, flowers, and chirping birds—it’s not just a pleasant sight; it’s a vital component of urban biodiversity. Green spaces help to cool urban heat islands, improve air quality, and even reduce stormwater runoff, making cities more resilient to climate change.
Another innovative approach to urban land management is the creation of wildlife corridors. These are designated pathways that connect fragmented habitats, allowing animals to move freely and safely between different areas. Think of them as highways for wildlife! By incorporating these corridors into urban planning, we can help maintain genetic diversity among animal populations and reduce the risk of extinction for vulnerable species. Wildlife corridors can be as simple as a green bridge over a busy road or as complex as a series of interconnected parks that span across a city.
Moreover, community involvement plays a crucial role in effective urban land management. When local residents are engaged in the decision-making process, they are more likely to support and participate in conservation efforts. Community gardens, for instance, not only provide fresh produce but also foster a sense of belonging and stewardship among residents. By organizing workshops, clean-up events, and educational programs, communities can take an active role in enhancing biodiversity in their urban environment.
To illustrate the impact of urban land management, let’s take a look at some successful case studies:
| City | Green Initiative | Impact on Biodiversity |
|---|---|---|
| Singapore | Gardens by the Bay | Increased habitat for pollinators and native species |
| New York City | High Line Park | Revived native plant species and attracted diverse wildlife |
| Melbourne | Urban Forest Strategy | Enhanced canopy cover, improved air quality, and provided habitats |
These examples show that when cities prioritize biodiversity through sustainable land management practices, they can create vibrant ecosystems that benefit both people and wildlife. It’s all about striking a balance between development and conservation, ensuring that urban areas can thrive without sacrificing the health of our planet.
As we continue to face the challenges of urbanization, it’s crucial to remember that our cities can be designed to coexist with nature. By adopting innovative strategies and fostering community engagement, urban land management can pave the way for a greener, more sustainable future.
- What is urban land management? Urban land management refers to the planning and regulation of land use in urban areas to balance development with environmental sustainability.
- How can green spaces benefit urban areas? Green spaces improve air quality, provide habitats for wildlife, and offer recreational opportunities for residents.
- What are wildlife corridors? Wildlife corridors are pathways that connect fragmented habitats, allowing animals to move freely and safely between areas.
- Why is community involvement important in urban land management? Engaging local communities fosters stewardship and enhances conservation efforts, leading to more successful outcomes.

Green Infrastructure
Green infrastructure is a game-changer in urban planning, weaving together nature and city life in a way that benefits both the environment and the community. Imagine walking through a bustling city, surrounded by towering buildings, yet you find pockets of lush greenery and vibrant parks that seem to breathe life into the concrete jungle. This is the essence of green infrastructure, where natural elements are integrated into urban landscapes to enhance biodiversity and improve the quality of life for residents.
One of the most exciting aspects of green infrastructure is its versatility. It can take many forms, from green roofs that provide insulation and reduce stormwater runoff to urban forests that act as carbon sinks and habitats for wildlife. These elements not only promote biodiversity but also offer recreational spaces for people to unwind and connect with nature. For instance, parks can serve as vital corridors for wildlife, allowing species to thrive even in densely populated areas.
Moreover, the benefits of green infrastructure extend beyond aesthetics. By incorporating natural systems into urban planning, cities can effectively manage rainwater, reduce heat island effects, and improve air quality. According to recent studies, areas with ample green infrastructure can experience a decrease in urban flooding by up to 30%. This is because plants and soil can absorb and filter rainwater, which helps mitigate the impact of heavy storms. The table below highlights some of the key benefits of green infrastructure:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Air Quality | Plants filter pollutants from the air, leading to cleaner, healthier environments. |
| Stormwater Management | Natural systems absorb and manage rainwater, reducing flooding risks. |
| Enhanced Biodiversity | Provides habitats for various species, promoting ecological balance. |
| Recreational Spaces | Offers areas for leisure and community activities, improving quality of life. |
Additionally, green infrastructure fosters community engagement. When local residents are involved in the planning and maintenance of green spaces, they develop a sense of ownership and pride. This connection to the environment can lead to more sustainable behaviors and a collective effort to preserve these natural resources. For example, community gardens not only provide fresh produce but also serve as educational platforms where people learn about local ecosystems and sustainable practices.
In conclusion, green infrastructure is not just a trend; it’s a necessary evolution in how we design our urban environments. By embracing nature within our cities, we can create spaces that benefit both human and ecological health. The integration of green elements into urban planning is a vital step toward fostering a more sustainable and biodiverse future. So, the next time you stroll through your city, take a moment to appreciate those green pockets – they are crucial for our planet's health and our well-being!
- What is green infrastructure? Green infrastructure refers to the practice of integrating natural elements into urban planning to enhance biodiversity and improve environmental quality.
- How does green infrastructure benefit cities? It provides benefits such as improved air quality, effective stormwater management, enhanced biodiversity, and recreational spaces for communities.
- Can communities get involved in green infrastructure projects? Absolutely! Community involvement is essential for the success of green infrastructure initiatives, as it fosters stewardship and a sense of ownership.
- What are some examples of green infrastructure? Examples include green roofs, urban forests, parks, community gardens, and permeable pavements.

Community Involvement
When it comes to land management and biodiversity, the role of community involvement cannot be overstated. Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is like planting seeds in fertile soil; it nurtures a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the environment. When people feel connected to their land, they are more likely to protect it. This connection fosters a collaborative spirit, where individuals and groups come together to address environmental challenges. Imagine a neighborhood where residents actively participate in tree planting, wildlife monitoring, and habitat restoration. This not only enhances biodiversity but also strengthens community bonds.
One of the most effective ways to involve communities is through education and outreach programs. These initiatives can empower individuals with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions about their environment. Workshops, school programs, and community meetings can serve as platforms for sharing information about sustainable practices and the importance of biodiversity. For instance, a local workshop on native plant gardening can inspire residents to create habitats that attract pollinators like bees and butterflies. This not only beautifies the community but also supports vital ecological processes.
Additionally, community-led projects can yield significant benefits. When locals are involved in land management decisions, they often bring unique insights and traditional knowledge that can lead to innovative solutions. For example, a community might decide to establish a community garden that utilizes organic farming techniques. This garden could become a hub for biodiversity, attracting various species while providing fresh produce for local families. Such initiatives demonstrate that when communities are empowered, they can create thriving ecosystems that benefit both people and nature.
Moreover, collaboration with local governments and organizations can amplify these efforts. Partnerships can provide resources, technical expertise, and funding for community projects. By working together, communities can develop comprehensive land management plans that prioritize biodiversity while addressing human needs. For instance, a town might collaborate with environmental NGOs to create green spaces that serve as wildlife corridors, allowing animals to thrive even in urban settings. The synergy between community involvement and institutional support can lead to sustainable outcomes that resonate for generations.
In conclusion, community involvement is a cornerstone of effective land management and biodiversity conservation. By fostering a sense of stewardship, providing education, and encouraging collaboration, we can create resilient ecosystems that not only support wildlife but also enhance the quality of life for all residents. As we move forward, it’s crucial to remember that every small action counts. Whether it’s planting a tree or participating in a local cleanup, each effort contributes to a larger goal of sustainability and ecological health.
- Why is community involvement important in land management?
Community involvement is essential because it fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility, leading to more effective conservation efforts. - How can communities participate in biodiversity conservation?
Communities can engage by participating in local conservation projects, attending educational workshops, and collaborating with local organizations. - What are some examples of community-led initiatives?
Examples include community gardens, tree planting events, and wildlife monitoring programs that encourage local participation. - How can local governments support community involvement?
Local governments can support by providing resources, technical assistance, and funding for community-led projects focused on biodiversity.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is biodiversity and why is it important?
Biodiversity refers to the variety of life on Earth, including the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms. It's crucial because it contributes to ecosystem resilience, offering essential services like pollination, water purification, and climate regulation. Think of it like a safety net; the more diverse it is, the better it can withstand environmental changes and human impacts.
- How do land management practices affect biodiversity?
Land management practices can have profound effects on biodiversity. For instance, traditional agriculture may lead to habitat destruction and reduced species diversity, while sustainable practices like organic farming and agroforestry can enhance ecological health. It's like choosing between a crowded, noisy city and a serene, green park; one supports life, while the other can stifle it.
- What are some sustainable agricultural practices?
Sustainable agricultural practices include techniques such as crop rotation, organic farming, and agroforestry. These methods minimize chemical use and preserve habitats, fostering a balanced ecosystem. Imagine a garden where plants help each other grow instead of competing for resources; that's the essence of sustainable agriculture!
- What role does urban land management play in biodiversity?
Urban land management is vital for mitigating the impacts of urbanization on biodiversity. By incorporating green spaces, parks, and wildlife corridors into city planning, we can create habitats that support various species. It's like creating little oases in a desert of concrete; these green spots can rejuvenate both nature and community life.
- Can community involvement really make a difference in land management?
Absolutely! Engaging local communities in land management decisions fosters a sense of stewardship and can lead to innovative conservation solutions. When people feel connected to their environment, they are more likely to take action to protect it. Think of it like a team sport; everyone plays a role in achieving a common goal!
- What is green infrastructure and how does it benefit biodiversity?
Green infrastructure refers to incorporating natural elements into urban planning, such as parks, green roofs, and urban forests. These initiatives enhance biodiversity by providing habitats for wildlife while also improving the quality of life for residents. Imagine living in a neighborhood where nature thrives alongside homes; that's the magic of green infrastructure!