The Impact of Sustainable Infrastructure on Urban Welfare
Sustainable infrastructure is more than just a buzzword; it’s a vital component of modern urban development that aims to enhance the quality of life for residents while preserving the environment for future generations. As cities around the globe grapple with issues like pollution, overcrowding, and climate change, the integration of sustainable practices into infrastructure planning has become increasingly important. But how exactly does sustainable infrastructure impact urban welfare? Let’s dive into this fascinating topic.
At its core, sustainable infrastructure encompasses systems that are designed to meet the needs of the present without jeopardizing the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This means that every aspect, from transportation to waste management, is carefully considered to minimize environmental impact while maximizing social benefits. Imagine a city where public transportation is not only efficient but also powered by renewable energy sources, or where parks and green spaces are strategically integrated into urban settings. These elements not only beautify cities but also improve mental health and encourage community engagement.
One of the most profound effects of sustainable infrastructure is its ability to promote public health. Clean air, accessible green spaces, and efficient waste management systems are just a few examples of how sustainability contributes to a healthier urban environment. When cities invest in sustainable practices, they are investing in the well-being of their residents. For instance, studies have shown that neighborhoods with ample green spaces can lead to reduced stress levels and improved physical health among residents. It’s like a breath of fresh air, literally and figuratively!
Moreover, the economic implications of sustainable infrastructure cannot be overlooked. Cities that prioritize sustainability often see a boost in job creation, as new projects require skilled labor and innovative solutions. This not only helps to reduce unemployment rates but also fosters a sense of community as residents come together to work on these initiatives. Additionally, sustainable infrastructure can lead to increased property values. When neighborhoods are equipped with eco-friendly amenities, they become more desirable places to live, which in turn drives up real estate prices. It’s a win-win situation for both residents and city planners.
However, the journey toward sustainable infrastructure isn’t without its challenges. Financial constraints can be a significant hurdle, as many cities struggle to allocate budgets for these ambitious projects. But there are various financing options available, from public-private partnerships to green bonds, that can help overcome these obstacles. It’s essential for city officials and stakeholders to collaborate and explore innovative funding solutions to bring these projects to life.
Political and social resistance can also pose challenges to the implementation of sustainable infrastructure. Stakeholders may have differing opinions on what constitutes sustainability or how resources should be allocated. Engaging communities through open dialogue and education can help mitigate these issues, ensuring that everyone has a voice in the planning process. After all, sustainable infrastructure should reflect the needs and desires of the community it serves.
In conclusion, the impact of sustainable infrastructure on urban welfare is profound and multifaceted. By prioritizing sustainable practices, cities can enhance public health, boost economic growth, and create vibrant communities that thrive for generations to come. As we continue to face environmental challenges, the importance of integrating sustainability into urban planning becomes increasingly clear. It’s time for cities to embrace this transformative approach and pave the way for a brighter, greener future.
- What is sustainable infrastructure?
Sustainable infrastructure refers to systems designed to meet current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs, focusing on environmental, social, and economic sustainability. - How does sustainable infrastructure benefit urban communities?
It improves public health, boosts the economy through job creation and increased property values, and enhances the overall quality of life by providing clean air, green spaces, and efficient services. - What are some challenges in implementing sustainable infrastructure?
Challenges include financial constraints, political opposition, and social resistance, which can hinder the progress of sustainable projects. - How can cities overcome financial barriers to sustainable infrastructure?
Cities can explore various financing options such as public-private partnerships, grants, and green bonds to fund sustainable projects. - Why is community engagement important in sustainable infrastructure projects?
Engaging the community ensures that the infrastructure meets the needs and desires of residents, fostering a sense of ownership and support for the projects.

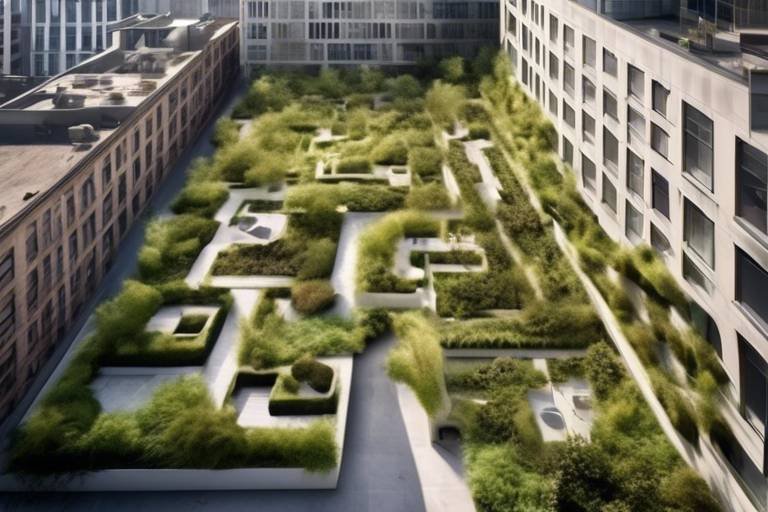
Understanding Sustainable Infrastructure
Sustainable infrastructure is not just a buzzword; it’s a vital approach to urban planning that emphasizes the importance of meeting our current needs without jeopardizing the ability of future generations to meet theirs. Imagine a city where clean air, green spaces, and efficient public transport are not just dreams but everyday realities. This vision is achievable through the principles of sustainable infrastructure, which advocate for systems that are environmentally friendly, economically viable, and socially equitable.
At its core, sustainable infrastructure integrates various elements that contribute to a holistic urban environment. These elements often include:
- Renewable Energy Sources: Utilizing solar, wind, and other renewable energy technologies to power urban systems.
- Efficient Water Management: Implementing systems that conserve water and manage stormwater effectively to prevent flooding.
- Green Building Practices: Constructing buildings with sustainable materials and energy-efficient designs.
- Transportation Solutions: Developing public transportation options that reduce reliance on fossil fuels and promote eco-friendly commuting.
The significance of integrating sustainability into urban planning cannot be overstated. As cities continue to grow, they face numerous challenges, including pollution, traffic congestion, and social inequality. By adopting sustainable infrastructure practices, cities can combat these issues head-on. For instance, green spaces not only enhance the aesthetic appeal of urban areas but also improve air quality and provide recreational opportunities for residents.
Moreover, sustainable infrastructure is about creating a resilient urban environment that can adapt to changing climate conditions. This adaptability is crucial as cities face increasing risks from climate change, such as extreme weather events and rising sea levels. By investing in sustainable practices, urban planners can help ensure that cities are not only livable today but also resilient for generations to come.
In essence, understanding sustainable infrastructure involves recognizing its multifaceted nature. It’s a blend of technology, design, and community engagement aimed at creating urban spaces that foster well-being and prosperity. As we delve deeper into the benefits and challenges of sustainable infrastructure in the following sections, it becomes clear that this is not merely an option but a necessity for the future of urban living.

Benefits of Sustainable Infrastructure
Sustainable infrastructure is not just a buzzword; it is a transformative approach that reshapes our urban environments for the better. The implementation of such systems brings a multitude of benefits that enhance the quality of life for city dwellers. Imagine walking through a city where clean air fills your lungs, parks are abundant, and public transport is efficient and eco-friendly. This is the vision that sustainable infrastructure aims to achieve. By integrating sustainability into the very fabric of urban planning, cities can experience profound changes that resonate through various aspects of daily life.
One of the most significant advantages of sustainable infrastructure is its capacity to improve public health. For example, the reduction of air pollution through cleaner transportation options and the incorporation of green spaces can lead to lower rates of respiratory diseases and other health issues. A study by the World Health Organization indicated that urban areas with extensive green spaces report better mental health outcomes and lower stress levels. Furthermore, sustainable infrastructure encourages active transportation modes, such as walking and cycling, which can contribute to a healthier population.
In addition to health benefits, sustainable infrastructure can lead to substantial economic savings. By investing in energy-efficient buildings and renewable energy sources, cities can significantly reduce their utility costs over time. For instance, municipalities that have adopted solar energy systems have reported savings of up to 40% on energy bills. These savings can be redirected towards other essential services, such as education and public safety, ultimately enhancing urban welfare.
Moreover, sustainable practices foster environmental protection. The implementation of green infrastructure, such as permeable pavements and urban forests, plays a crucial role in managing stormwater runoff, reducing the risk of flooding, and improving water quality. By mitigating the impacts of climate change, cities can create resilient communities that are better equipped to handle environmental challenges. This is not just about saving the planet; it's about ensuring a livable future for generations to come.
To summarize, the benefits of sustainable infrastructure can be categorized as follows:
- Public Health: Improved air quality and increased physical activity.
- Economic Savings: Reduced utility costs and increased funding for essential services.
- Environmental Protection: Enhanced resilience against climate change and improved water management.
As cities worldwide grapple with the challenges of rapid urbanization and climate change, the case for sustainable infrastructure becomes increasingly compelling. It is not merely a choice but a necessity for creating vibrant, healthy, and sustainable urban spaces that benefit everyone.
Q: What is sustainable infrastructure?
A: Sustainable infrastructure refers to systems and structures that meet current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This includes energy-efficient buildings, renewable energy sources, and green spaces.
Q: How does sustainable infrastructure improve public health?
A: By reducing air pollution, promoting active transportation, and increasing access to green spaces, sustainable infrastructure contributes to better physical and mental health outcomes for urban residents.
Q: What are some economic benefits of sustainable infrastructure?
A: Sustainable infrastructure can lead to significant cost savings through energy efficiency, job creation in green sectors, and increased property values in neighborhoods with sustainable features.
Q: What challenges do cities face when implementing sustainable infrastructure?
A: Common challenges include financial constraints, political opposition, and social resistance, but these can be addressed through strategic planning and community engagement.

Economic Advantages
When we talk about sustainable infrastructure, it's not just about being eco-friendly; it's also about boosting the economy in ways that can be both surprising and beneficial. Imagine a city where green parks, efficient public transport, and renewable energy sources are the norm. This isn't just a dream—it's a reality that many urban areas are striving to achieve through sustainable practices. The economic advantages these initiatives bring are profound and multifaceted, making a strong case for their implementation.
One of the most significant economic benefits of sustainable infrastructure is job creation. When cities invest in projects like solar energy installations, green roofs, and efficient public transit systems, they require a workforce that is skilled and ready to tackle these challenges. This demand for skilled labor not only creates new jobs but also stimulates local economies. For instance, a city that embraces solar energy might see a surge in employment opportunities for electricians, engineers, and construction workers. The ripple effect of these jobs can lead to increased spending in local businesses, further enriching the community.
Furthermore, sustainable infrastructure can lead to increased property values. Think about it: neighborhoods that are well-planned, with ample green spaces and efficient transport links, tend to attract more residents and businesses. This, in turn, drives up property values. A recent study indicated that homes located near parks and public transportation hubs can see their values increase by as much as 15% to 25% compared to similar properties without such amenities. This is a win-win situation; property owners benefit from higher values, while cities enjoy increased tax revenues that can be reinvested into further improvements.
Moreover, the economic benefits extend beyond immediate job creation and property value enhancement. Sustainable infrastructure can lead to long-term savings for cities. By investing in energy-efficient buildings and renewable energy sources, municipalities can significantly reduce their utility costs over time. For example, a city that implements a comprehensive energy efficiency program may reduce its energy consumption by 20% to 30%, translating into millions of dollars saved annually. These savings can then be redirected into essential services like education, healthcare, and public safety, ultimately enhancing the overall quality of life for residents.
To further illustrate these points, let’s take a look at a few key statistics:
| Economic Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Job Creation | Increased employment opportunities in construction, engineering, and renewable energy sectors. |
| Property Values | Homes near sustainable infrastructure can see value increases of 15-25%. |
| Energy Savings | Potential reduction in energy costs by 20-30%, leading to significant budget reallocations. |
In conclusion, the economic advantages of sustainable infrastructure are clear. By investing in these initiatives, cities not only create jobs and enhance property values but also ensure long-term savings that can be reinvested into the community. It's a cycle of growth that benefits everyone—from homeowners to local businesses, and ultimately, the city as a whole. So, the next time you see a green roof or a new bike lane, remember that it’s more than just an aesthetic improvement; it’s an investment in a thriving urban future.
- What is sustainable infrastructure? Sustainable infrastructure refers to systems designed to meet current needs without compromising future generations, balancing economic, environmental, and social factors.
- How does sustainable infrastructure create jobs? These projects require skilled labor for construction, maintenance, and operation, leading to new employment opportunities in various sectors.
- Can sustainable infrastructure increase property values? Yes, areas with sustainable features like parks and efficient transport often see property values rise due to increased desirability.
- What are the long-term savings associated with sustainable infrastructure? By reducing energy consumption and improving efficiency, cities can save significantly on utility costs, allowing for reinvestment in public services.

Job Creation
When we think about sustainable infrastructure, one of the most exciting outcomes is the potential for . Imagine a city where green spaces flourish, public transport is efficient, and buildings are energy-efficient. All these improvements don't just pop up out of thin air; they require a dedicated workforce. Sustainable projects often need a variety of skilled labor, from engineers and architects to construction workers and environmental specialists. This means that investing in sustainable infrastructure can lead to a surge in job opportunities across multiple sectors.
For instance, consider the installation of solar panels. Not only does this contribute to a cleaner environment, but it also creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. According to recent studies, the renewable energy sector alone has seen a significant increase in employment, with jobs growing at a rate much faster than the overall economy. This trend is a clear indication that sustainable infrastructure is not just an environmental necessity but also an economic boon.
Moreover, the ripple effect of these job opportunities can be profound. As new jobs are created, local economies benefit from increased spending, leading to more businesses opening and thriving. This creates a vibrant community where residents feel invested in their environment and economy. In fact, a recent report indicated that for every job created in the renewable energy sector, approximately three additional jobs are generated in the local economy due to increased demand for goods and services.
Additionally, the jobs created from sustainable infrastructure projects are often more stable and better paying. Many of these positions require specialized training and skills, which can lead to higher wages compared to traditional jobs. This not only helps lift families out of poverty but also fosters a sense of pride and ownership within the community. When people are employed in meaningful work, they are more likely to engage in their neighborhoods, volunteer, and contribute to local initiatives, creating a virtuous cycle of improvement.
In conclusion, the job creation aspect of sustainable infrastructure is a powerful argument for its implementation. Not only does it provide immediate employment opportunities, but it also strengthens the economic fabric of communities. As cities worldwide embrace sustainable practices, they are not just investing in a greener future but are also paving the way for a more prosperous and equitable society.
- What types of jobs are created by sustainable infrastructure projects?
Jobs can range from construction and engineering to roles in project management, environmental consulting, and maintenance of green technologies.
- How do sustainable jobs compare to traditional jobs?
Sustainable jobs often require specialized skills and training, which can lead to higher wages and more job security compared to many traditional positions.
- Can sustainable infrastructure projects help reduce unemployment?
Yes, by creating new job opportunities and stimulating local economies, sustainable projects can significantly help reduce unemployment rates.

Property Value Enhancement
When we talk about sustainable infrastructure, one of the most exciting aspects is its undeniable ability to enhance property values. Imagine living in a neighborhood that boasts beautiful parks, clean streets, and efficient public transport. Wouldn't you feel more inclined to invest in a home there? The link between sustainability and property value is not just a theory; it’s backed by data and real-world examples that show how green initiatives can transform urban landscapes.
Studies have shown that properties located near green spaces, such as parks or community gardens, often see an increase in their market value. These areas not only provide aesthetic appeal but also improve the quality of life for residents. According to a report by the National Association of Realtors, homes near parks can command prices up to 20% higher than similar homes located further away. This is a clear indication that buyers are willing to pay a premium for the perks that come with sustainable living environments.
Furthermore, sustainable infrastructure projects such as green roofs and solar energy installations can significantly boost the attractiveness of a property. These features not only lower utility costs for homeowners but also demonstrate a commitment to environmental responsibility. In an age where more buyers are prioritizing sustainability, properties that incorporate these elements are likely to stand out in a crowded market.
Here’s a quick breakdown of how sustainable infrastructure can enhance property values:
- Proximity to Green Spaces: Increased demand for homes near parks and recreational areas.
- Energy Efficiency: Homes with solar panels or energy-efficient designs often have lower operating costs, making them more appealing.
- Community Appeal: Neighborhoods with sustainable infrastructure tend to foster a stronger sense of community, attracting more buyers.
Moreover, the impact of sustainable infrastructure on property values can be seen in various cities across the globe. For instance, in Portland, Oregon, the city’s commitment to sustainability has led to a significant rise in property values in neighborhoods where green initiatives have been implemented. Homebuyers are not just looking for a place to live; they are seeking a lifestyle that aligns with their values, and sustainable infrastructure plays a pivotal role in that choice.
In conclusion, the enhancement of property values through sustainable infrastructure is a win-win scenario. Not only do homeowners benefit from increased equity in their properties, but communities also thrive as they become more attractive to potential residents. As cities continue to embrace sustainable practices, we can expect to see a lasting positive impact on urban real estate markets.

Environmental Impact
Sustainable infrastructure is not just a buzzword; it’s a game-changer for our planet. By embracing sustainable practices, cities can significantly reduce their carbon footprints and promote a healthier environment. Imagine a world where urban areas are not just concrete jungles but thriving ecosystems that support biodiversity. This transformation is possible through innovative approaches to urban planning and development.
One of the most profound environmental impacts of sustainable infrastructure is its ability to mitigate climate change. For example, the incorporation of renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, into urban designs can drastically lower greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, sustainable practices, such as rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling, can help cities manage water resources more efficiently, reducing the strain on local water supplies.
In addition to reducing emissions, sustainable infrastructure enhances biodiversity. Urban green spaces, including parks and community gardens, provide habitats for various species, from birds to pollinators. The integration of green roofs and vertical gardens not only beautifies buildings but also creates vital ecosystems in densely populated areas. These green spaces serve as crucial refuges for wildlife, promoting a balanced urban ecology.
Another key aspect of sustainable infrastructure is its role in improving air quality. Traditional urban designs often lead to high levels of air pollution, which can have detrimental effects on public health. However, by implementing green transportation systems, such as bike lanes and electric public transit, cities can encourage residents to choose cleaner modes of transportation. This shift can lead to a significant decrease in air pollutants and a corresponding improvement in the overall health of the population.
The benefits of sustainable infrastructure extend beyond just environmental health; they also contribute to the social well-being of urban populations. By creating cleaner, greener spaces, cities can enhance the quality of life for their residents. The psychological benefits of being surrounded by nature are well-documented, leading to improved mental health and increased community cohesion.
To illustrate the environmental impact of sustainable infrastructure, consider the following table that summarizes some key benefits:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Carbon Footprint Reduction | Lowering greenhouse gas emissions through renewable energy and energy-efficient systems. |
| Biodiversity Enhancement | Creating habitats and green spaces that support various species in urban settings. |
| Improved Air Quality | Encouraging sustainable transport options to reduce pollution levels. |
| Community Well-being | Enhancing mental health and social cohesion through access to green spaces. |
In conclusion, the environmental impact of sustainable infrastructure is profound and multifaceted. It not only addresses pressing issues like climate change and pollution but also fosters a flourishing urban ecosystem that benefits both people and the planet. As cities around the globe continue to adopt sustainable practices, we can look forward to a future where urban living and environmental stewardship go hand in hand.
- What is sustainable infrastructure? Sustainable infrastructure refers to systems that meet current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs, emphasizing environmental health and resource efficiency.
- How does sustainable infrastructure benefit cities? It provides numerous advantages, including reduced carbon emissions, improved public health, enhanced biodiversity, and increased property values.
- What are some examples of sustainable infrastructure? Examples include green roofs, solar energy systems, rainwater harvesting, and efficient public transportation systems.
- What challenges do cities face in implementing sustainable infrastructure? Common challenges include financial constraints, political opposition, and the need for community engagement.

Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Infrastructure
Despite the myriad benefits that sustainable infrastructure offers, the road to its implementation is often fraught with challenges. One of the most significant hurdles is the financial constraints faced by municipalities and governments. Budget limitations can severely restrict the ability to initiate and maintain sustainable projects. For instance, many cities struggle to allocate funds for renewable energy systems, green public transportation, and eco-friendly building materials. The upfront costs associated with these initiatives can be daunting, leading to a reluctance to invest in sustainable solutions.
To tackle these financial challenges, cities can explore various financing options. Public-private partnerships (PPPs) have emerged as a viable solution, allowing for shared investment and risk. Additionally, cities can seek grants and subsidies from governmental and non-governmental organizations aimed at promoting sustainability. By diversifying funding sources, municipalities can alleviate some of the financial pressure and pave the way for sustainable infrastructure projects.
Another significant barrier is the political and social resistance that often accompanies sustainable infrastructure initiatives. Stakeholders, including local businesses, residents, and even political leaders, may oppose changes due to perceived threats to their interests or a lack of understanding of the benefits. For example, a community might resist the introduction of a new public transit system, fearing it will disrupt their daily lives or decrease property values. To overcome this resistance, effective community engagement is crucial. Educating the public about the long-term benefits of sustainable infrastructure can help mitigate fears and foster support.
Moreover, implementing sustainable infrastructure requires a shift in policy frameworks. Existing regulations may not align with sustainability goals, creating additional hurdles. For instance, zoning laws that favor traditional building practices can stifle the development of eco-friendly structures. Policymakers must work to revise these regulations, ensuring they support sustainable practices rather than hinder them.
In summary, while the challenges in implementing sustainable infrastructure can seem overwhelming, they are not insurmountable. By addressing financial constraints through innovative funding mechanisms and fostering community engagement to combat political resistance, cities can move closer to realizing sustainable urban environments. The journey may be complex, but the rewards—improved quality of life, economic growth, and a healthier planet—make it a worthy endeavor.
- What are the main challenges in implementing sustainable infrastructure? The main challenges include financial constraints, political resistance, and outdated policy frameworks.
- How can cities overcome financial limitations? Cities can explore public-private partnerships, seek grants, and diversify funding sources to alleviate financial pressure.
- Why is community engagement important? Engaging the community helps to educate them about the benefits of sustainable infrastructure, reducing resistance and fostering support.

Financial Constraints
When it comes to implementing sustainable infrastructure, one of the most significant hurdles cities face is . Imagine trying to build a magnificent bridge with only a handful of coins in your pocket—it’s simply not feasible. Cities often operate under tight budgets, and the upfront costs associated with sustainable projects can be daunting. This leads to a complex web of challenges where decision-makers must weigh the immediate financial implications against long-term benefits.
Many sustainable initiatives require substantial initial investments, which can deter local governments from pursuing them. For instance, projects like solar energy installations or green building retrofits often have high upfront costs, despite the fact that they can lead to considerable savings in the long run. But how do cities balance these financial demands with the pressing need for modernization and sustainability?
To tackle these financial constraints, cities can explore various financing options, such as:
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Collaborating with private entities can alleviate some of the financial burdens on local governments. These partnerships can leverage private investment to fund sustainable projects while sharing the risks and rewards.
- Grants and Subsidies: Many governments and organizations offer grants specifically aimed at promoting sustainability. Cities can tap into these funds to support their infrastructure projects.
- Green Bonds: Issuing green bonds allows municipalities to raise capital specifically for environmentally friendly projects. Investors are often attracted to these bonds due to their positive impact on the environment.
Moreover, cities can also consider innovative financing models, such as performance-based contracts, where payments are tied to the successful delivery of sustainable outcomes. This approach not only ensures accountability but also aligns financial incentives with sustainability goals.
However, it's crucial to recognize that these financial strategies aren't without their challenges. For example, securing funding through grants often involves a lengthy application process and stringent eligibility criteria. Additionally, navigating the complexities of PPPs can be a daunting task for local governments, especially those lacking experience in such arrangements.
In summary, while financial constraints present significant challenges to implementing sustainable infrastructure, they are not insurmountable. By exploring diverse funding options, engaging with private partners, and leveraging innovative financing models, cities can pave the way for a more sustainable future. The key lies in understanding that the investment made today can yield substantial returns tomorrow, both economically and environmentally.
Q: What are some common financing options for sustainable infrastructure projects?
A: Common financing options include public-private partnerships, grants and subsidies, and green bonds. These methods can help alleviate financial burdens on local governments.
Q: How can cities ensure they are making a wise investment in sustainable infrastructure?
A: Cities can conduct thorough cost-benefit analyses, engage stakeholders, and explore innovative financing models to ensure that their investments yield long-term benefits.
Q: What role do community stakeholders play in financing sustainable projects?
A: Community stakeholders can provide valuable input and support for sustainable projects, which can help secure funding and ensure that initiatives align with local needs and values.

Political and Social Resistance
Implementing sustainable infrastructure is not just about the technology or the design; it often runs into the murky waters of . Imagine trying to build a beautiful garden in a community that is divided over its purpose and benefits. This is the reality many cities face when they attempt to introduce sustainable projects. Various stakeholders, including local governments, businesses, and citizens, may have differing opinions about the necessity and feasibility of these initiatives. This resistance can manifest in numerous ways, from public protests to political lobbying against proposed projects.
One of the primary reasons for this resistance is the fear of change. People are naturally inclined to stick to what they know, and sustainable infrastructure often requires shifts in lifestyle, economic models, and even cultural norms. For example, the introduction of bike lanes may be met with skepticism by drivers who worry about losing road space, while businesses may fear a drop in foot traffic. These concerns are valid and need to be addressed through open dialogue and education.
Moreover, the complexity of financing sustainable infrastructure can create a breeding ground for political opposition. When budgets are tight, and priorities are competing, sustainable projects may be viewed as luxuries rather than necessities. This perception can lead to a lack of political will, where elected officials hesitate to champion these initiatives for fear of alienating constituents who prioritize immediate economic concerns over long-term environmental benefits.
To effectively engage communities and mitigate resistance, it is crucial to foster a sense of ownership and involvement among residents. This can be achieved through:
- Community Workshops: Hosting workshops that invite community members to voice their opinions and ideas can help align interests and build consensus.
- Transparent Communication: Providing clear and accessible information about the benefits of sustainable infrastructure can dispel myths and reduce fear.
- Pilot Projects: Implementing small-scale pilot projects allows communities to experience the benefits firsthand, making them more likely to support larger initiatives.
Ultimately, navigating the waters of political and social resistance requires patience, understanding, and a commitment to collaboration. By addressing concerns and involving stakeholders in the planning process, cities can transform skepticism into support, paving the way for a more sustainable future.
Q1: What are the main reasons for resistance to sustainable infrastructure?
A1: Resistance often stems from fear of change, financial concerns, and differing priorities among stakeholders.
Q2: How can communities be engaged in sustainable infrastructure projects?
A2: Communities can be engaged through workshops, transparent communication, and pilot projects that allow residents to see the benefits firsthand.
Q3: Why is political support crucial for sustainable infrastructure?
A3: Political support is essential for securing funding and resources necessary for implementing sustainable projects, as well as for overcoming opposition.

Case Studies of Successful Sustainable Infrastructure
When we talk about sustainable infrastructure, it’s not just a concept floating around in academic circles; it’s a reality that’s transforming cities across the globe. Real-world examples of sustainable infrastructure projects showcase the tangible benefits these initiatives bring to urban welfare. Let’s dive into some standout case studies that illustrate how cities are embracing sustainability and the positive impacts these projects have on their communities.
One of the most compelling examples comes from Singapore, a city-state renowned for its innovative approach to urban planning. The introduction of green roofs across various buildings has not only beautified the skyline but has also provided crucial environmental benefits. These green spaces help to reduce the urban heat island effect, improve air quality, and promote biodiversity by providing habitats for various species. For instance, the famous ParkRoyal on Pickering hotel features extensive green terraces that contribute to the city’s overall green cover while also enhancing the guests’ experience. This initiative exemplifies how integrating nature into urban settings can yield multiple benefits.
Another noteworthy case is the implementation of public transportation innovations in Amsterdam. Known for its extensive bike lanes and pedestrian-friendly design, Amsterdam has taken sustainable transportation a step further with its electric tram system and bike-sharing programs. These initiatives not only reduce carbon emissions but also encourage a healthier lifestyle among residents. The city's commitment to sustainability is evident in its comprehensive strategy that prioritizes public transport, making it a model for urban mobility. The integration of electric buses and trams has led to a significant decrease in traffic congestion and pollution, enhancing the overall quality of life for its citizens.
To further illustrate the impact of these case studies, let’s take a look at some key statistics:
| City | Project | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Singapore | Green Roofs | Reduced heat, improved air quality, increased biodiversity |
| Amsterdam | Electric Public Transport | Lower emissions, reduced traffic, healthier lifestyle |
These examples not only highlight the successful implementation of sustainable infrastructure but also serve as a beacon for other cities looking to enhance urban welfare. By investing in sustainable projects, cities can create environments that are not only livable but also resilient against the challenges posed by climate change.
However, the journey towards sustainable urban infrastructure is not without its hurdles. As we explore these case studies, it’s essential to recognize that each city faces unique challenges and opportunities. The key takeaway is that with the right vision and community engagement, sustainable infrastructure can lead to a brighter, more sustainable future.
What is sustainable infrastructure?
Sustainable infrastructure refers to systems and structures designed to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This includes eco-friendly buildings, renewable energy systems, and efficient public transportation.
How does sustainable infrastructure benefit urban areas?
It enhances urban welfare by improving public health, boosting economic growth, and protecting the environment. Sustainable practices can lead to cleaner air, job creation, and increased property values.
What are some examples of sustainable infrastructure?
Examples include green roofs, solar energy installations, electric public transport systems, and urban parks. Cities like Singapore and Amsterdam have implemented these initiatives successfully.
What challenges do cities face in implementing sustainable infrastructure?
Cities often encounter financial constraints, political resistance, and social opposition when trying to implement sustainable projects. Engaging communities and securing funding are critical for overcoming these challenges.

Green Roofs in Urban Areas
Green roofs are rapidly gaining popularity as a transformative solution for urban environments. Imagine a city skyline dotted with lush greenery instead of just concrete and glass; that's the vision that green roofs help bring to life. These innovative structures involve growing vegetation on rooftops, which not only enhances aesthetic appeal but also delivers a multitude of environmental and social benefits. By integrating nature into urban spaces, green roofs contribute significantly to urban welfare.
One of the most compelling advantages of green roofs is their ability to improve air quality. Plants naturally filter pollutants and absorb carbon dioxide, making the air cleaner and healthier for city dwellers. In fact, studies have shown that a well-designed green roof can reduce air pollution by up to 30%. This is akin to having a mini-forest right on top of a building, providing a breath of fresh air in densely populated areas.
Furthermore, green roofs play a crucial role in managing stormwater. Traditional urban landscapes often struggle with drainage issues, leading to flooding during heavy rains. However, green roofs can absorb significant amounts of rainwater, reducing runoff and mitigating flood risks. This not only protects the infrastructure but also helps recharge groundwater supplies. It's like having a sponge on your roof that soaks up water instead of letting it cascade down into the streets.
Additionally, green roofs can enhance biodiversity in urban settings. They provide habitats for various species, including birds, insects, and even small mammals. This is particularly important in cities where natural habitats are scarce. By creating these green sanctuaries, urban areas can support a wider range of wildlife, which in turn contributes to a healthier ecosystem. Think of it as building a small nature reserve that benefits both the environment and the community.
Moreover, green roofs can lead to energy savings for buildings. The vegetation acts as an insulating layer, reducing the need for heating in winter and cooling in summer. This not only lowers energy bills but also decreases the overall carbon footprint of the building. Imagine slashing your energy costs while simultaneously doing your part for the planet—it's a win-win situation!
In terms of social benefits, green roofs can also serve as recreational spaces. They can be designed as gardens, parks, or even community gathering spots, allowing residents to connect with nature and each other. This fosters a sense of community and improves mental well-being, making urban life more enjoyable. Just picture yourself lounging on a rooftop garden, surrounded by greenery, while enjoying a sunny afternoon with friends.
To illustrate the impact of green roofs, consider the following table showcasing some successful implementations across major cities:
| City | Project Name | Area (sq ft) | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chicago | City Hall Green Roof | 23,000 | Energy savings, biodiversity |
| New York | Brooklyn Grange | 2.5 acres | Community engagement, local food production |
| Toronto | Toronto-Dominion Centre | 45,000 | Stormwater management, air quality improvement |
As cities continue to grow and face the challenges of climate change and urbanization, green roofs present a viable solution that enhances urban welfare. They are not just a trend; they represent a shift towards more sustainable living in urban areas. By embracing green roofs, we can create healthier, more vibrant cities that prioritize both people and the planet.
- What is a green roof? A green roof is a roof that is partially or completely covered with vegetation, soil, and a growing medium, which can provide various environmental benefits.
- How do green roofs help with energy efficiency? Green roofs provide insulation, reducing the need for heating and cooling, thus lowering energy costs.
- Can green roofs be installed on any building? Most buildings can support a green roof, but structural assessments are necessary to ensure safety and feasibility.
- What types of plants are suitable for green roofs? Drought-resistant plants, succulents, and native species are often recommended due to their low maintenance and adaptability.
Public Transportation Innovations
In the quest for sustainable urban development, have emerged as a game changer. These innovations not only enhance urban mobility but also play a pivotal role in reducing emissions and improving the overall quality of life in cities. Imagine a bustling city where the air is cleaner, traffic congestion is minimized, and residents can effortlessly navigate their urban landscape. This vision is becoming a reality in many parts of the world, thanks to groundbreaking advancements in public transit systems.
One of the most exciting developments in public transportation is the rise of electric and hybrid buses. These vehicles are designed to operate with minimal environmental impact, significantly reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional diesel buses. Cities like Los Angeles and Shenzhen have already made substantial investments in electric bus fleets, leading to a noticeable improvement in air quality and a reduction in noise pollution. The transition to electric buses not only benefits the environment but also offers long-term cost savings for municipalities due to lower fuel and maintenance costs.
Another innovative approach is the implementation of smart public transportation systems. These systems utilize technology to enhance the efficiency and convenience of transit services. For instance, real-time tracking apps allow passengers to see when their bus or train will arrive, reducing wait times and improving overall satisfaction. Additionally, data analytics can help city planners optimize routes and schedules based on actual usage patterns, ensuring that resources are allocated effectively. Cities like Singapore and Barcelona are leading the charge in this area, showcasing how technology can transform public transportation into a more user-friendly experience.
Moreover, multimodal transportation hubs are gaining popularity as cities seek to integrate various forms of transport. These hubs allow passengers to seamlessly transition between buses, trains, bicycles, and even ride-sharing services. For example, the Grand Central Terminal in New York City is not just a train station; it serves as a vibrant hub where commuters can access multiple transportation options, enhancing connectivity and reducing reliance on personal vehicles. This integration fosters a culture of public transit use, making it a more attractive option for daily commutes.
As cities continue to innovate, the concept of mobility as a service (MaaS) is also gaining traction. This model allows users to plan, book, and pay for multiple types of transportation through a single application. Imagine being able to hop on an electric scooter, take a bus, and then catch a train—all with a single tap on your smartphone. This level of convenience encourages more people to choose public transportation over private vehicles, ultimately leading to reduced traffic congestion and lower emissions.
In conclusion, the innovations in public transportation are not merely trends; they represent a profound shift towards more sustainable urban living. As cities around the globe embrace these advancements, they pave the way for a future where public transit is not just a means of getting from point A to point B, but a cornerstone of urban welfare. By investing in electric vehicles, smart technologies, multimodal hubs, and integrated service platforms, cities are transforming their transportation systems to be more efficient, accessible, and environmentally friendly.
- What are public transportation innovations? These are advancements in transit systems that improve efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance user experience.
- How do electric buses benefit cities? Electric buses reduce greenhouse gas emissions, lower noise pollution, and offer long-term cost savings for municipalities.
- What is mobility as a service (MaaS)? MaaS is a model that allows users to plan, book, and pay for multiple types of transportation through a single platform.
- Why are multimodal transportation hubs important? They facilitate seamless transitions between different modes of transport, encouraging public transit use and reducing reliance on personal vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is sustainable infrastructure?
Sustainable infrastructure refers to the systems and facilities that are designed to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It emphasizes the integration of environmental, social, and economic considerations into urban planning.
- How does sustainable infrastructure benefit urban welfare?
By implementing sustainable infrastructure, cities can enhance public health, save on long-term costs, and protect the environment. These benefits contribute to a higher quality of life for residents, making urban areas more livable and attractive.
- Can sustainable infrastructure create jobs?
Absolutely! Sustainable projects often require skilled labor, which leads to job creation in various sectors. This not only boosts local economies but also fosters community development through employment opportunities.
- What are the financial challenges of implementing sustainable infrastructure?
Funding sustainable projects can be tough due to budget constraints and competing priorities. However, there are various financing options available, such as public-private partnerships, grants, and green bonds, to help overcome these barriers.
- How can communities overcome resistance to sustainable infrastructure projects?
Engaging stakeholders through open communication, education, and collaboration is key. By addressing concerns and involving the community in decision-making, resistance can be minimized, leading to smoother project implementation.
- What are some successful examples of sustainable infrastructure?
There are many inspiring case studies, such as the implementation of green roofs in urban areas and innovative public transportation solutions. These projects have shown significant benefits in terms of environmental impact and urban mobility.
- How does sustainable infrastructure impact property values?
Sustainable infrastructure can enhance property values by making neighborhoods more desirable. Features like green spaces, efficient public transport, and eco-friendly buildings attract buyers and can lead to increased market demand.
- What role does public transportation play in sustainable infrastructure?
Public transportation is a cornerstone of sustainable infrastructure. Innovative solutions in this area can reduce emissions, alleviate traffic congestion, and improve urban mobility, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable urban environment.



















